Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Advanced Management Techniques
This comprehensive guide explores atopic dermatitis, highlighting its symptoms across different age groups, causes, triggers, and advanced management strategies. From skincare to medical treatments, learn how to effectively control this chronic skin condition and improve quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Advanced Management Techniques
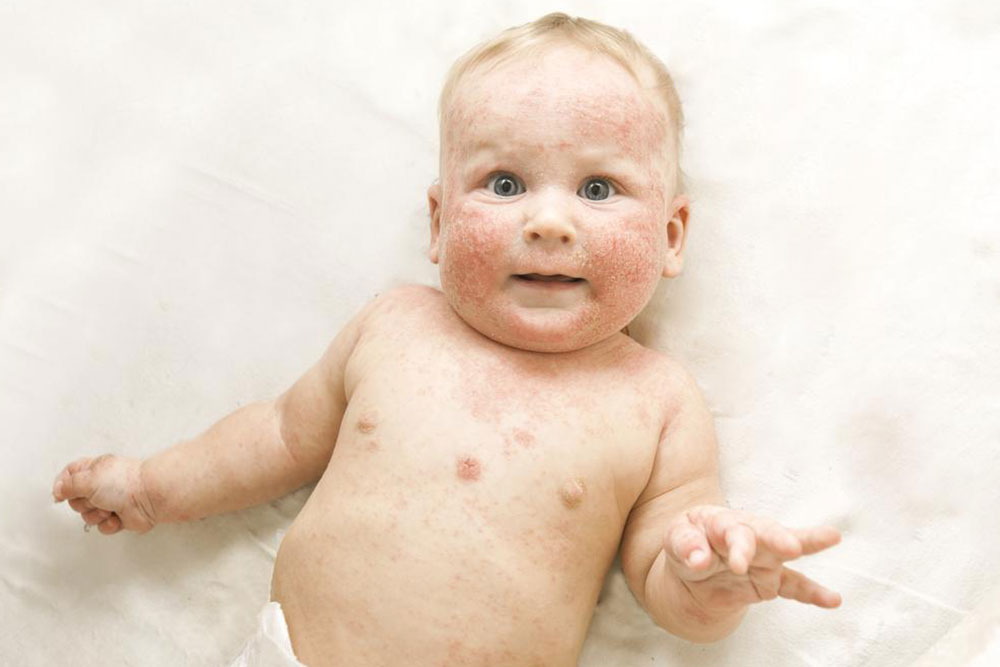
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a persistent inflammatory skin condition that can cause significant discomfort and affect quality of life. Characterized by dry, red, itchy, and swollen skin, this condition often has a hereditary component, making genetics a key factor in its development. Understanding the complex symptoms, potential triggers, and effective management strategies is crucial for those affected, whether they are infants, children, or adults.
This skin disorder affects millions worldwide and can appear at any age, although it is most prevalent during childhood. Its chronic nature means that management is often ongoing, with various treatments tailored to individual cases. Proper skincare, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions play vital roles in controlling symptoms and preventing complications.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Symptoms vary depending on age, skin type, and severity but generally include several hallmark signs:
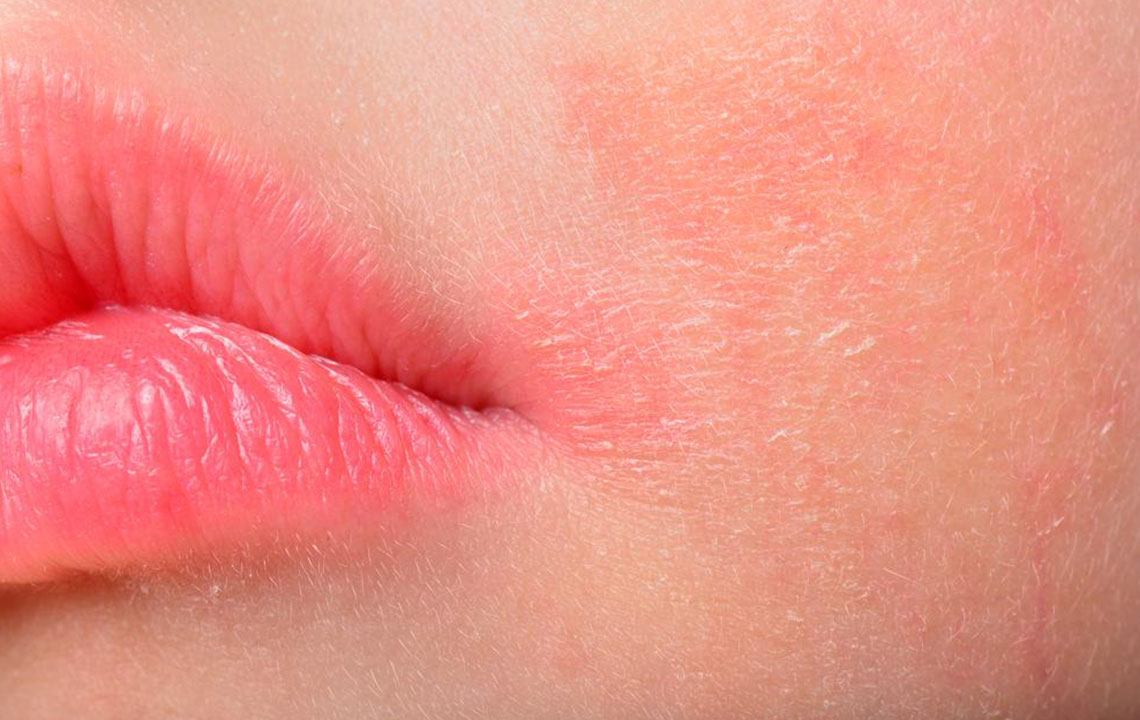
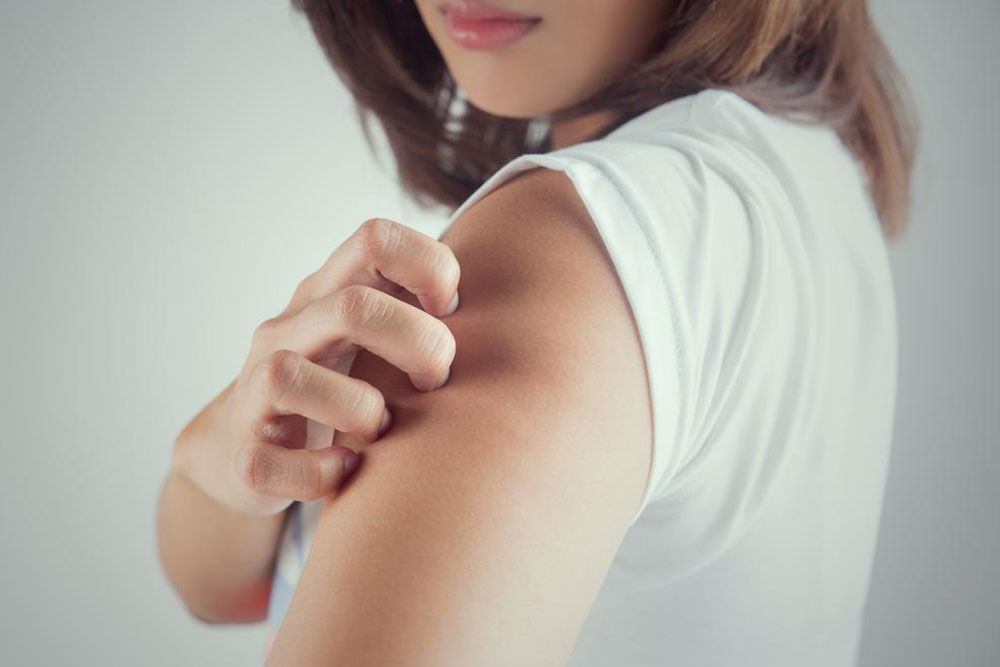
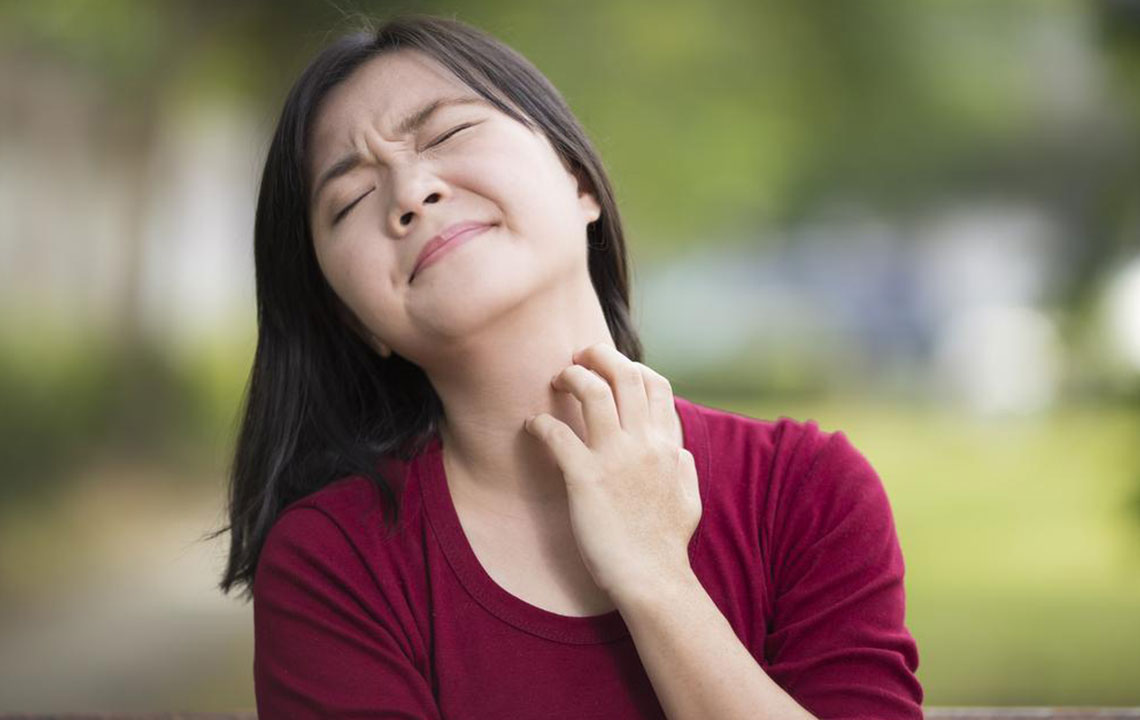
Persistent dry, itchy skin that can be intensely uncomfortable
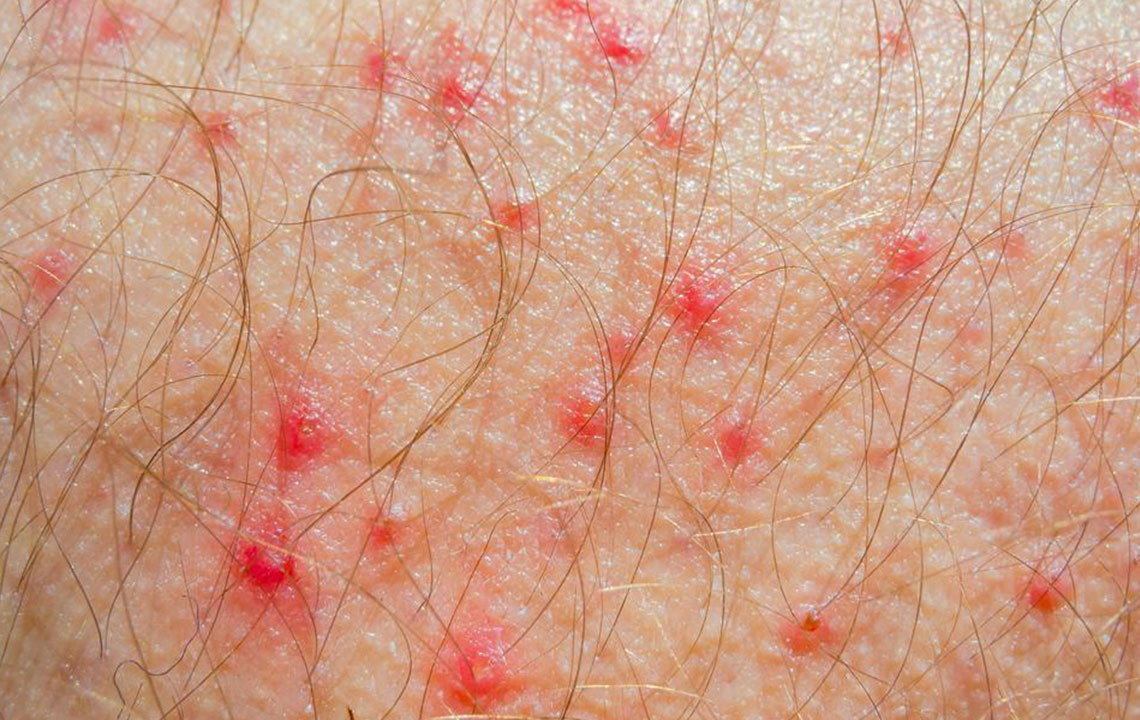
Formation of small, fluid-filled blisters that can break open and crust over
Skin becomes thickened, scaly, or discolored over time due to frequent scratching
In some cases, oozing or crusting of the skin, especially during flare-ups
Since the presentation of symptoms can differ across age groups, understanding where and how these signs manifest is important for accurate diagnosis.
How Atopic Dermatitis Presents Across Age Groups
Infants and Young Children: Rashes commonly appear on the cheeks, scalp, and behind the ears. These areas become red, inflamed, and often itch excessively. The discomfort usually leads to disturbed sleep and irritability, making caregiving more challenging. Because the skin barrier is still developing, the condition tends to be more severe in this age group.
Older Children (Over Two Years): As children grow, the rash often shifts to the insides of elbows, behind the knees, around the neck, and on the wrists and ankles. The initial red patches might thicken and turn into nodular lesions if scratching persists, leading to a more chronic form of eczema. The skin in affected areas can become leathery or hyperpigmented over time.
Adults: In adults, the facial area and neck are frequently affected. The skin may appear dry, cracked, or scaly, with episodes of intense itching. Persistent inflammation can result in skin discoloration and a leathery texture, impacting self-esteem and daily functioning.
Underlying Causes and Contributing Factors
While the precise cause of atopic dermatitis remains complex, it is generally linked to a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental influences. A defective skin barrier makes the skin more vulnerable to irritants, allergens, and microbes, leading to inflammation.
Genetics: A history of allergies such as asthma, hay fever, or eczema in the family increases the risk.
Environmental triggers: Pollen, pet dander, dust mites, harsh soaps, detergents, temperature changes, and exposure to wool or synthetic fabrics can precipitate flare-ups.
Immune system dysregulation also plays a role, with an overactive immune response to benign stimuli causing persistent inflammation.
Effective Management and Treatment Strategies
Controlling atopic dermatitis involves a multi-pronged approach aimed at alleviating symptoms, repairing the skin barrier, preventing infections, and minimizing triggers. Here are some of the most effective strategies:
Moisturization: Regular application of barrier-repair moisturizers is fundamental. Using thick creams or ointments containing ceramides restores the skin’s protective layer, reducing dryness and itching.
Trigger Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding known irritants and allergens such as wool, certain fragrances, pollen, and dust mites can significantly reduce flare-ups.
Gentle Skin Care: Using mild, fragrance-free cleansers and lukewarm water for bathing helps prevent further skin irritation. Aquaphor, Eucerin, or similar ointments are recommended for daily use.
Bathing Techniques: Short lukewarm baths or bleach baths (adding a small amount of bleach to the bathwater) can help reduce bacteria on the skin, lessen oozing, and control infection risk. Typically, 10-minute baths are sufficient, followed by immediate moisturization.
Medications: Topical corticosteroids are the mainstay for managing inflammation during flare-ups. They should be used as prescribed and in consultation with healthcare providers. In severe or stubborn cases, topical calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be prescribed.
Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can help relieve intense itching, especially during sleep, enhancing comfort and rest.
Supplements and Diet: Vitamin D supplementation and probiotics might have a role in reducing inflammation and improving skin health, although research is ongoing. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods is generally beneficial.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light may be recommended for chronic cases unresponsive to topical treatments, helping modulate immune responses in the skin.
Preventing Complications and Promoting Long-Term Skin Health
The ultimate goals of treatment are to reduce symptoms, minimize flare-ups, prevent skin infections, and prevent skin thickening or scarring. Maintaining consistent skin care routines, avoiding known triggers, and adhering to prescribed medications are critical components of a successful management plan.
Considering the psychological impact of visible skin conditions, support groups and counseling may also be advisable for coping strategies and emotional well-being.
In summary, while atopic dermatitis can be a challenging condition, advances in dermatology and skin care have provided effective management options. Early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and diligent skin care routines can help those affected lead healthier, more comfortable lives.