Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Common Skin Rashes and Skin Conditions
This comprehensive guide provides in-depth information on recognizing and understanding common skin rashes. It covers various types, including psoriasis, hives, fungal infections, bacterial rashes, and viral conditions like chickenpox. The article emphasizes the importance of early detection, understanding symptoms, triggers, and seeking professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Designed to help readers identify skin conditions accurately, it offers practical tips for prevention and management, ensuring better skin health and faster recovery.
Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Common Skin Rashes and Skin Conditions
Skin rashes are among the most common dermatological issues, often signaling underlying health conditions or reactions to environmental factors, allergens, or medications. Recognizing the type of skin rash promptly can be critical for effective treatment and management. While online images and descriptions can provide initial clues, they are not always sufficient for an accurate diagnosis. Visiting a healthcare professional remains essential for proper evaluation. This detailed guide aims to help you understand the most prevalent types of skin rashes, their appearances, causes, and when to seek medical attention. It covers a wide range of conditions, from chronic issues like psoriasis to infectious ones like chickenpox, ensuring you are better equipped to identify and manage skin health concerns.
Understanding skin rashes begins with recognizing their distinct features and knowing the variety of factors that trigger them. Skin rashes can manifest as changes in skin color, swelling, itching, blistering, or patches of thickened skin. Each rash often has characteristic signs that can aid in differentiation. Accurate identification is vital because different rashes require different treatment approaches. Some, like heat rash, are temporary and manageable, while others, such as bacterial or fungal infections, might need prescribed medications. Below, we explore the most common skin rashes in detail, including their symptoms, causes, and recommended actions.
Psoriasis: A chronic autoimmune skin condition where skin cells multiply at an accelerated rate, roughly ten times faster than normal. This rapid cell growth leads to the formation of thick, scaly patches that often appear on areas like the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Psoriasis plaques are usually well-defined, reddish, and covered with silvery scales, which can sometimes crack or bleed. The exact cause is unknown, but genetics and immune system factors play significant roles. Psoriasis can be triggered by stress, infections, certain medications, or skin injuries. Managing psoriasis involves topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications, depending on severity.
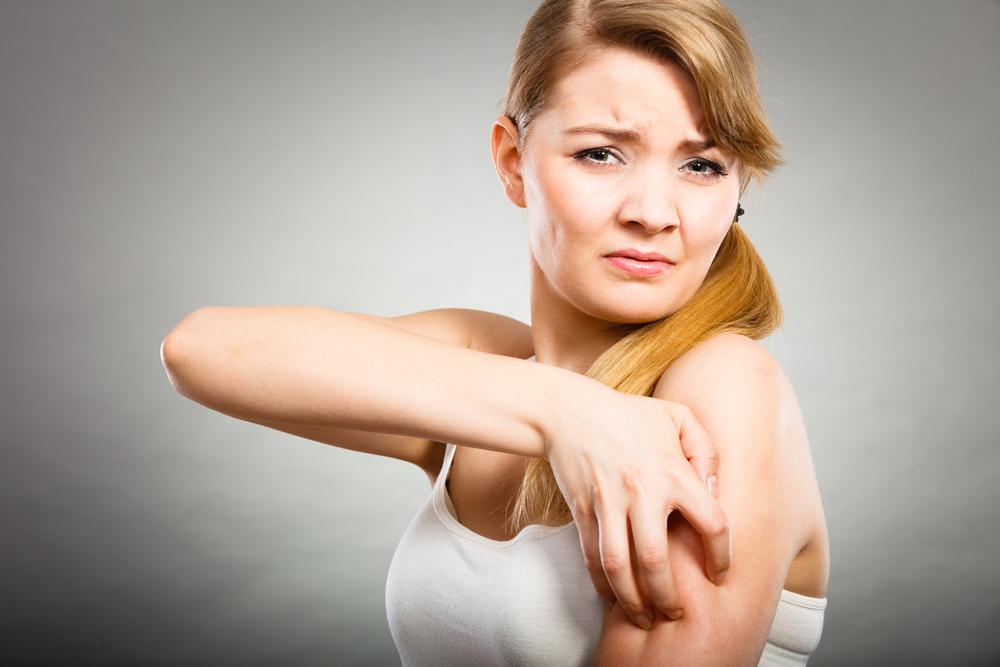
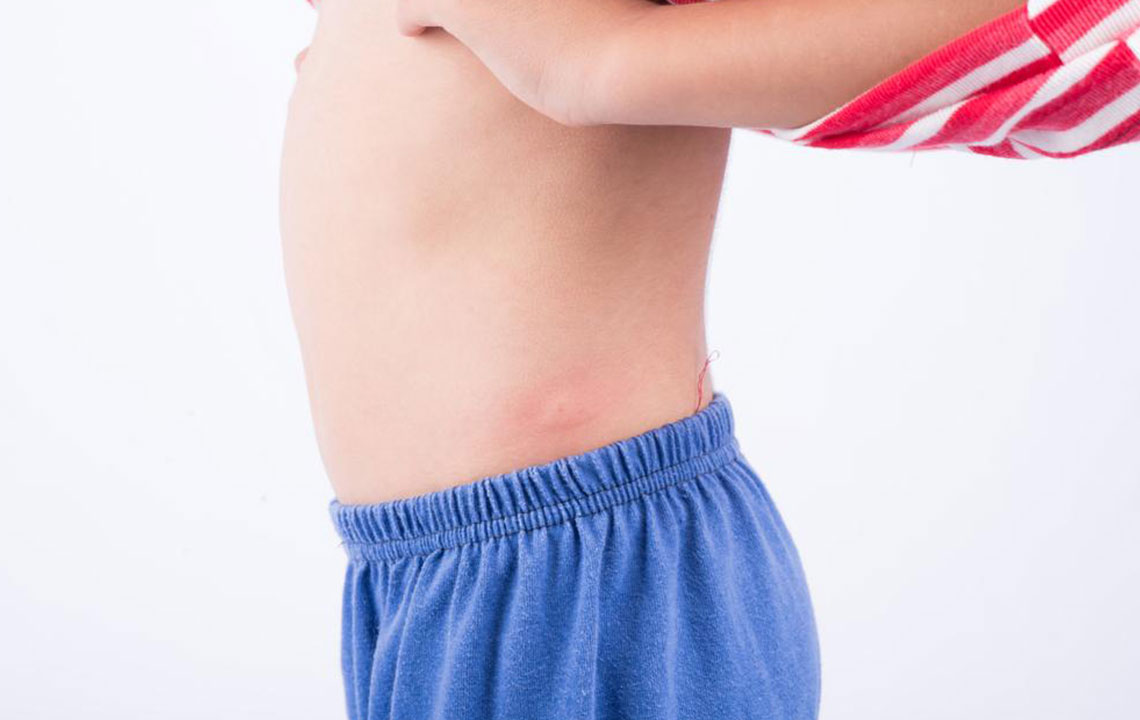
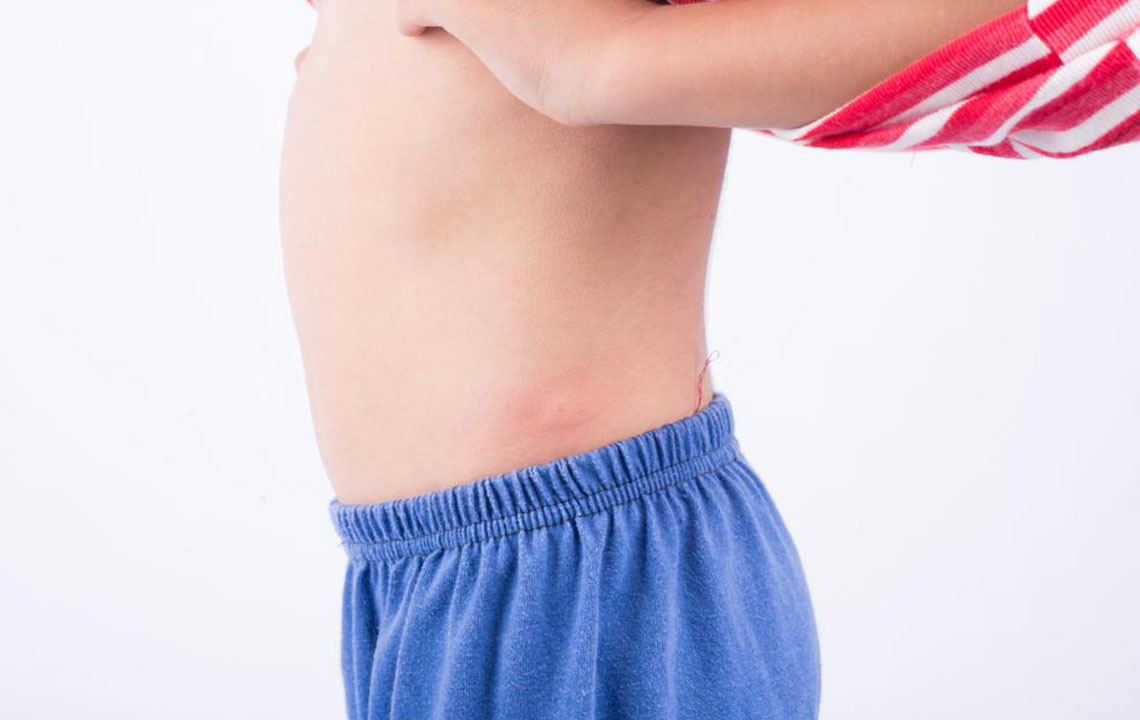
Hives (Urticaria): Characterized by red, swollen bumps or welts that tend to be itchy and sometimes cause a burning sensation. Hives result from the release of histamine and other chemicals during allergic reactions, which can be triggered by foods, insect stings, medications, stress, or environmental factors. They can appear suddenly and may last from a few hours to several days. Chronic hives persist for longer periods and require medical evaluation to identify underlying causes. Antihistamines are usually effective in relieving symptoms.
Drug Rashes: These are allergic reactions to medications and can manifest quickly following drug intake. The rash may resemble hives, or it might involve blisters, bumps, or more widespread redness. Some drug rashes are mild, while others can be severe or indicative of allergic contact dermatitis. Recognizing the medication involved is crucial, and discontinuation often alleviates symptoms. Severe reactions, like Stevens-Johnson syndrome, require immediate medical intervention.
Heat Rash (Miliaria): Common in hot and humid environments, heat rash occurs when sweat ducts become blocked, trapping sweat under the skin. It appears as tiny, red, itchy bumps, often in areas with friction such as neck, chest, back, or groin. Excessive sweating and heat exposure are typical triggers. Prevention includes staying cool, wearing loose clothing, and maintaining good hygiene. Mild cases resolve on their own, but persistent or infected heat rash may require medical care.
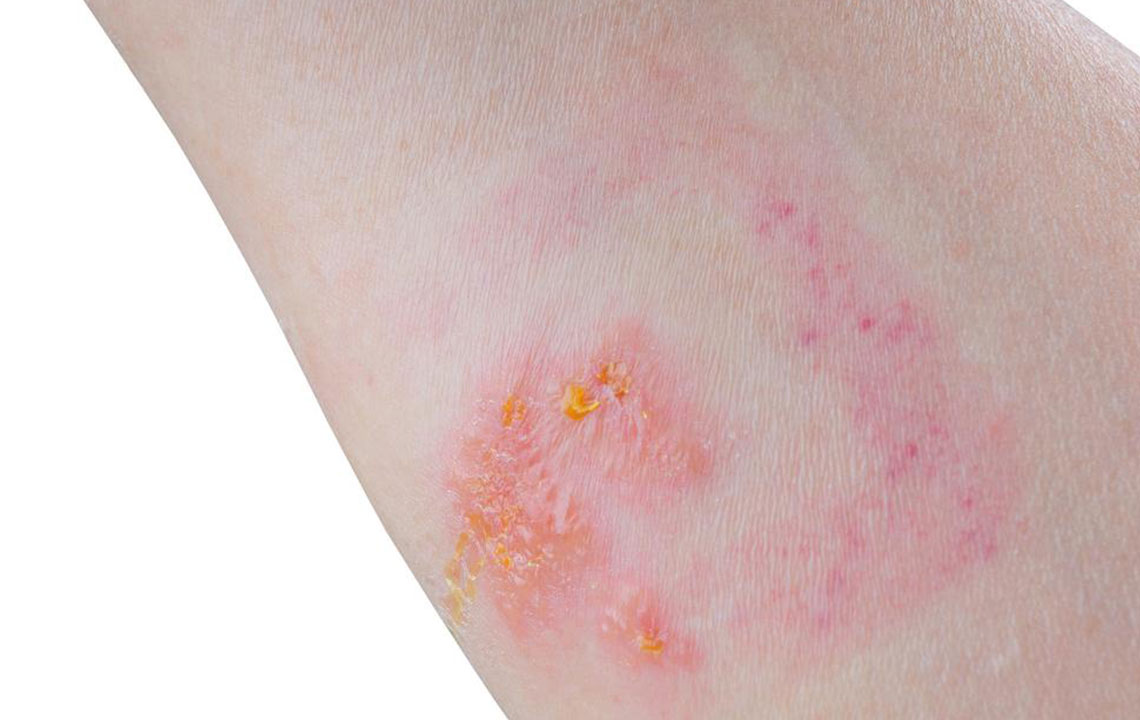
Fungal Infections: These rashes are caused by overgrowth of yeast or fungi, such as those from the Candida or Dermatophyte family. They often appear as itchy, ring-shaped lesions with clear centers and scaly borders, known as tinea or ringworm. Fungal rashes can occur anywhere on the body but are common in moist areas like the groin, feet, or underarms. Effective treatment involves antifungal creams, oral medications in severe cases, and maintaining dryness in affected areas.
Bacterial Rashes: Examples include cellulitis and impetigo. Bacterial rashes are often painful, red, swollen, and may produce pus or crusting. Cellulitis involves deep skin infection requiring prompt antibiotic therapy. Bacterial infections typically involve breaks or cuts in the skin, providing entry points for bacteria. Proper wound care and hygiene are essential to prevent bacterial skin infections.
Parasite-Induced Rashes: For instance, scabies caused by the human itch mite presents as intense itching and rash, especially in the webs of fingers, wrists, and waistline. Scabies causes small blisters or bumps and spreads through skin contact. Treatment includes topical scabicides and cleaning of clothing and bedding to eliminate mites. Other parasitic rashes may involve different organisms and vectors, requiring specific therapies.
Tinea (Ringworm): A common fungal infection characterized by ring-shaped rashes with scaly, raised borders. The center may appear clearer or less affected than the edges, which are often itchy. Tinea can affect skin on the body, scalp, groin (also called jock itch), and feet (athlete’s foot). Maintaining hygiene, keeping the skin dry, and applying antifungal medications help manage this condition effectively.
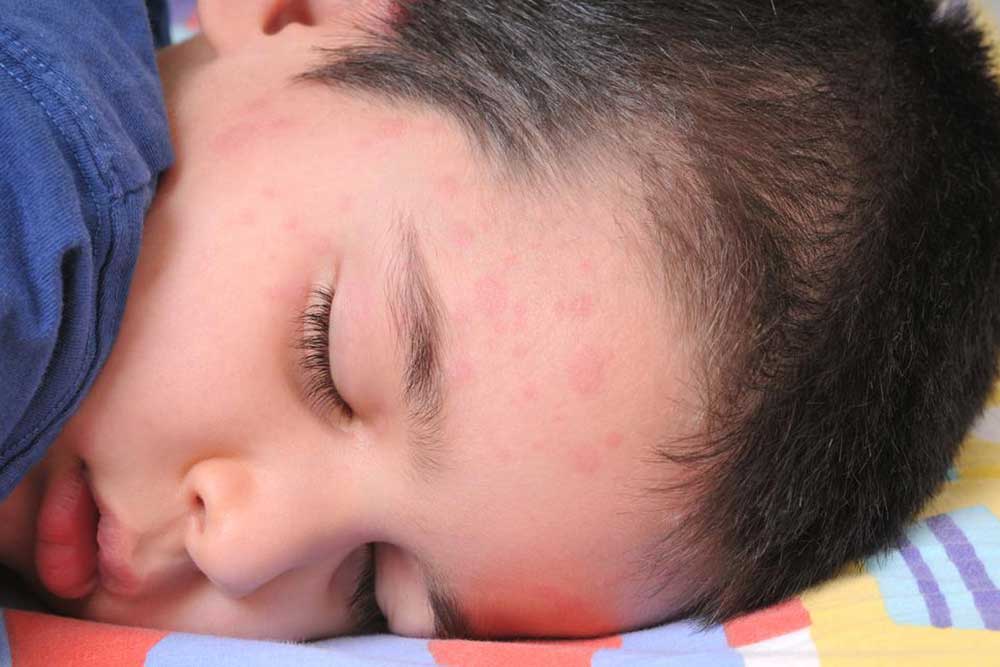
Chickenpox (Varicella): A highly contagious viral infection marked by red, itchy blisters that evolve into fluid-filled vesicles. The rash typically starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads over the body. Other symptoms include fever, fatigue, and loss of appetite. In children, chickenpox is usually mild, but it can cause complications in adults or immunocompromised individuals. Vaccination is the most effective prevention method. Treatment focuses on relieving itching and managing symptoms.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: An infectious viral illness commonly affecting children, characterized by ulcers and rashes around the mouth, on palms, and soles of the feet. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, and irritability. Good hygiene practices can prevent its spread. Usually self-limiting, it requires supportive care such as pain relief and hydration.
While photographs and online resources can offer guidance in identifying skin conditions, they are not substitutes for professional medical advice. If you experience persistent, worsening, or severe symptoms, visiting a healthcare provider is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Maintaining good skin hygiene, avoiding known triggers, and seeking timely medical care can significantly improve skin health and overall well-being.