Ultimate Guide to Managing and Treating Atopic Dermatitis Effectively
Discover comprehensive strategies to effectively manage atopic dermatitis, including skincare routines, trigger avoidance, and available medical treatments. Learn how to control symptoms and improve quality of life with practical tips and latest advances in care.
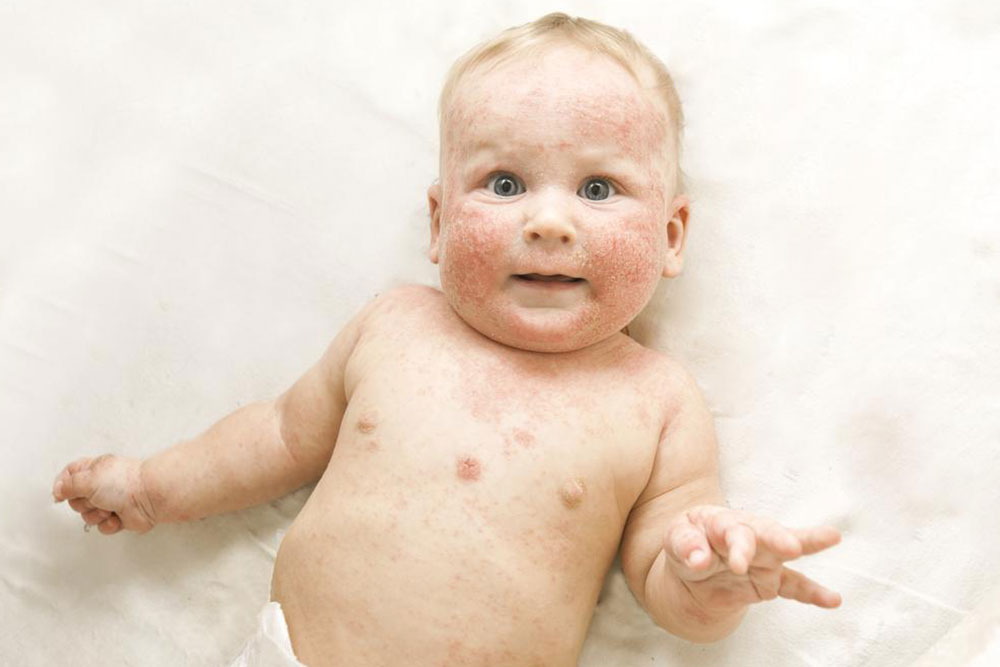
Ultimate Guide to Managing and Treating Atopic Dermatitis Effectively
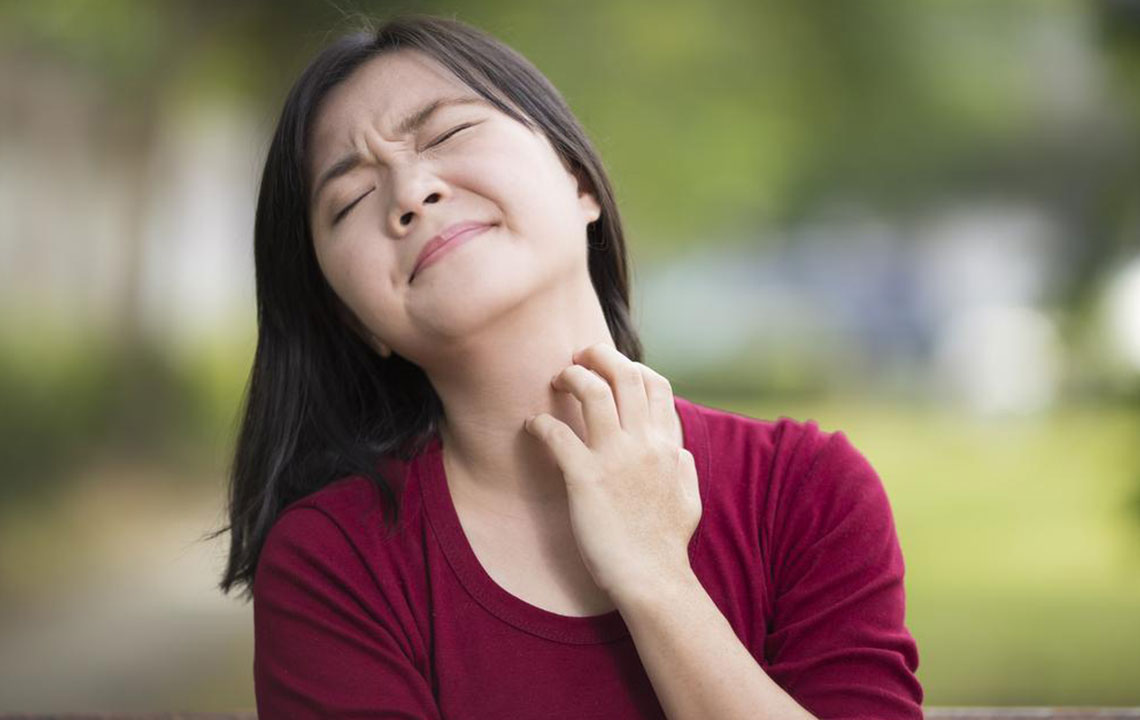
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is one of the most common and persistent skin conditions faced by millions worldwide. This chronic inflammatory skin disorder is characterized by intense itching, redness, dryness, and scaling, significantly affecting the quality of life of those who suffer from it. While it can occur at any age, it is especially prevalent among infants and young children, though many adults continue to experience symptoms well into their later years.
Understanding atopic dermatitis involves exploring its causes, symptoms, and most effective management strategies. This comprehensive guide aims to provide detailed insights into how to control and reduce the discomfort associated with this condition through proper skincare, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing skin inflammation that manifests as dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It is part of a group of allergic conditions called atopy, which also includes asthma and allergic rhinitis. The skin barrier in individuals with atopic dermatitis tends to be compromised, making the skin more susceptible to irritants and allergens. This susceptibility leads to the characteristic symptoms and flare-ups.
Causes and Contributing Factors
Genetics: A family history of eczema, asthma, or allergic rhinitis increases the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to dust mites, pollen, pet dander, or tobacco smoke can trigger symptoms.
Climate Conditions: Cold, dry weather worsens skin dryness and irritation.
Skin Irritants: Soaps, detergents, fragrances, and certain fabrics can provoke flare-ups.
Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate symptoms in many individuals.
Dietary Factors: Some foods may trigger allergic reactions, contributing to flare-ups in sensitive individuals.
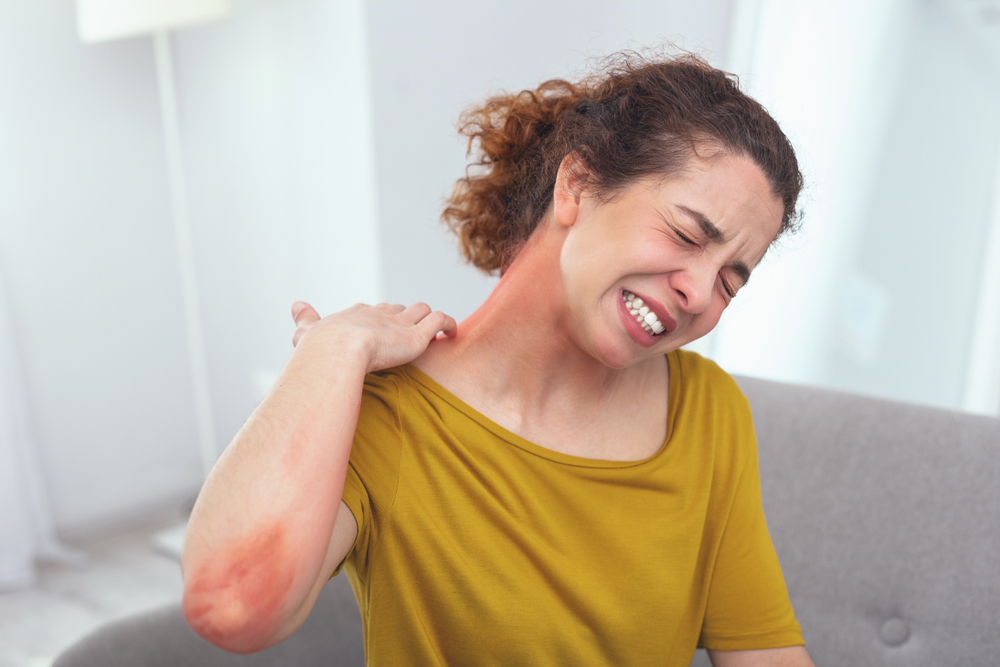
Symptoms and Signs
Persistent Dryness and Flakiness: Skin becomes rough and scaly.
Itching: Intense and often worsening at night or during stress.
Redness and Inflammation: Especially in the folds of the elbows, behind the knees, face, neck, and hands.
Leaks and Weeping: During acute flare-ups, the skin may ooze or develop crusts.
Thickened Skin: Chronic scratching can lead to lichenification, which is thick, leathery skin.
Diagnosis and When to See a Doctor
Diagnosing atopic dermatitis involves clinical evaluation and patient history. No specific test confirms the condition, but tests may be performed to identify triggers. Seek medical advice if you notice persistent or worsening symptoms, signs of infection, or if self-care measures fail to provide relief.
Effective Management Strategies
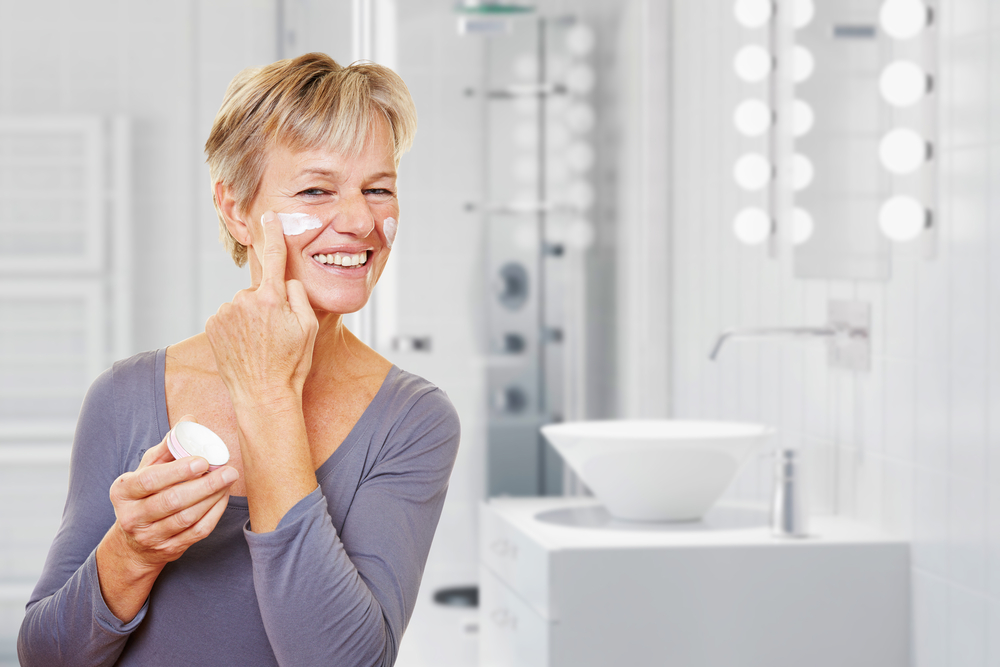
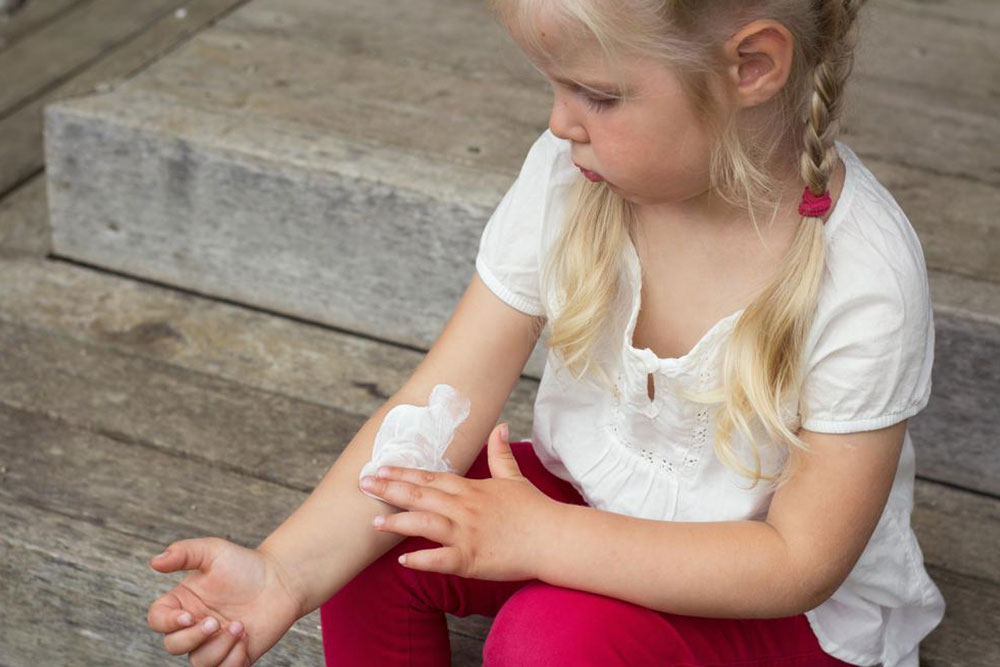
1. Skincare and Moisturization
Regularly applying emollients and moisturizers forms the cornerstone of managing atopic dermatitis. Products containing thick creams or ointments like petroleum jelly, aquaphor, or ceramide-rich formulations help restore the skin barrier and reduce dryness. Moisturize immediately after bathing to lock in hydration.
2. Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and minimizing exposure to known irritants and allergens is crucial. Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and laundry detergents. Opt for soft, breathable fabrics like cotton. Maintain indoor humidity levels, especially during winter months, to prevent skin from drying out.
3. Medical Treatments
Topical Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups.
Calcineurin Inhibitors: Immunomodulators like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus help control chronic inflammation without steroid-associated side effects.
Antihistamines: May alleviate severe itching and improve sleep.
Antibiotics or Antifungals: Prescribed if secondary bacterial or fungal infections occur.
4. Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications
Stress management through relaxation techniques can help reduce flare-ups. Maintaining a healthy diet that avoids known food triggers can also be beneficial for some individuals.
Long-term Care and Prevention
Consistent skin care routines, environmental controls, and vigilance in avoiding triggers empower individuals with atopic dermatitis to manage their condition proactively. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help tailor treatments as needed and monitor for any complications, such as skin infection or worsening of symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Help
If symptoms persist despite home remedies, worsen rapidly, or if signs of infection—such as pus, increased redness, swelling, or fever—appear, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Chronic or severe cases may require prescription medications or advanced therapies to keep symptoms under control.
Emerging Treatments and Future Outlook
Advances in understanding the genetic and immune mechanisms of atopic dermatitis are leading to innovative therapies, including biologics targeting specific immune pathways. These new options offer hope for more effective and personalized treatment plans for severe cases.
Conclusion
While atopic dermatitis remains a lifelong condition, effective management is entirely possible with a comprehensive approach that combines skincare, trigger avoidance, and appropriate medical treatment. Educating oneself about the condition and maintaining consistent habits can greatly improve quality of life and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.