The Ultimate Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Advanced Treatments
Explore this detailed guide on atopic dermatitis, covering its causes, symptoms, types, and modern treatment options. Learn how early diagnosis and tailored management can improve quality of life for those affected by this common skin condition. This comprehensive overview also provides tips on recognizing symptoms and preventing flare-ups to ensure healthier, more comfortable skin for children and adults alike.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis: An In-Depth Look into Causes, Types, and Effective Treatments
Atopic dermatitis, commonly referred to as eczema, is a widespread chronic skin condition that significantly impacts the lives of millions worldwide. Known for its characteristic itchy, inflamed, and dry skin, atopic dermatitis can appear in various areas of the body, often presenting differently depending on the individual’s age, genetics, and environmental factors. While it is a long-term condition without a definitive cure, understanding its underlying causes, recognizing the different types, and exploring effective management strategies are crucial steps toward improving quality of life. This guide aims to provide comprehensive insights into every aspect of atopic dermatitis, from its biology to modern treatment options, equipping you with the knowledge necessary to navigate this complex skin disorder effectively.
What is atopic dermatitis and how does it develop?
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by a malfunction in the skin’s barrier function, resulting in excessive dryness, susceptibility to irritants, and increased vulnerability to infections. The skin’s outermost layer, the epidermis, usually acts as a protective barrier, preventing external irritants, allergens, and pathogens from entering the body. In individuals with atopic dermatitis, this barrier is compromised, leading to frequent flare-ups and persistent symptoms. The condition is strongly linked to immune system irregularities, where the immune response overreacts to common environmental triggers, causing inflammation and redness. Despite extensive research, the precise root cause remains elusive, but a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and immune dysfunction is believed to contribute to its development.
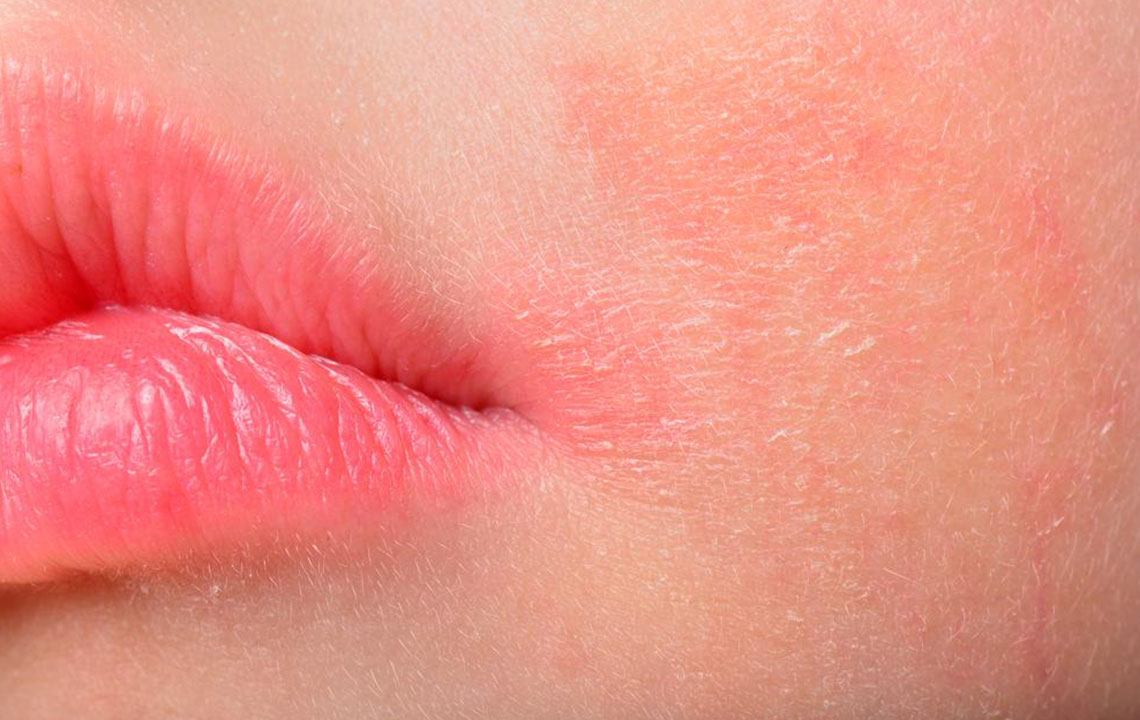
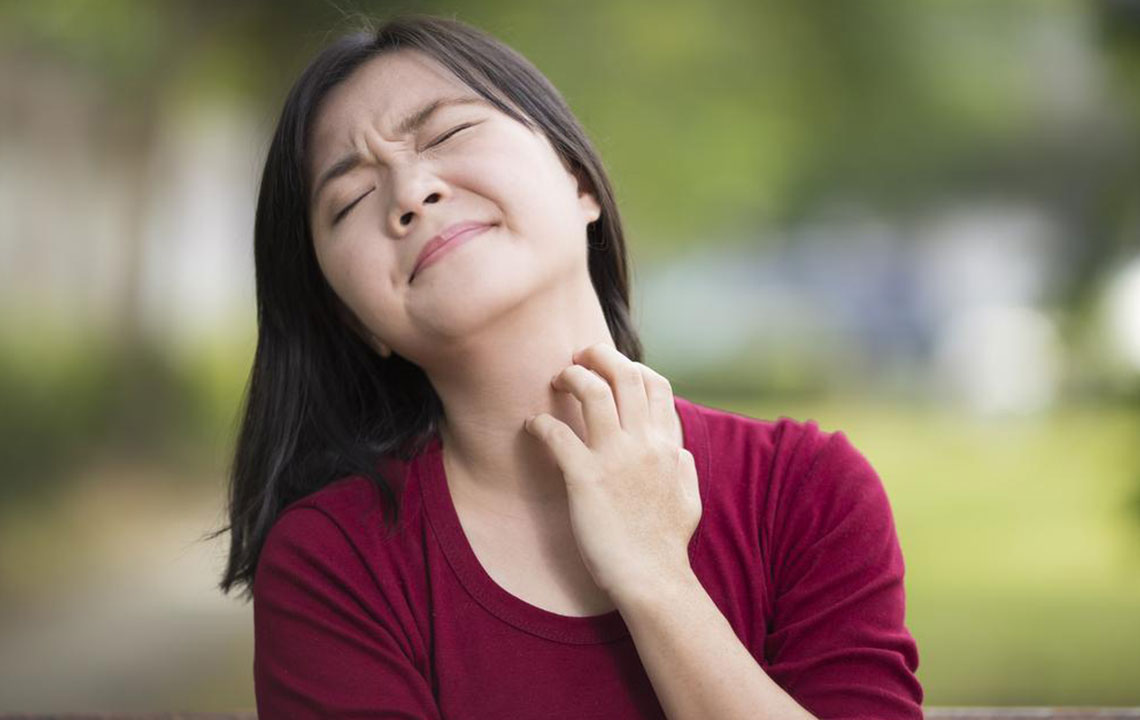
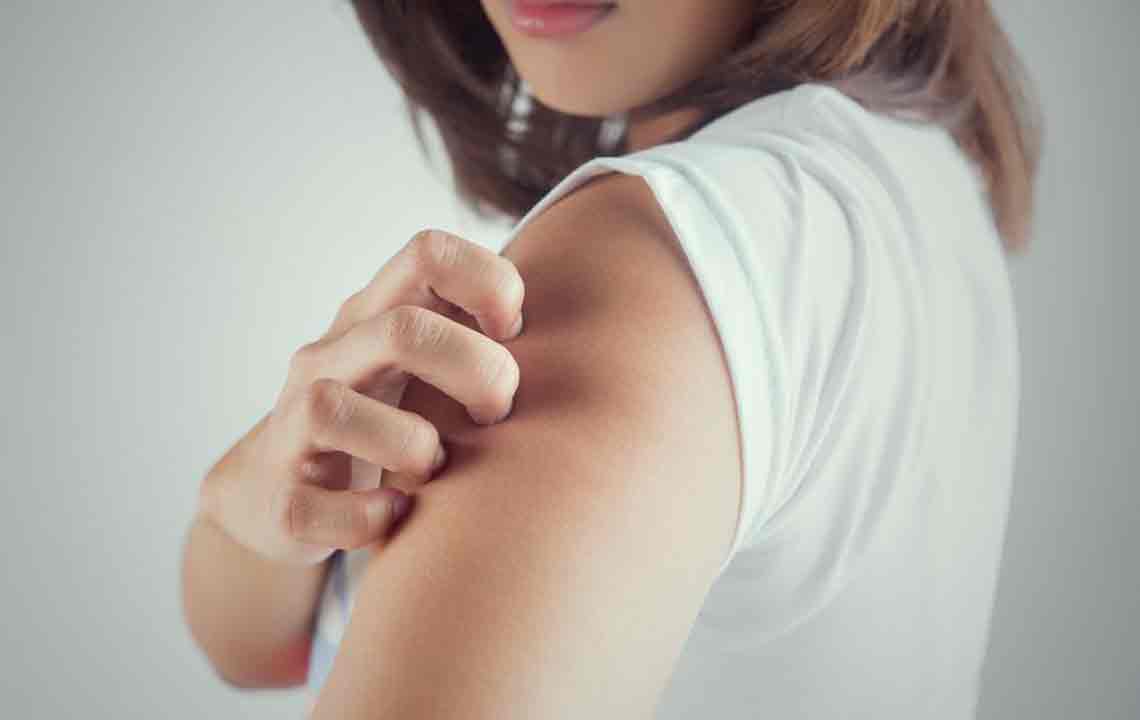
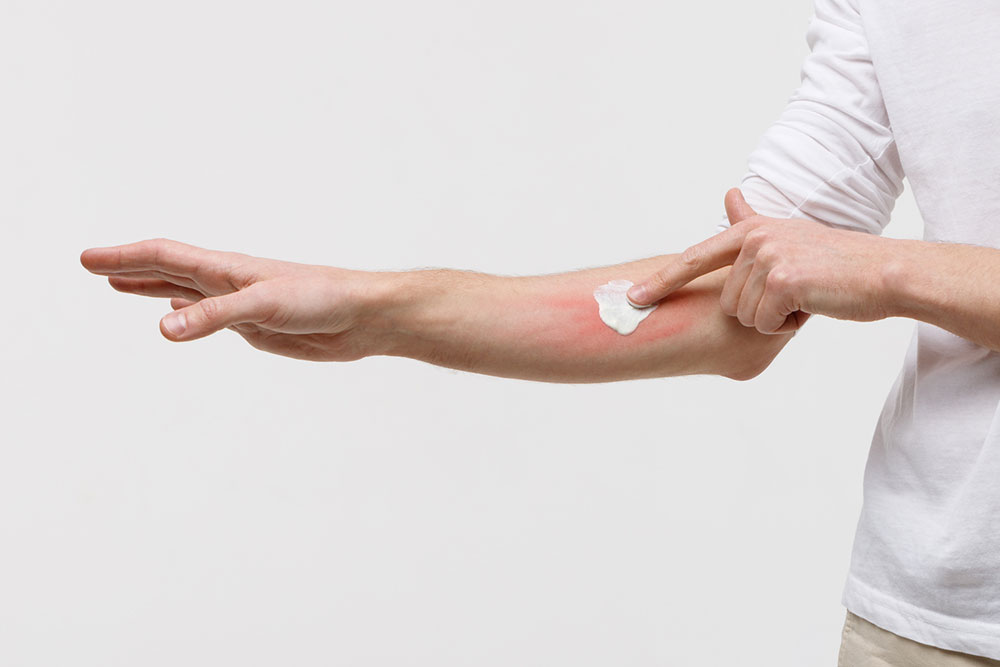
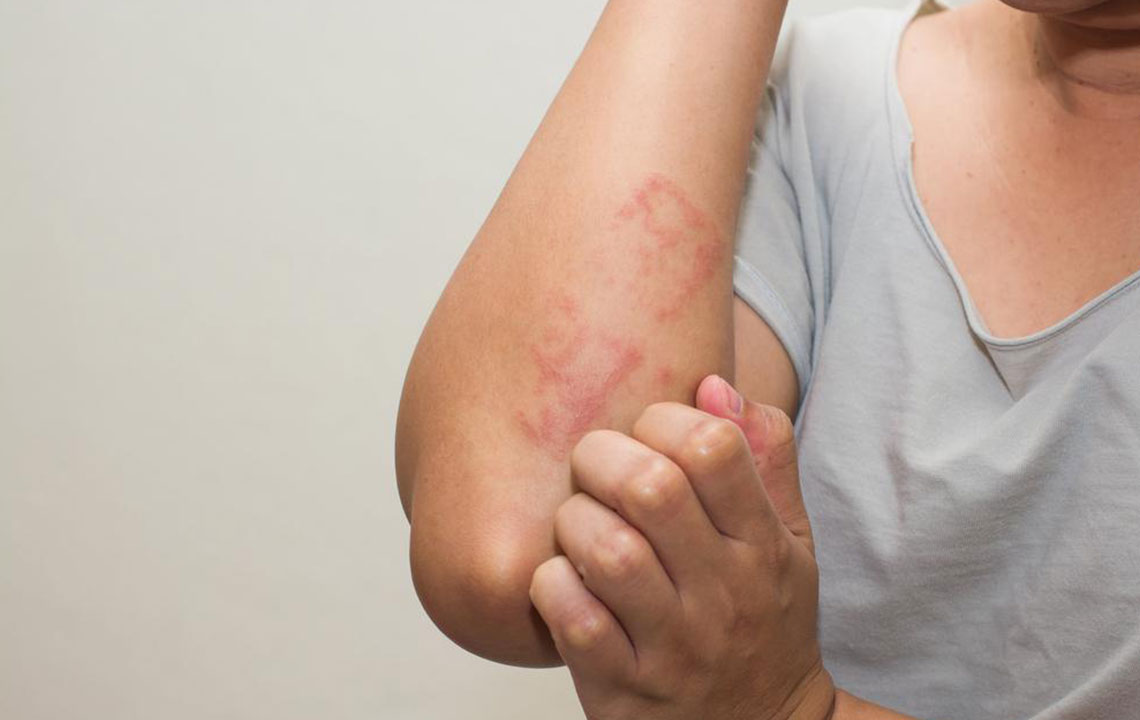
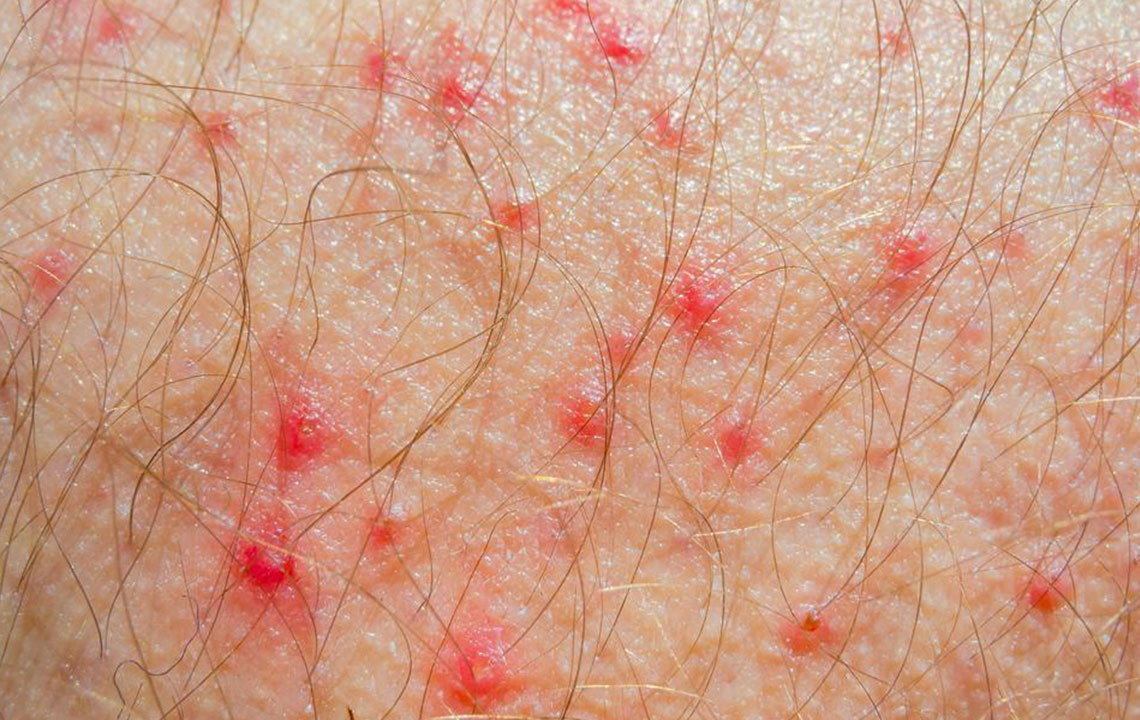
Symptoms can range from mild irritation to severe inflammation, including redness, swelling, itching, scaling, cracking, and oozing lesions. Recognizing these visual signs is essential for early diagnosis and management. To aid in identification, visual aids such as dermatology images of atopic dermatitis are widely available and often used by healthcare professionals to distinguish this condition from other skin issues.
Atopic dermatitis manifests in various forms, each with unique features and implications. These include contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, nummular eczema, and stasis dermatitis, each caused by different triggers or underlying health issues. Understanding these variants is vital for targeted treatment approaches and avoiding triggers that could exacerbate the condition.
Contact dermatitis results from direct contact with irritating substances like chemicals, soaps, or plants such as poison ivy, causing flaky, thickened skin and painful blisters. Seborrheic dermatitis, often related to stress or genetic factors, appears as greasy, yellowish scales on areas rich in oil glands like the scalp, face, and behind the ears. Allergic dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to allergens such as pollen, animal dander, or specific foods, leading to rashes and swelling. Nummular eczema, a rare form characterized by coin-shaped lesions, tends to be persistent and challenging to treat. Stasis dermatitis predominantly affects the lower limbs due to circulatory issues, resulting in dark patches, swelling, and skin ulcerations. Recognizing these variations assists healthcare providers in diagnosing and managing each form effectively.
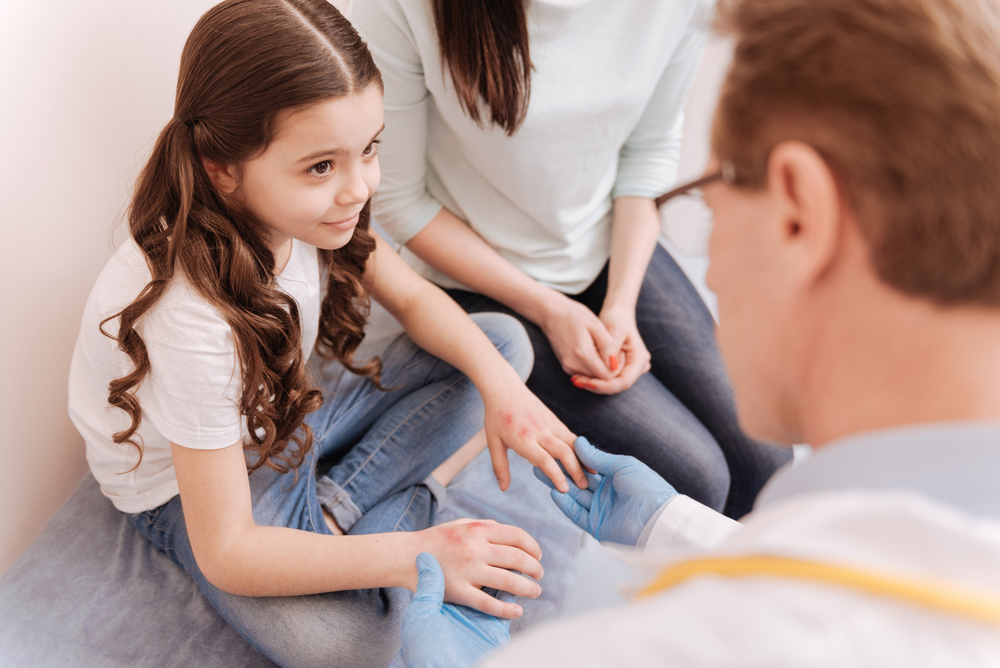
Most cases of atopic dermatitis begin in early childhood, with symptoms appearing before age five in many cases. Infantile presentations include widespread rashes that can affect the face, scalp, and limbs. A significant number of children continue to experience symptoms into adulthood, where the condition may become more localized but still cause discomfort and emotional distress. Persistent itching and skin breakdown can interfere with sleep and daily activities, emphasizing the importance of early intervention. If your child develops a persistent rash or if you experience recurrent skin issues, it is crucial to seek prompt evaluation from a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Data indicates that about 10% of newborns are affected by atopic dermatitis, with many carrying the condition into adulthood. Currently, over 15 million Americans suffer from this disorder, highlighting its prevalence and the importance of increased awareness and education. Managing atopic dermatitis involves a combination of skincare routines, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments, including topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, antihistamines, and in severe cases, systemic therapies. Staying informed about new research and emerging therapies can significantly improve outcomes and help individuals lead healthier lives despite the chronic nature of the condition.