Comprehensive Guide to Common Skin Rashes: Types, Causes, and Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive article explores common skin rashes, including contact dermatitis, rosacea, and scabies. It details their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, emphasizing the importance of early dermatological consultation. Perfect for those seeking understanding and relief from skin rashes, this guide covers signs to watch for and effective management strategies to improve skin health.

Comprehensive Guide to Common Skin Rashes: Types, Causes, and Treatment Strategies
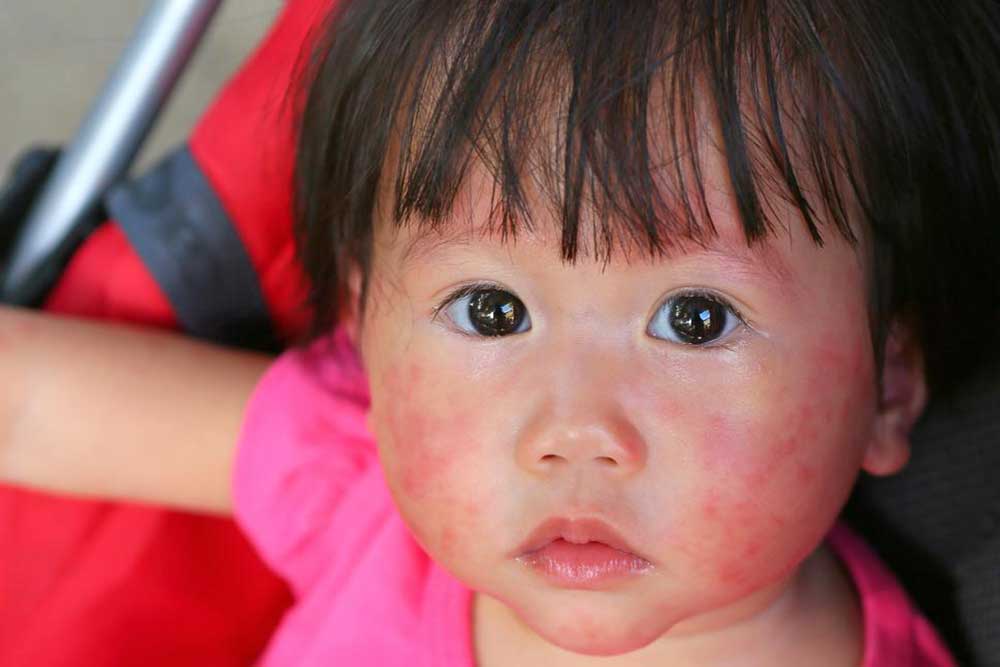
Skin rashes represent a widespread dermatological issue characterized by noticeable changes in skin color, texture, and appearance. These alterations often manifest as red, inflamed, and itchy patches that can cause discomfort and concern. While skin rashes can occur at any stage of life, they are particularly prevalent among infants, who have more sensitive skin and weaker immune responses. Recognizing the different types of skin rashes and understanding their underlying causes is essential for effective management and relief. Consulting a healthcare professional, especially a dermatologist, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Exploring the Major Types of Skin Rashes
Skin rashes develop rapidly after exposure to various internal and external triggers. Their visual appearance and accompanying symptoms can help determine their classification, severity, and appropriate treatment approach. The key is to recognize the distinctive features of each rash type and understand their common causes.
Below is an in-depth overview of the most common skin rashes:
Contact Dermatitis
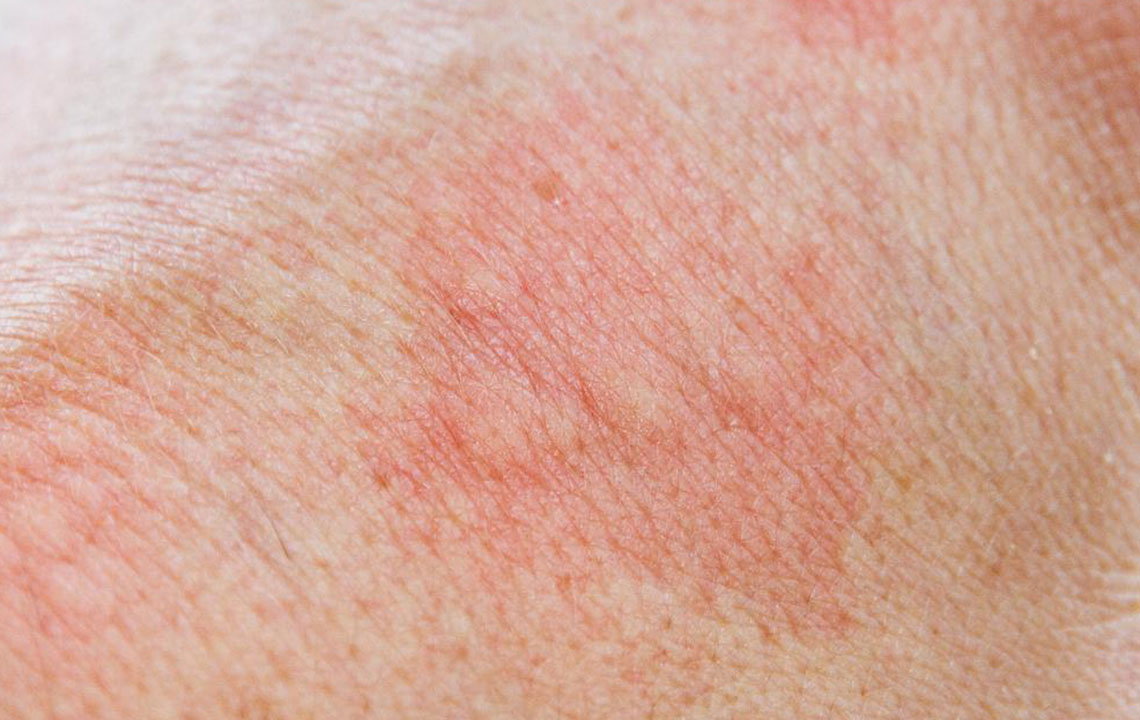
Contact dermatitis is characterized by dry, scaly, and inflamed skin that appears shortly after contact with an irritant or allergen. It generally manifests as two types: allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis.
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts adversely to allergens such as nickel in jewelry, poison ivy, latex, or fragrances. This reaction often results in blistering, intense itching, redness, and swelling, which may extend beyond the contact area.
Irritant contact dermatitis, on the other hand, is caused by prolonged or repeated exposure to harsh chemicals or physical irritants like bleach, industrial detergents, or battery acids. It typically presents as dry, rough, and possibly cracked skin without significant itching but may crust or ulcer if severe.
Rosacea
Rosacea affects about 16 million Americans annually and is a chronic inflammatory skin condition primarily affecting the central face, including the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. Its hallmark signs include persistent redness, visible blood vessels, swollen bumps, and sometimes pus-filled sores. Although the exact cause remains uncertain, researchers suspect a combination of genetic factors, vascular abnormalities, and bacterial interactions, especially involvement of bacteria like Helicobacter pylori. Common triggers include spicy foods, alcohol consumption, extreme temperatures, stress, and certain skincare products.
Scabies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by an infestation of the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The mite burrows into the superficial layers of the skin, creating tiny, serpentine burrows that serve as sites for egg deposition. Symptoms include intense itching, especially at night, redness, and a rash characterized by small blisters and pustules. Areas typically affected include the wrists, elbows, armpits, waistlines, and genital areas. The incubation period can be up to six weeks after initial infestation, and if untreated, the rash and itching tend to intensify over time.
Causes and Transmission of Scabies
The scabies mite reproduces on the skin surface, burrowing to lay eggs beneath the skin. Transmission usually occurs through skin-to-skin contact with an infested person, often during close or prolonged interactions. It can also spread through contaminated clothing, bedding, or towels. Since the mites can survive for several days off the human body, hygiene measures are vital in controlling outbreaks.
If you notice any symptoms like persistent itching, rashes, or blistering, especially in the discussed areas, seeking immediate dermatological consultation is essential. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.
Effective management of skin rashes depends on identifying the specific type and understanding the triggers involved. A dermatologist may recommend topical medications, oral drugs, lifestyle modifications, or allergen avoidance strategies to relieve symptoms and address underlying causes. Maintaining good skin hygiene, avoiding known irritants, and promptly treating infections are critical steps towards skin health.
In conclusion, skin rashes are a common but diverse group of dermatological conditions that require proper identification for effective treatment. Whether caused by allergic reactions, infections, or other underlying issues, early consultation with a healthcare professional improves outcomes and ensures the proper care for your skin health.