Comprehensive Guide to Managing Atopic Dermatitis Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies for managing atopic dermatitis, a common chronic skin condition. It covers diagnosis, medication options, lifestyle changes, and triggers control to help patients reduce flare-ups and improve skin health. Suitable for patients of all ages, the article emphasizes the importance of personalized treatment plans, skincare routines, and lifestyle adjustments to enhance quality of life and lessen the impact of eczema.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Atopic Dermatitis Effectively
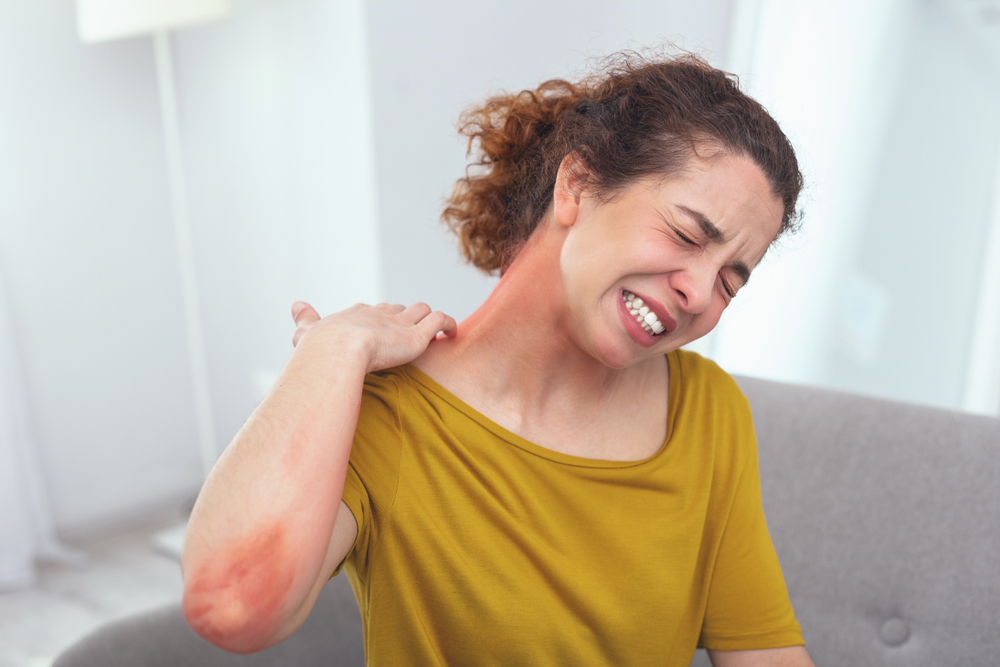
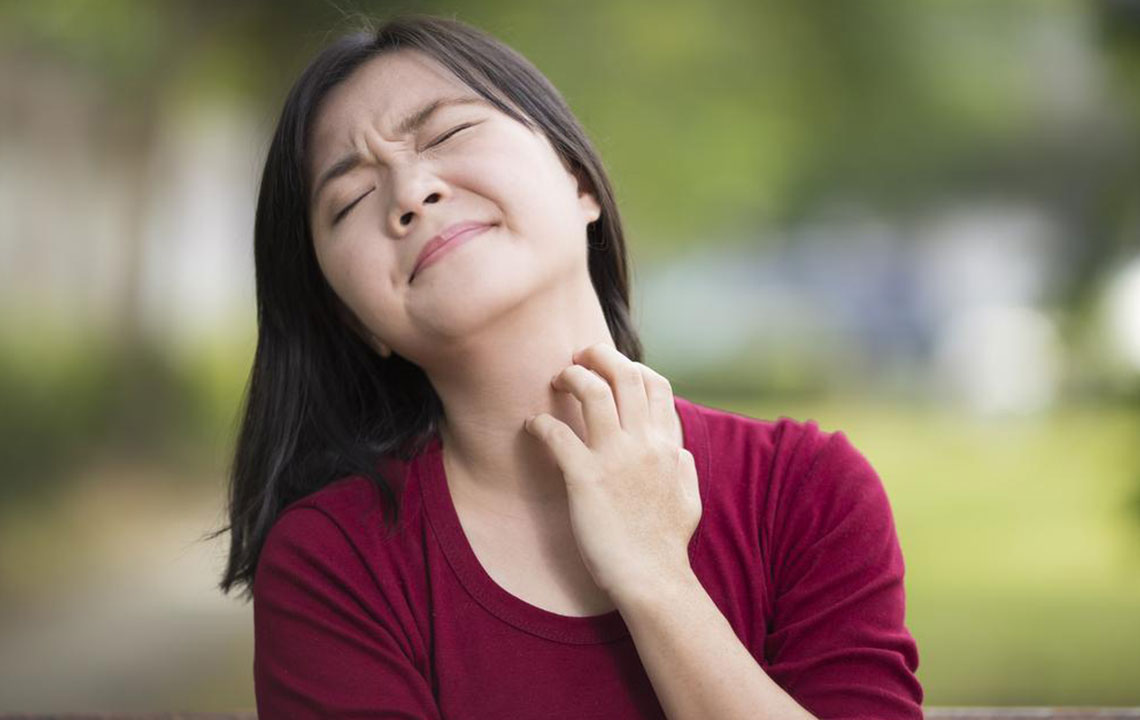
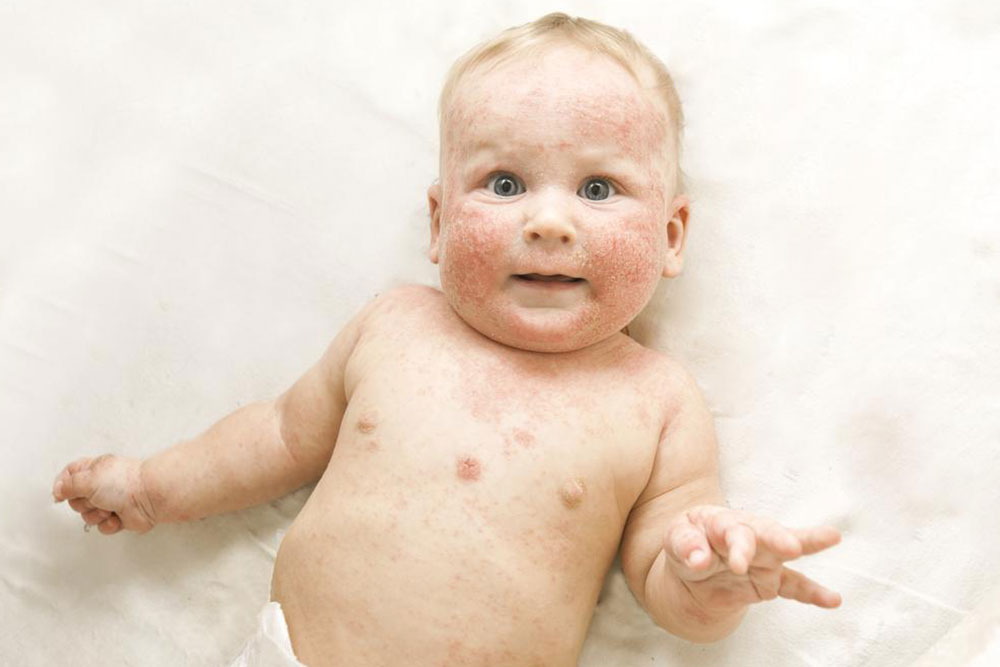
Atopic dermatitis, commonly referred to as eczema, is a persistent and often troublesome skin condition affecting millions worldwide. It is characterized by intense itchiness, redness, dryness, and inflammation of the skin. While it is most prevalent among children, adults can also develop this condition, and it often fluctuates in severity over time. Managing atopic dermatitis requires a multifaceted approach that involves understanding the condition, identifying triggers, following proper skincare routines, and utilizing appropriate medical treatments. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore effective strategies for managing atopic dermatitis, preventive measures, treatment options, and lifestyle adjustments that can help improve quality of life for those affected.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a complex chronic inflammatory skin disorder influenced by genetic, environmental, and immune factors. It often runs in families, especially among those with a history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever. Although the exact cause remains unknown, the skin barrier in affected individuals tends to be impaired, leading to increased sensitivity and susceptibility to irritants, allergens, and microbes. This results in the characteristic symptoms of eczema.
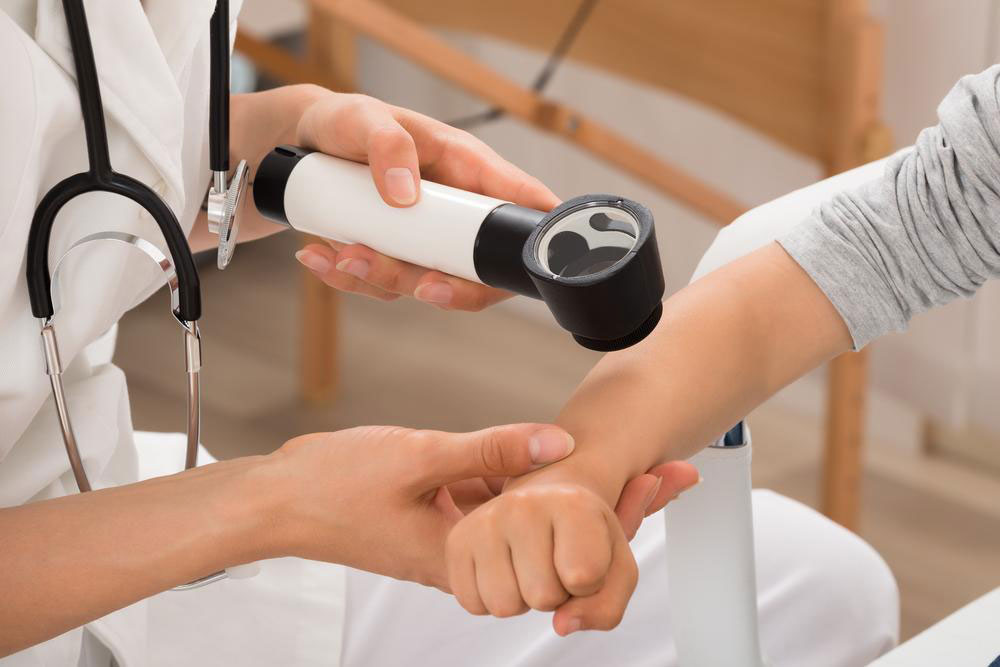
Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on characteristic symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. Unlike some other skin conditions, atopic dermatitis does not typically require elaborate laboratory tests for diagnosis. However, doctors may perform patch testing or allergy testing to identify specific triggers such as foods, environmental allergens, or contact irritants. Recognizing these triggers is vital for formulating an effective management plan.
Being aware of the socioeconomic impact of this condition is equally important, as persistent symptoms can affect mental health, self-esteem, and daily functioning. Education about the condition empowers patients and caregivers to adopt proactive steps towards control and relief.
For children experiencing eczema, it's crucial for caregivers to inform healthcare providers about any food allergies or sensitivities. This information helps tailor treatments effectively and may prevent flare-ups triggered by dietary factors.
Effective Medications for Eczema Relief
Topical creams and ointments
Corticosteroid creams and ointments are the cornerstone of eczema treatment. They rapidly reduce inflammation, redness, and itching. Proper application is essential—applying after moisturizing maximizes their effectiveness. It's important not to overuse corticosteroids to prevent skin thinning and other side effects.
Antibiotics
When bacterial infections are present or there are open sores, antibiotic ointments or oral antibiotics may be necessary. Preventing bacterial colonization is key to managing outbreaks.
Anti-inflammatory medications
In severe cases of atopic dermatitis, doctors may prescribe systemic corticosteroids like prednisone for short-term use. Additionally, newer biologic agents such as dupilumab have shown promising results for stubborn cases by targeting immune pathways involved in allergy and inflammation. These medications are usually prescribed under careful supervision due to potential side effects.
Additional Therapies and Lifestyle Modifications
Wet dressings and occlusive therapy
Applying moist dressings over affected areas, especially in children, can reduce inflammation, hydrate the skin, and facilitate medication penetration. This technique often provides rapid relief from acute flare-ups.
Phototherapy
Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly narrowband UVB therapy, can be highly effective for refractory eczema. It helps modulate immune responses and reduce skin inflammation. However, due to potential risks like skin aging and increased cancer risk, phototherapy should be administered under medical supervision and reserved for severe cases that do not respond to topical treatments.
Home care and lifestyle strategies
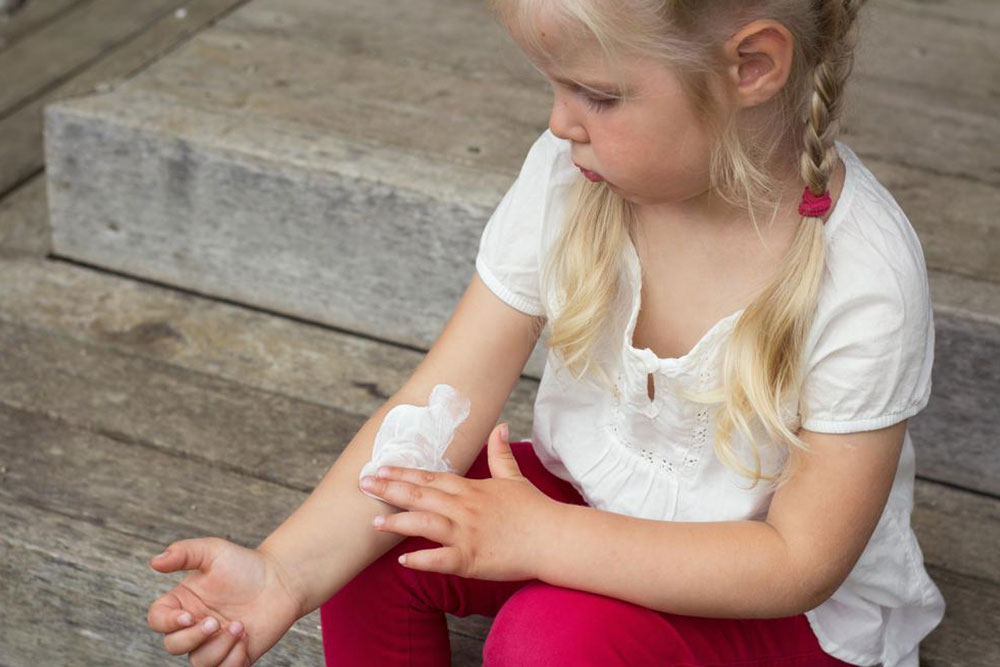
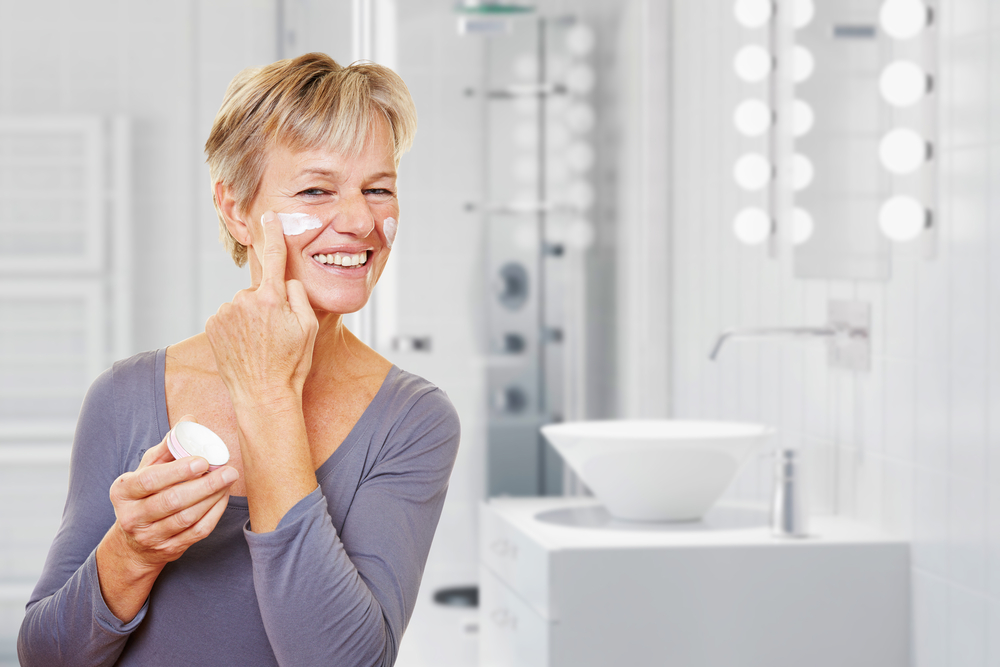
Regular moisturizing with emollients is fundamental to restoring and maintaining the skin barrier. Using hypoallergenic, fragrance-free products helps minimize irritation. Avoiding known irritants such as harsh soaps, detergents, and synthetic clothing is equally important. Humidifiers can add moisture to dry indoor air, decreasing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Wearing soft, natural fabrics like cotton also reduces friction and irritation.
Stress management
Psychological stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Incorporating stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or relaxation exercises can help manage flare-ups.
In addition to these measures, regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor the condition, adjust treatments, and address any new concerns. Patient education and adherence to treatment plans significantly enhance outcomes and improve the patient's quality of life.
In conclusion, managing atopic dermatitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes proper diagnosis, medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and awareness of triggers. By understanding and implementing these strategies, individuals living with eczema can significantly reduce flare-ups, control symptoms, and lead healthier, more comfortable lives.