Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Different Types of Skin Rashes and Effective Management
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of skin rashes, their characteristics, causes, and effective treatment options. Learning to identify rash symptoms early can lead to prompt medical attention, promoting healthy skin and preventing complications. The article emphasizes prevention through good hygiene and proper skincare routines, providing valuable insights for managing common dermatological issues effectively.

Skin rashes are a common dermatological concern that can significantly affect an individual's quality of life. These rashes manifest as patches of skin that are irritated, swollen, itchy, or discolored, and their appearance can vary widely depending on the underlying cause. Recognizing the different types of skin rashes is essential for effective treatment and prevention. This comprehensive guide aims to educate readers on the various skin rashes, their characteristic features, causes, and appropriate responses to ensure optimal skin health.
Understanding what causes skin rashes is the first step toward effective management. Rashes can occur due to allergic reactions, infectious agents, chronic skin conditions, insects, or environmental factors. The timing of their appearance—whether they develop suddenly or gradually—along with their specific features, helps in identifying the underlying issue. For mild rashes that resolve on their own, DIY skin care routines and avoiding known irritants might suffice. However, persistent, worsening, or severe rashes require prompt consultation with healthcare professionals, especially dermatologists, for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Preventing skin rashes involves maintaining good hygiene, staying hydrated, avoiding known allergens, and protecting the skin from environmental irritants. A proactive skin care routine can prevent many common skin issues, fostering healthier skin and reducing the risk of complications. This guide covers the most common types of skin rashes, their distinctive features, causes, and recommended treatments, providing vital information for accurate self-assessment and timely medical intervention.
Detailed Overview of Common Skin Rashes and Their Distinguishing Features
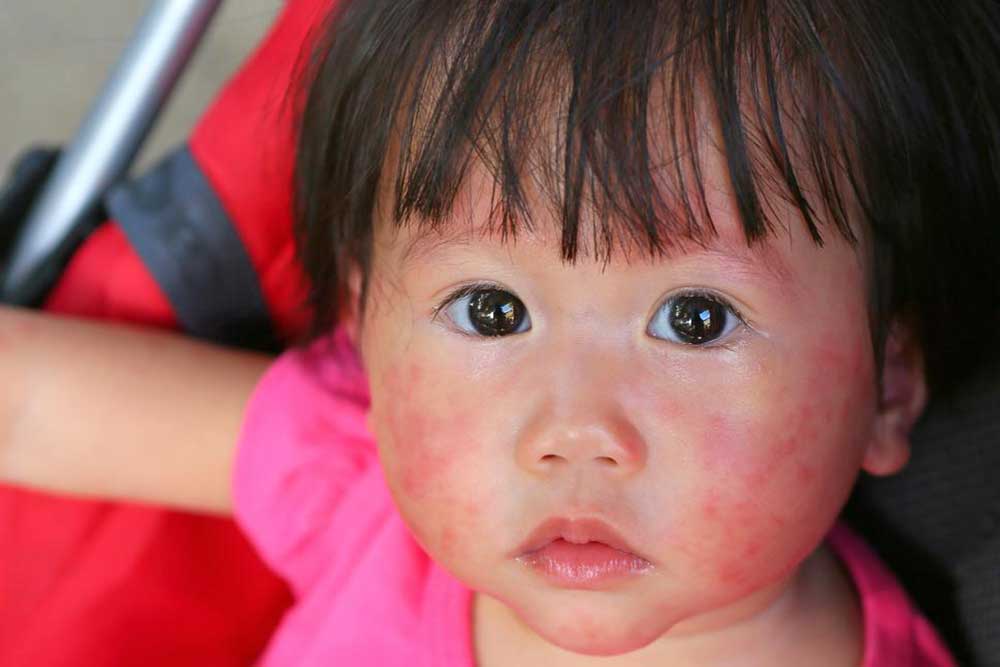
Contact Dermatitis: Characterized by red, inflamed, itchy, and sometimes burning skin. It occurs after contact with irritants such as soaps, chemicals, plants like poison ivy, or certain cosmetics. The rash often appears quickly after exposure and improves with prompt washing and avoiding the irritant. In some cases, topical steroids or antihistamines are recommended for relief.
Insect Bites and Stings: These manifest as raised bumps or welts, often accompanied by redness, swelling, and itching. Bites from mosquitoes, fleas, bedbugs, or spiders can cause localized reactions. Some bites, particularly from ticks or fire ants, may require medical attention due to potential transmission of disease or severe allergic reactions. Applying cold compresses and antihistamines can help alleviate symptoms, but medical evaluation is essential for severe cases.
Fungal Infections: These often present as itchy, scaly, or cracking skin patches, primarily in warm, moist areas such as the groin, armpits, or under breast folds. Fungal infections include ringworm, candidiasis, and athlete's foot. Proper hygiene, antifungal creams or medications, and keeping the affected area dry are crucial for treatment and prevention.
Scabies: Caused by microscopic mites, scabies results in tiny red bumps, intense itching, especially at night, and skin lines. Commonly affected areas include wrists, elbows, between fingers, and waistline. Immediate medical treatment with topical or oral medications is vital, along with cleaning bedding and clothing to prevent re-infestation.
Allergic Reactions and Hay Fever: These may produce widespread redness, swelling, hives (raised itchy welts), and sometimes blistering. Usually triggered by pollen, certain foods, medications, or insect venom. Managing allergies with antihistamines and avoiding triggers significantly reduces symptoms.
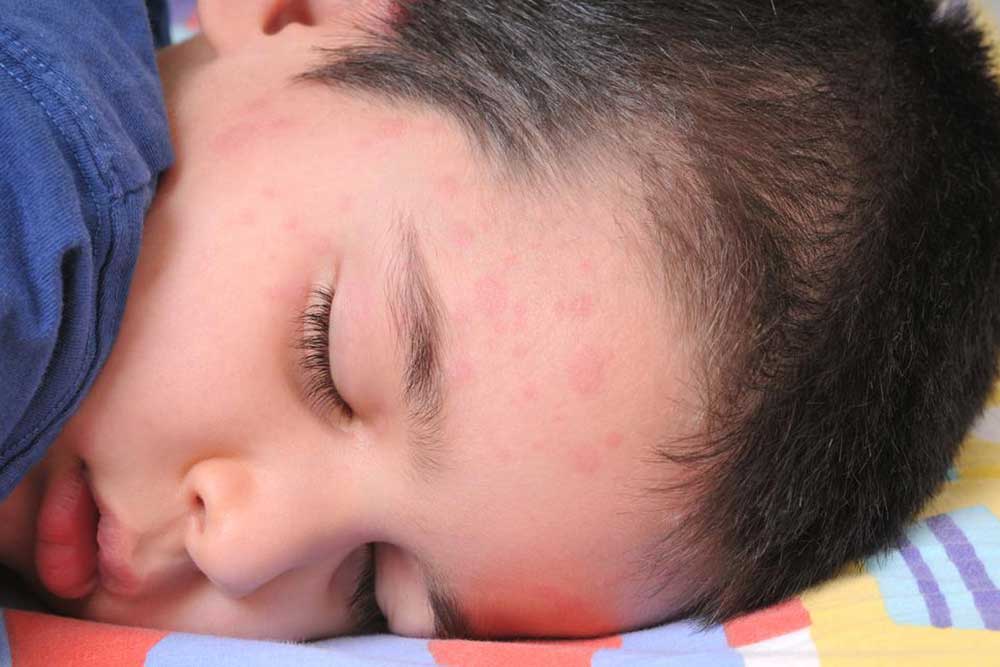
Measles: This contagious viral infection causes a distinctive red rash that typically begins on the face, spreading downward. Associated symptoms include cough, high fever, sore throat, and Koplik spots inside the mouth. Early diagnosis and isolation are important to prevent spreading and to start supportive care.
Candidiasis (Yeast Infection): These rashes usually occur in skin folds such as armpits, groin, or under breasts, producing redness, soreness, and sometimes a watery or cottage-cheese-like discharge. Contributing factors include poor hygiene, sweating, or tight clothing. Effective hygiene, antifungal treatments, and breathable clothing usually resolve the issue.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): A chronic condition characterized by dry, flaky, itchy skin that often affects the elbows, knees, and neck. Scratching can lead to secondary infections. Management involves moisturizers, antihistamines, and topical steroids to reduce inflammation.
Shingles (Herpes Zoster): This painful blistering rash is caused by reactivation of the chickenpox virus in nerve tissues. It manifests as nerve pain followed by a band or patch of blisters, typically on the face or torso. Immediate antiviral treatment can reduce severity and duration.
It is critically important to seek medical advice if a rash persists beyond a few days, worsens, or is accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever, pain, or swelling. Proper skin hygiene, adequate hydration, and routine skincare are foundational to preventing many skin rashes. Recognizing early signs and understanding their underlying causes facilitate timely treatment, which can minimize discomfort, prevent complications, and promote overall skin health.