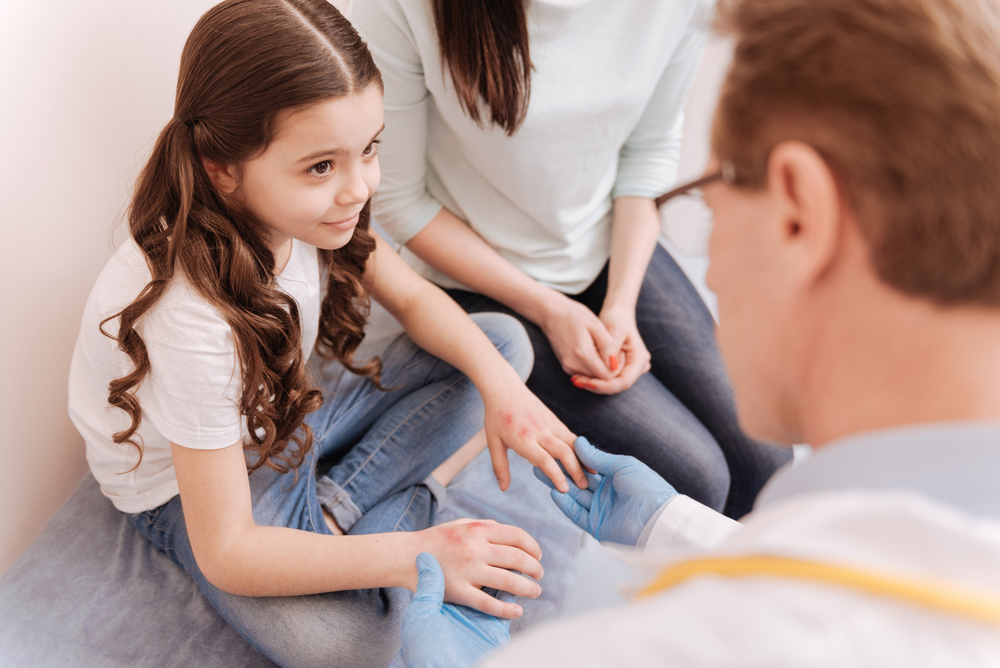
Comprehensive Guide to Causes of Chronic Itchy Skin and When to Seek Medical Help
Persistent itchy skin can originate from numerous causes, from allergic reactions to systemic illnesses. Recognizing the signs and understanding when to seek medical attention is crucial for effective treatment. This comprehensive guide covers common causes such as contact dermatitis, eczema, sunburn, medication reactions, dry skin, hives, dandruff, psoriasis, infections, and underlying health conditions. Addressing chronic pruritus promptly can help prevent complications and improve quality of life. If your skin itchiness persists or worsens, consulting a healthcare professional is highly recommended for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.

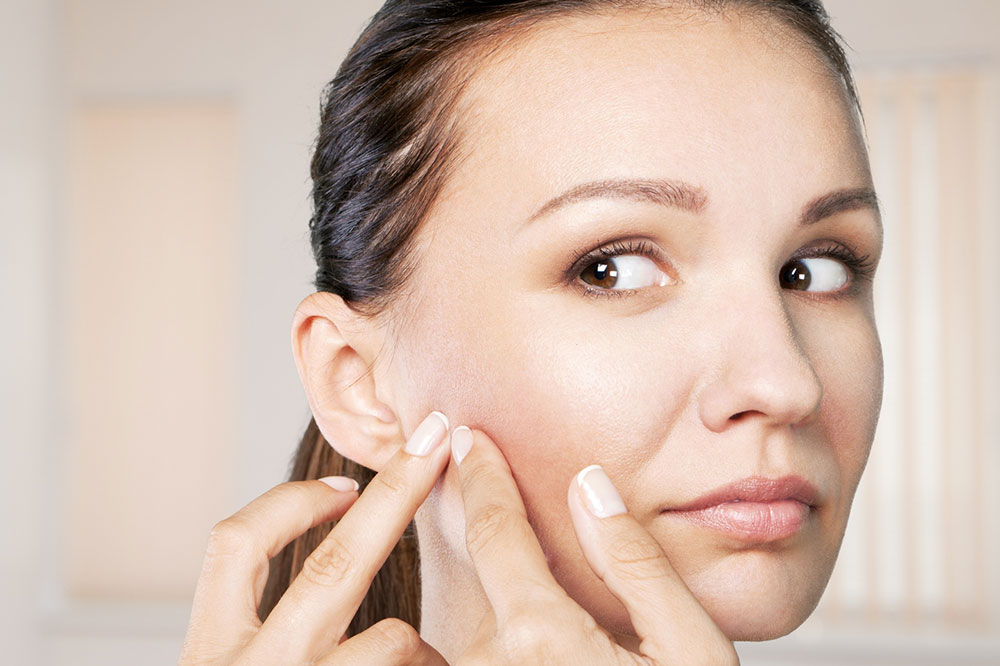
Comprehensive Guide to Causes of Chronic Itchy Skin and When to Seek Medical Help
Persistent itching can be an incredibly uncomfortable and disruptive experience, often leaving individuals searching for answers. While occasional itching resulting from minor irritants or insect bites is normal, ongoing or recurrent itchiness may signal an underlying health condition that requires attention. Understanding the various causes of chronic itchy skin is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. This detailed guide explores the main reasons behind persistent pruritus and highlights when it’s critical to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
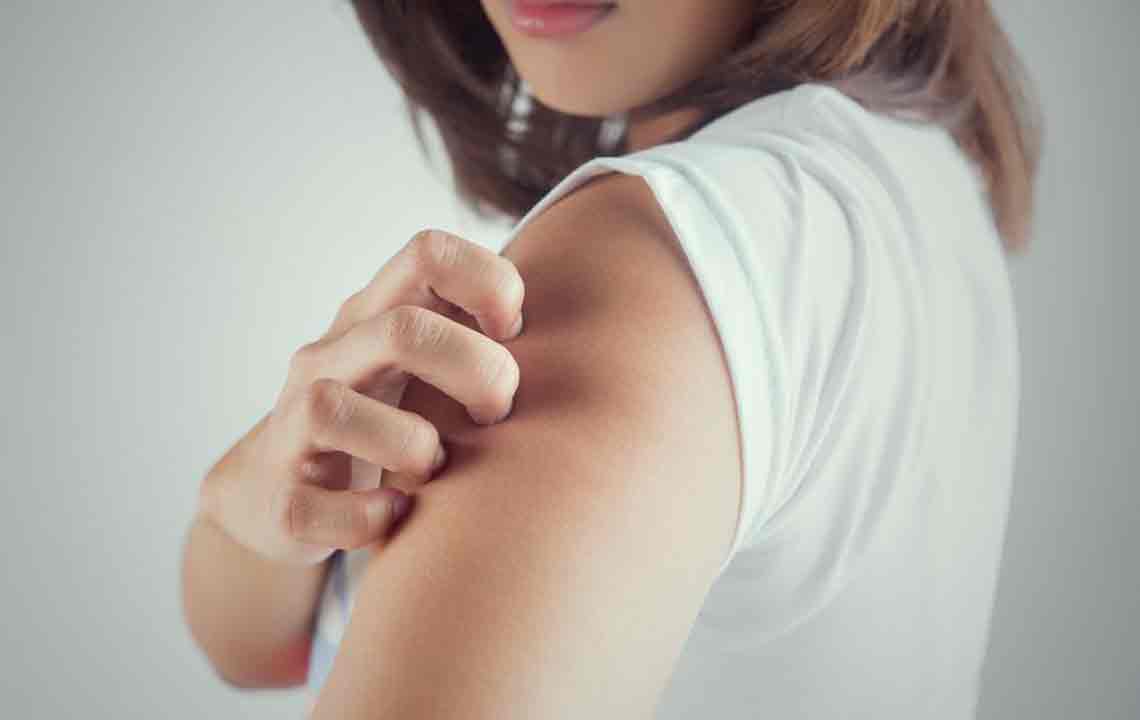
Itching, medically known as pruritus, can affect localized areas or the entire body. Its appearance may accompany other skin abnormalities such as rashes, dryness, flaky patches, cracked skin, blistering, or redness. Recognizing these signs and understanding their potential causes can help in identifying the root of the problem and seeking appropriate care.
Below are some of the most common causes of persistent and troublesome skin itchiness:
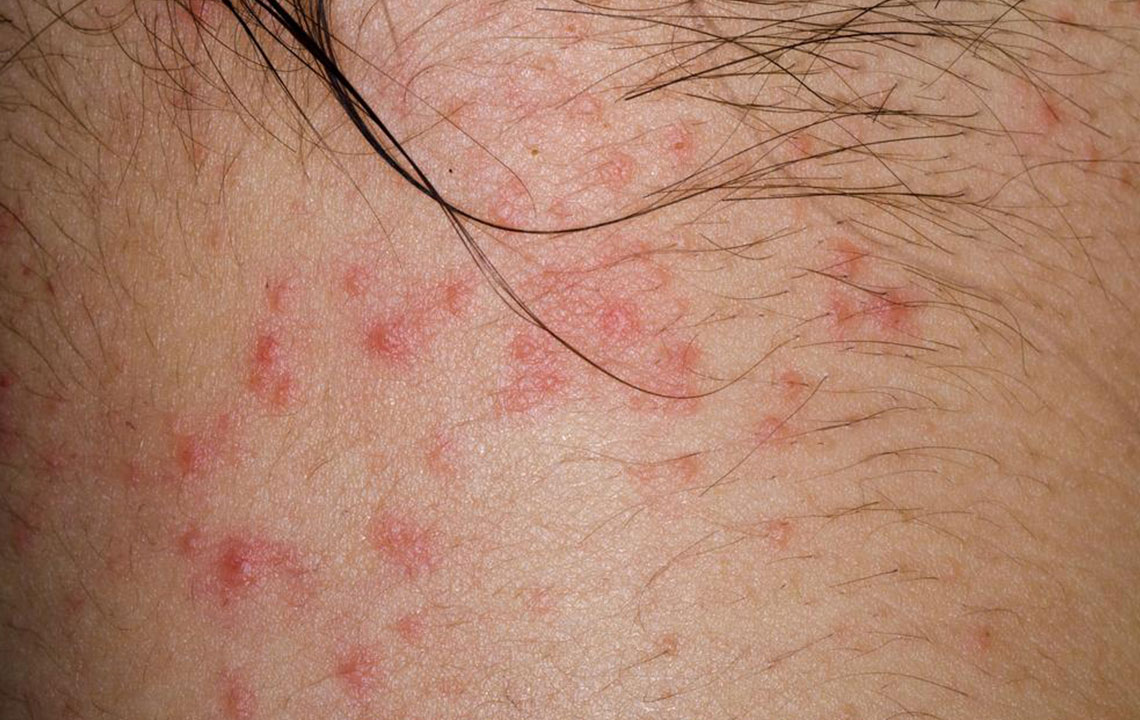
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a prevalent cause of itching that results when the skin reacts to specific environmental allergens. These triggers include soaps, deodorants, fabrics, cosmetics, metals like nickel, and even certain plants or pollen. Repeated exposure can lead to redness, swelling, peeling, and intense itching, often localized to specific areas where contact occurs. Recognizing irritants and avoiding exposure can significantly reduce symptoms. In some cases, topical corticosteroids or antihistamines may be prescribed to manage inflammation and itching.
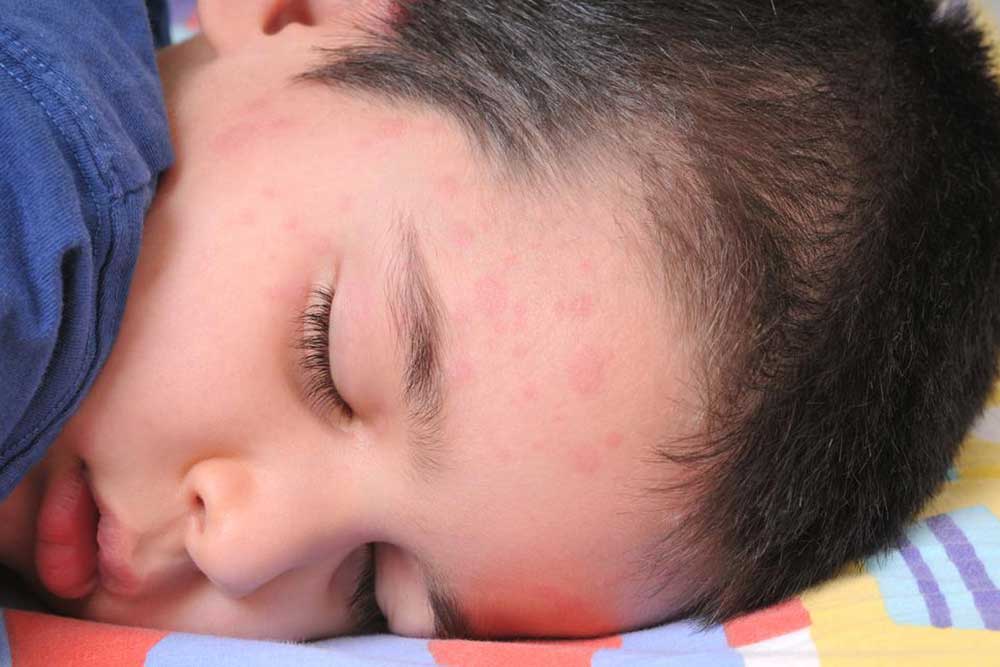
Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by itchy, dry, and scaly patches that may become inflamed, cracked, or infected if scratched excessively. It commonly appears in children but can affect adults too. Eczema often runs in families and is associated with other allergic conditions such as asthma or hay fever. Managing eczema involves skin hydration through regular moisturizers, avoiding known irritants, and in some cases, using medicated creams or systemic therapy to control flare-ups.
Sunburn
Prolonged sun exposure can damage the skin’s protective barrier, leading to inflammation, peeling, and painful redness. Sunburned skin often becomes intensely itchy as it heals, especially if blisters form. Sun protection measures, including applying broad-spectrum sunscreens, wearing protective clothing, and minimizing sun exposure during peak hours, are essential in preventing burns. For existing sunburns, cooling lotions, aloe vera, and antihistamines can help alleviate discomfort.
Medication Reactions
Certain medications are known to cause allergic reactions or skin sensitivities that manifest as itching, rashes, or hives. Common culprits include blood pressure drugs, estrogen therapy, allopurinol (used for gout), diuretics, and opioids. These reactions can range from mild to severe, sometimes accompanied by swelling or respiratory symptoms. If you suspect your medication is causing skin issues, consult your healthcare provider immediately to adjust or change your prescription safely.
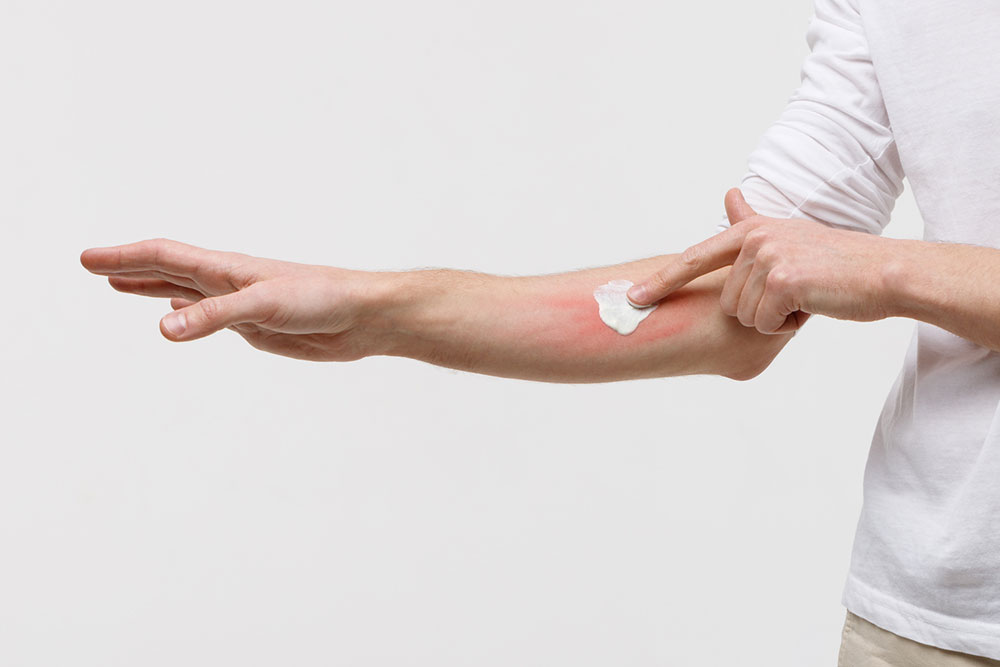
Dry Skin (Xerosis)
Dry skin is a frequent cause of itching, especially in colder months or in individuals with low humidity environments. Lack of moisture makes the skin flaky, rough, and prone to inflammation, leading to persistent itchiness. Regularly applying emollients, avoiding hot showers, and using gentle cleansers can significantly improve skin hydration. Maintaining proper hydration and using humidifiers indoors also help prevent dry skin from becoming itchy and irritated.
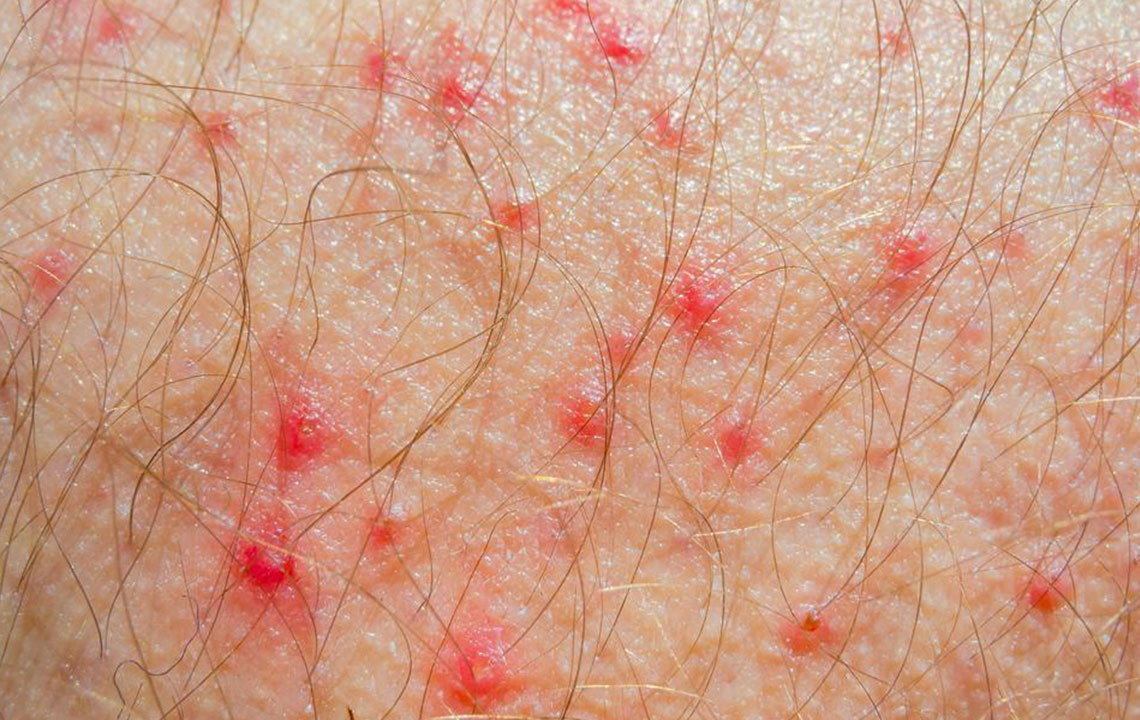
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives are raised, itchy welts that appear suddenly on the skin due to allergic reactions. Triggers include heat, stress, certain foods, insect bites, and exposure to allergens like pollen or pet dander. Hives can resolve quickly or persist for days, often recurring with re-exposure to triggers. Anti-itch medications like antihistamines are typically effective in controlling symptoms. Severe cases may require corticosteroid treatment and identification of the allergy source.
Dandruff and Scalp Conditions
Chronic dandruff involves dry, flaky scalp skin, leading to itching and discomfort. Fungal overgrowth, particularly Malassezia yeast, can worsen dandruff and cause scalp irritation. Proper scalp hygiene, medicated shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, ketoconazole, or coal tar can manage dandruff effectively. Untreated dandruff can cause hair thinning and persistent irritation, emphasizing the importance of early intervention.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by abnormal rapid skin cell turnover, resulting in thick, scaly patches that often itch and cause discomfort. The patches may be red, inflamed, and covered with silvery scales. Psoriasis can flare unpredictably, triggered by stress, infections, medications, or skin injuries. Treatments include topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medications aimed at modulating immune response and reducing skin cell proliferation.
Fungal, Bacterial, and Other Infections
Fungal infections such as athlete's foot or ringworm thrive in moist environments and can cause intense itching, redness, and rash formation. Bacterial infections like impetigo can also cause localized itching and skin breakdown. Proper hygiene, antifungal or antibacterial medications, and keeping the skin dry are crucial in treating these conditions. Preventative measures include wearing breathable clothing and avoiding prolonged moisture exposure.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Persistent or unexplained itchiness may be a symptom of more serious health issues, including shingles, nerve damage, multiple sclerosis, thyroid disorders, HIV/AIDS, or even internal cancers such as lymphoma or Hodgkin’s disease. Certain systemic illnesses affect the skin, causing generalized itchiness that does not resolve with topical treatments. Additionally, psychological factors like depression and anxiety can lead to compulsive scratching, exacerbating the condition. When itching persists without an obvious cause, comprehensive medical evaluation is essential.
It is crucial to recognize that in some cases, chronic itching might be a sign of severe underlying diseases, such as liver disease, kidney dysfunction, or thyroid problems. These conditions require prompt diagnosis and specialized treatment. If you experience persistent, unexplained, or worsening itchiness, consulting a healthcare provider is vital. Early diagnosis enables effective management, reduces discomfort, and prevents potential complications that can significantly impact your quality of life.