Effective Techniques for Managing Atopic Dermatitis and Improving Skin Health
This comprehensive article explores effective strategies for managing atopic dermatitis, including medical treatments, skincare routines, and lifestyle modifications. It emphasizes the importance of personalized care, recognizing triggers, and maintaining emotional well-being. By understanding the condition and adopting a consistent management plan, individuals can significantly improve their skin health and quality of life despite the chronic nature of eczema. The article provides practical tips for at-home care and highlights the significance of professional guidance in controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups.
Effective Techniques for Managing Atopic Dermatitis and Improving Skin Health
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, affects over 18 million people across the country, making it one of the most widespread chronic skin conditions. This condition often begins in childhood but can persist into adulthood, significantly impacting the quality of life for those affected. Understanding comprehensive management strategies is essential for controlling symptoms, preventing flare-ups, and maintaining healthy skin. This detailed guide explores various approaches, from medical treatments to lifestyle adjustments, ensuring individuals can navigate their condition with confidence and ease.
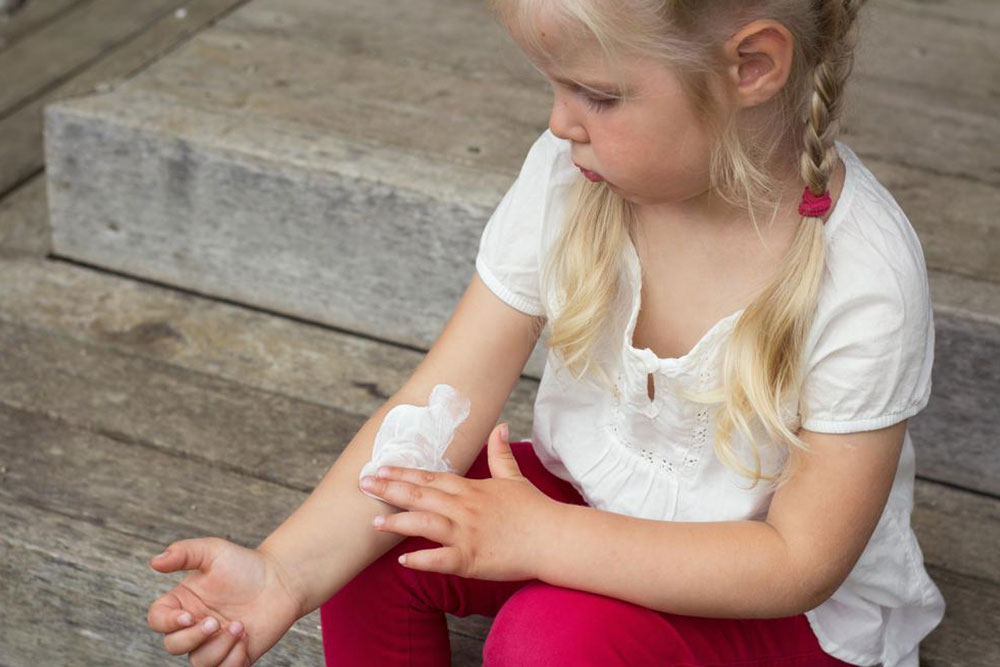
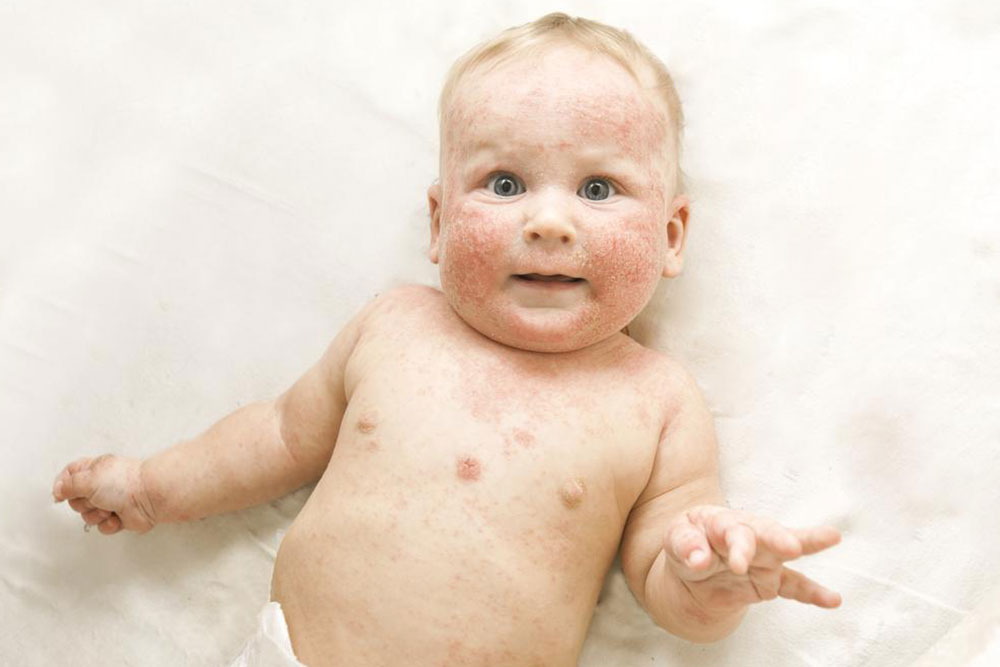
What is atopic dermatitis? Atopic dermatitis is characterized by inflamed, itchy skin that is often dry, red, and covered with patches that may appear brown, scaly, or flaky. It tends to appear on the face, scalp, and other flexible areas like behind the knees and elbows in children. While genetic predisposition plays a significant role, environmental factors, including allergens and irritants, can exacerbate symptoms. The skin’s impaired barrier function makes it more susceptible to external triggers, leading to persistent discomfort and additional skin infections if not managed properly. Moreover, many patients with atopic dermatitis also suffer from related allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever, indicating a complex interplay between skin health and immune response.
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis can vary widely but typically include notably dry and scaly skin, persistent redness, intense itching, and the presence of small bumps or open sores caused by scratching. In infants, initial signs are often observed on the face, forehead, and scalp. The condition is driven by a combination of genetic factors, environmental exposures, and immune system responses. For some, food allergies play a role in flare-ups, while others may have a family history of atopic diseases, increasing their susceptibility. Identifying triggers and managing exposure is key to controlling the condition effectively.
Although no cure exists currently for atopic dermatitis, a combination of targeted treatments and lifestyle modifications can substantially reduce symptoms and improve overall skin health. Diagnosis generally involves a thorough review of medical history, skin examination, and sometimes allergy testing. Tailored treatment plans are created to suit individual needs, incorporating topical medications, antibiotics if bacterial infections are present, and innovative biologic therapies for resistant or severe cases.
Additional therapies such as light (phototherapy) and wet dressings are employed to soothe the skin and promote healing. Adherence to proper skincare routines, avoiding known irritants, and effective stress management are integral components of treatment. Special care with infants—using gentle, fragrance-free products and moisturizing regularly—can prevent exacerbations and ensure healthy development. Consistent self-care combined with professional medical guidance enables patients to lead more comfortable lives despite the chronic nature of this skin disorder.
Practical at-home care tips: Regularly moisturizing with suitable emollients helps to restore the skin barrier and reduce flare-ups. Using anti-itch creams or oral antihistamines can alleviate discomfort. To prevent scratching, keep nails trimmed and consider protective coverings like bandages or gloves. Warm baths with natural soothing agents such as colloidal oatmeal can relieve irritation. Selecting gentle, fragrance-free soaps and detergents, along with stress-reduction techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises, can further support skin health. Participating in support groups and seeking counseling when needed can also provide emotional relief and practical advice for managing daily challenges associated with atopic dermatitis.