Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Techniques
This comprehensive guide explores atopic dermatitis, detailing its causes, symptoms, and the latest management strategies. From skin care routines to medication options, learn how to effectively control this chronic skin condition and improve life quality. Early diagnosis and tailored treatments are essential to prevent complications and reduce flare-ups, helping individuals live more comfortably with eczema.

Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Techniques
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide across all age groups. Despite its widespread prevalence, especially among children, this condition can persist into adulthood if not properly managed. With nearly 18 million people impacted globally, understanding the intricacies of atopic dermatitis is vital for diagnosis, management, and improving quality of life.
Early detection combined with effective management strategies plays a crucial role in preventing discomfort, mitigating persistent itching, and avoiding skin damage. Proper treatment not only reduces symptoms but also minimizes the risk of secondary infections such as herpes simplex virus or staphylococcus bacteria, which can complicate the condition and prolong recovery.
Exploring the Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
Although the precise origins of atopic dermatitis remain elusive, scientific research indicates a strong genetic component intertwined with environmental and allergic factors. It is widely believed that this condition results from a combination of inherited predispositions and environmental exposures that trigger immune responses, leading to inflammation and skin barrier dysfunction. Common triggers and related factors include:
Pollen, dust mites, mold spores, pet dander, and other airborne allergens that provoke immune reactions.
Harsh or irritating soaps, detergents, and skincare products that strip natural oils from the skin, leading to increased dryness and irritation.
Chemicals, fumes, or pollutants that induce allergic responses or irritate sensitive skin.
Sudden or extreme weather changes, like exposure to hot water or cold environments, which can weaken the skin barrier.
Psychological stress, anxiety, or emotional distress that can exacerbate flare-ups.
Dietary triggers, especially in children with food allergies, which vary from person to person and can worsen symptoms.
Incorrect or excessive skin washing, particularly during winter months, resulting in further skin dryness.
Identifying the Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of atopic dermatitis is essential for prompt treatment and effective management. Though presentation may vary among individuals, some common signs include:
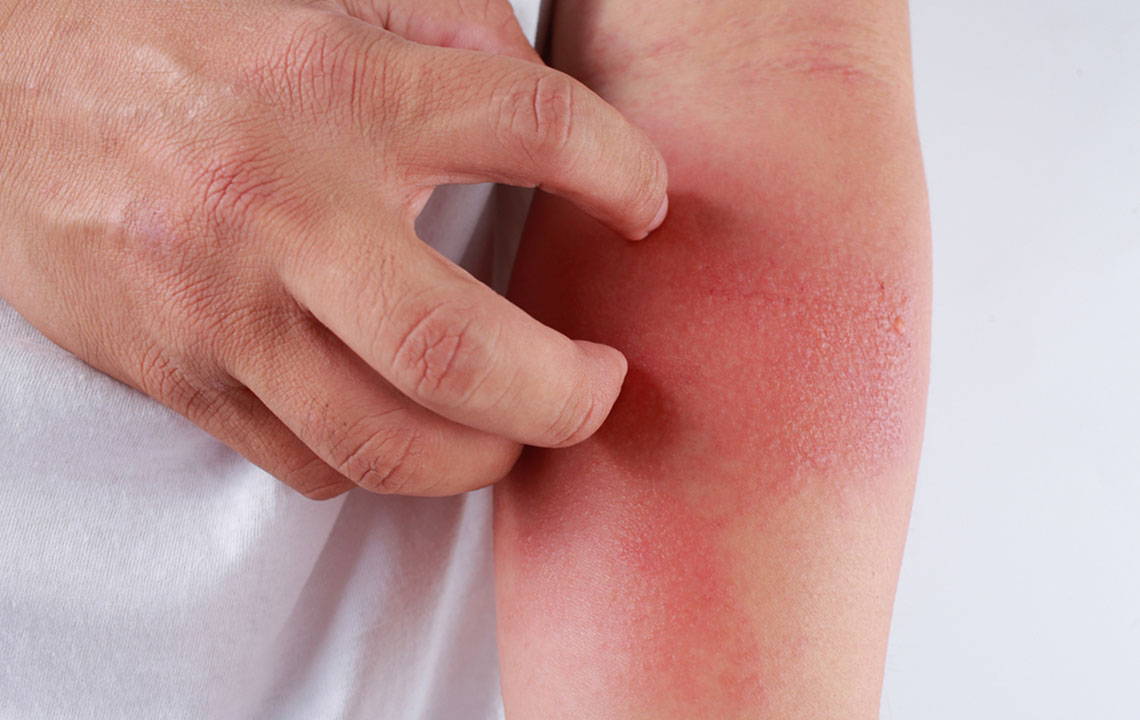
Intense itching, often worsened during night-time, disrupting sleep and daily activities.
Dry, cracked, thickened, or leathery skin resulting from continuous scratching.
Swelling and redness in affected areas, which can become sensitive or tender to touch.
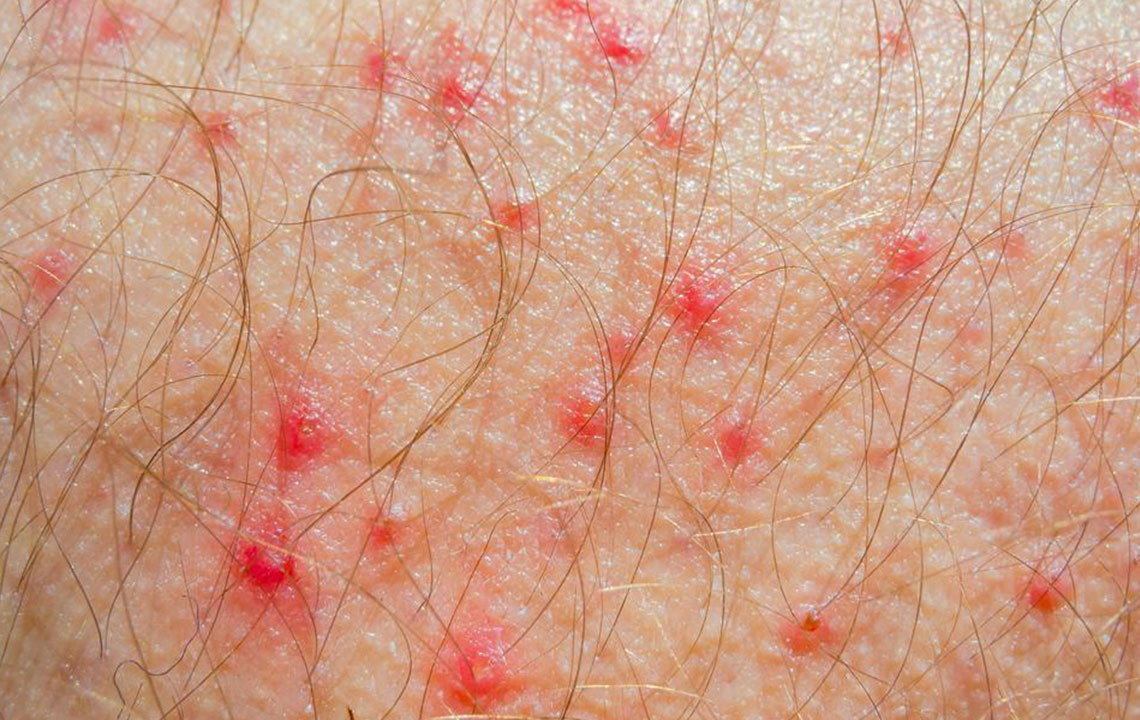
The appearance of brownish or reddish patches, especially on the hands, feet, face, and behind the knees or elbows.
Small bumps or papules that may weep or ooze clear fluid when scratched or irritated.
Management and Treatment Options for Atopic Dermatitis
While there is currently no cure for atopic dermatitis, a variety of treatment approaches can effectively control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve the overall quality of life. An individualized treatment plan, often developed in collaboration with healthcare providers, is vital for optimal results. Here are some of the most commonly recommended strategies:
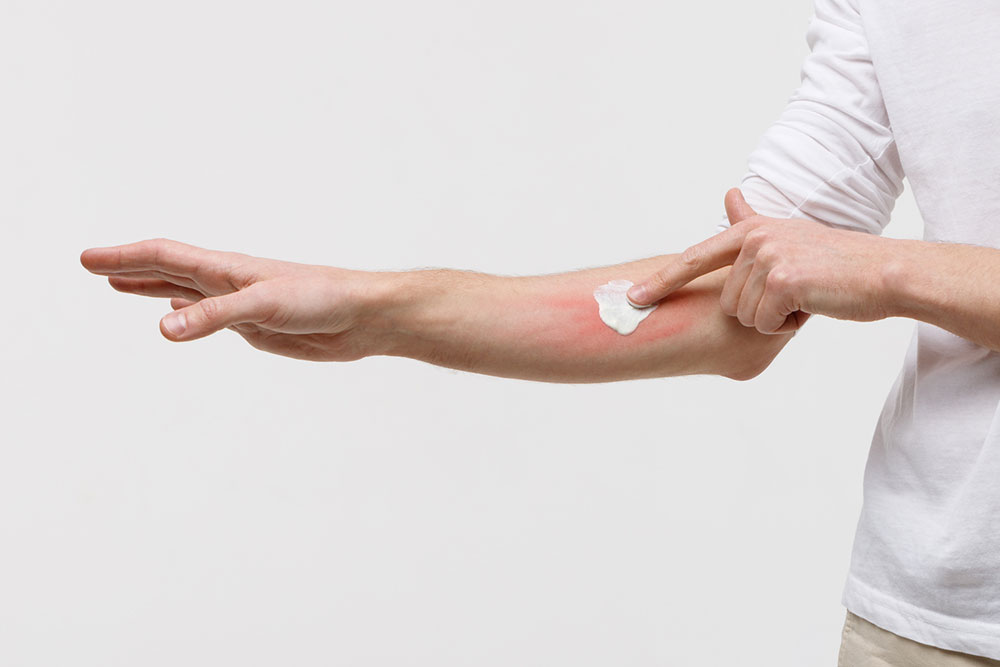
Moisturization Is Key
Restoring and maintaining skin hydration is the cornerstone of managing eczema. Frequently applying emollients helps to reinforce the skin's natural barrier, preventing moisture loss and alleviating dryness. Proper moisturizing is especially critical during dry seasons or in cold climates, where skin tends to become more vulnerable.
Emollients and Hydrating Lotions
These products contain ingredients like glycerin, urea, or ceramides that help to lock in moisture. Regular use can significantly diminish dryness, scaling, and cracking, providing relief from uncomfortable symptoms.
Topical Corticosteroids
Mild to potent steroid creams and ointments are effective in reducing inflammation, redness, and swelling during flare-ups. When used appropriately and under medical supervision, they are safe and yield rapid symptom relief. However, prolonged or improper use should be avoided due to potential side effects like skin thinning.
Tar-Based Treatments
Coal tar and pine tar preparations have been used historically to control itching, inflammation, and scaling. Though effective, these treatments can emit strong odors and may stain clothing or bedding, leading some patients to prefer alternative options.
Antiseptic and Bacterial Control
To prevent secondary bacterial infections, healthcare providers might recommend antiseptic solutions or bath additives containing dilute bleach or iodine. These help reduce bacterial colonies on the skin, which can worsen eczema symptoms.
Antibiotics and Antiviral Medications
In cases where bacterial skin infections such as impetigo or herpes simplex virus are present, prescribed antibiotics are administered, either topically or orally, to control bacterial overgrowth and facilitate healing. Care should be taken to avoid unnecessary long-term antibiotic use to prevent resistance.
Oral Antihistamines
To combat persistent itching and aid sleep, doctors often prescribe antihistamines, especially in resistant or severe cases. They are particularly beneficial for children or individuals whose eczema is exacerbated by allergic responses.
Phototherapy and Light-Based Therapies
For severe, unresponsive conditions, ultraviolet (UV) light therapy — administered under medical supervision — can provide significant relief. This treatment involves carefully controlled UV exposure, which reduces inflammation but also carries potential risks such as skin aging or increased cancer risk if used excessively. It is usually reserved for adults or older children who have not responded to other therapies.
In conclusion, understanding the causes, symptoms, and management options for atopic dermatitis is essential for effective control and maintaining a good quality of life. Advances in skincare, medications, and treatment options continue to improve outcomes for those affected by this chronic skin condition. Consulting healthcare providers for personalized treatment plans remains the most effective approach to managing atopic dermatitis efficiently.