Comprehensive Guide to Types and Causes of Skin Rashes
This comprehensive guide explores the diverse types of skin rashes, their causes, symptoms, and treatments. From fungal infections to autoimmune disorders, learn how to recognize and manage these common skin conditions effectively. Early diagnosis and proper care are essential to prevent complications and ensure skin health.
In-Depth Exploration of Various Skin Rashes and Their Origins
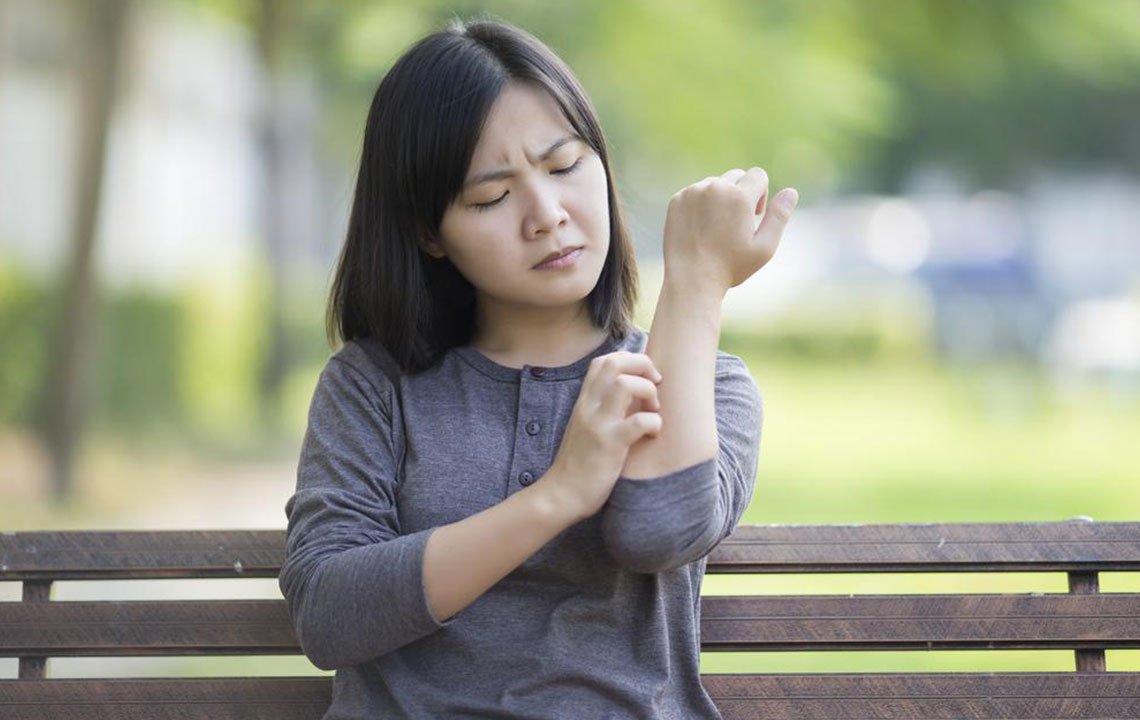
Skin rashes are localized or widespread areas of skin that exhibit alterations in color, texture, or both. They often manifest as redness, itching, bumps, swelling, or irritation, and can be indicative of underlying health issues or external triggers. Recognizing different types of skin rashes is crucial for timely and effective treatment, as some rashes are benign while others signal serious health conditions. Factors contributing to skin rashes include infections, allergies, autoimmune disorders, environmental exposures, and stress. Proper diagnosis by a healthcare provider ensures appropriate care and relief.
Major Types of Skin Rashes and Their Characteristics
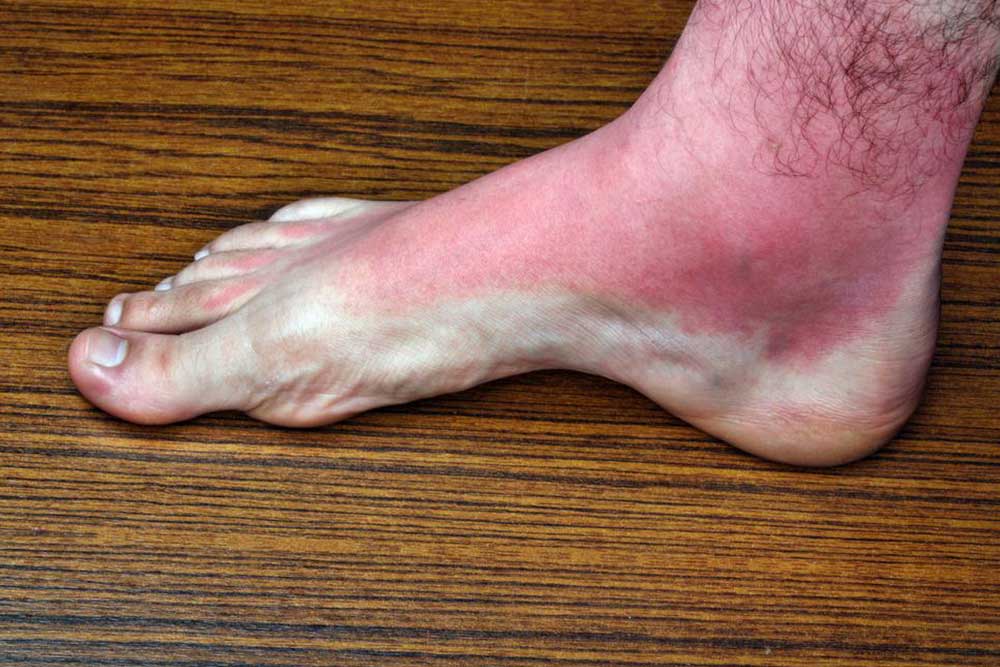
Ringworm (Tinea): Caused by a fungal infection, ringworm presents as ring-shaped, scaly patches with raised borders. It is highly contagious and commonly affects areas like the scalp, body, feet, and groin. The center often looks clear, giving the characteristic ring appearance. Treatment involves antifungal medications, either topical or oral, depending on severity.
Contact Dermatitis: This inflammatory skin reaction occurs after contact with allergens or irritants such as cosmetics, soaps, plants, or metals. Symptoms include redness, swelling, blisters, and itching. Avoiding the causative agent and using anti-inflammatory creams or antihistamines helps manage the condition.
Allergic Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): A chronic condition often affecting the hands, arms, and face, characterized by itchy, inflamed, flaky, and sometimes cracked skin. It is typically associated with allergies or asthma and requires moisturizers, corticosteroids, and allergy management strategies.
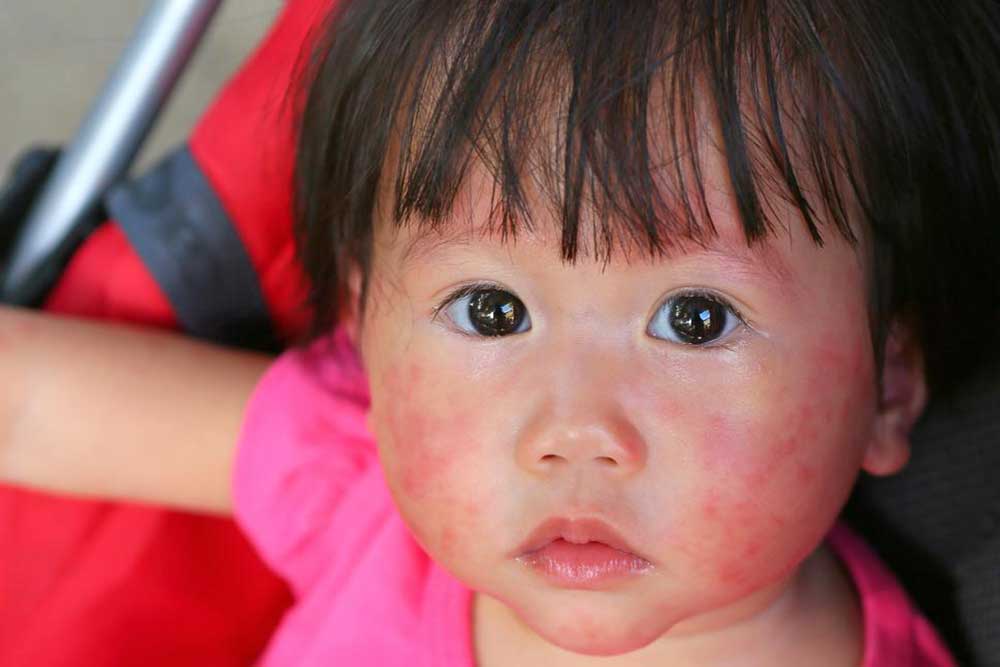
Diaper Rash: Common among infants, diaper rash manifests as red, irritated skin in the diaper area. It is caused by prolonged exposure to moisture, friction, and irritants in urine or feces. Frequent diaper changes, gentle cleaning, and barrier creams are primary treatments.
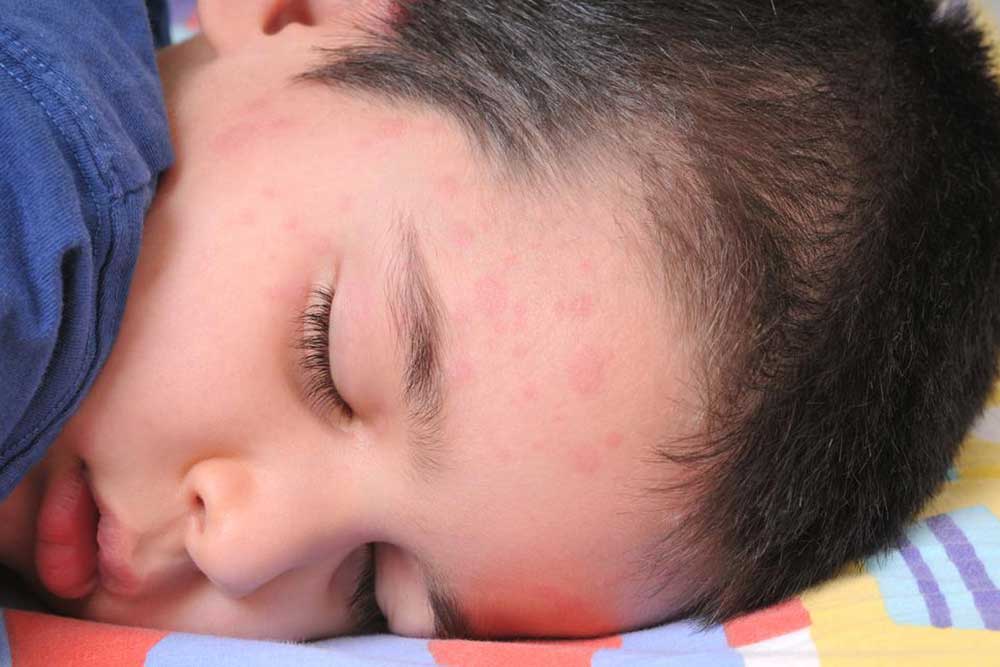
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: A contagious viral illness prevalent in children under five. It causes flat, red blisters on the gums, tongue, palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and sometimes the genital area. The condition resolves spontaneously, with supportive care to ease discomfort.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): An inflammatory skin disorder characterized by dry, flaky, red, or greasy skin, often accompanied by itching and hair loss. It tends to recur and may be triggered by allergens, irritants, or environmental factors.
Psoriasis: An autoimmune disease that results in thick, silvery, scaly plaques mainly on the knees, elbows, scalp, and lower back. Psoriasis is chronic, and management includes topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications to control symptoms.
SLE (Lupus): Systemic lupus erythematosus is a complex autoimmune disorder exhibiting butterfly-shaped rashes across the nose and cheeks, which worsen with sun exposure. Other symptoms may include joint pain, fatigue, and organ involvement. Early diagnosis and immunosuppressive treatments are essential.
Shingles (Herpes Zoster): Caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, shingles presents as painful, burning, fluid-filled blisters usually on one side of the torso or face. It often occurs in older adults or immunocompromised individuals. Antiviral medications, pain relievers, and sometimes corticosteroids are used for treatment.
Understanding the different types of skin rashes, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options is vital for effective management. Proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional helps prevent complications and alleviates discomfort.