Comprehensive Guide to Managing Atopic Dermatitis: Effective Strategies and Treatments
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies and treatments for managing atopic dermatitis, emphasizing the importance of moisturization, trigger avoidance, and medical therapies. With detailed insights into symptom control and lifestyle modifications, it provides valuable information for patients and caregivers aiming to improve quality of life despite this chronic skin condition.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Atopic Dermatitis: Effective Strategies and Treatments
Innovative Approaches to Managing Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms
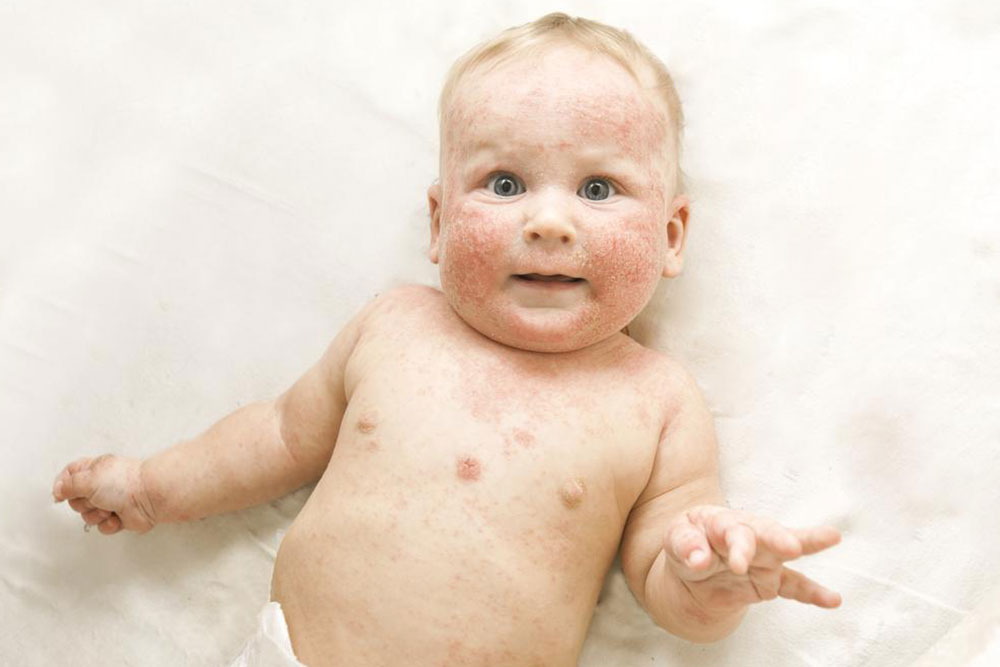
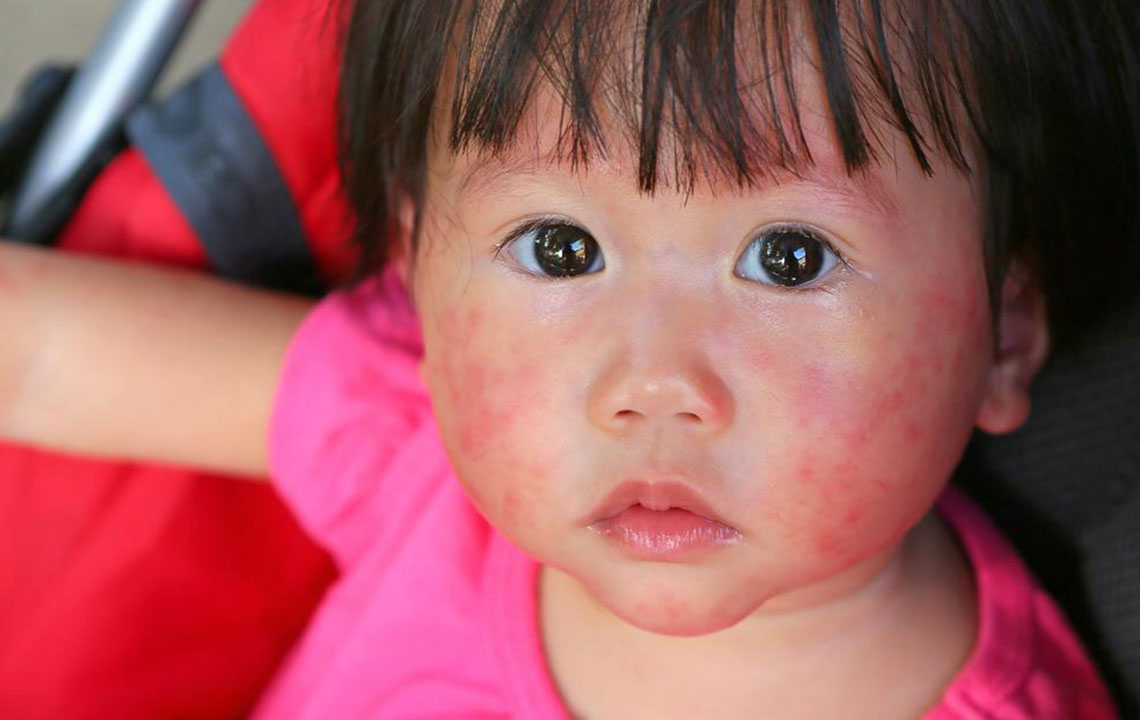
Atopic dermatitis, widely recognized as eczema, is a chronic skin disorder characterized by intense itching, dryness, redness, cracking, and inflammation. This condition affects a significant portion of the population worldwide, with a higher prevalence among infants and children, often manifesting before their first birthday. While it predominantly begins in early childhood, adults are also susceptible, particularly in cases where the condition persists or reappears later in life. The persistent nature of atopic dermatitis can significantly impact the quality of life, leading to discomfort, sleep disturbances, and emotional distress. Despite its chronicity, many individuals experience periods of remission, especially with proper management.
Currently, there is no definitive cure for atopic dermatitis. However, advances in dermatological research have yielded numerous effective treatments that help control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve skin health. Understanding these options, along with lifestyle modifications, can empower patients and caregivers to better manage this complex condition.
Standard and Advanced Treatments for Symptom Relief
Effective management begins with a combination of approaches tailored to individual needs. The cornerstone treatments include:
**Moisturizers and Emollients**: Regular application of thick, fragrance-free moisturizers helps maintain skin hydration, restore the skin barrier, and prevent dryness—a key factor in flare-ups.
**Topical Corticosteroids**: These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments are the primary treatment for reducing redness, swelling, and itching during flare-ups. They should be used under medical supervision to avoid side effects.
For more persistent or sensitive areas, additional options are available, such as:
**Calcineurin Inhibitors (Tacrolimus or Pimecrolimus)**: Prescription medications suitable for delicate skin regions like the face or eyelids, especially when corticosteroids are ineffective or unsuitable.
**Antihistamines**: Oral antihistamines can help alleviate severe itching, thereby reducing the urge to scratch and further skin damage.
**Specialized Clothing and Bandages**: Using soft, breathable clothing or occlusive bandages can protect irritated skin and promote healing by preventing scratching and reducing irritation from external factors.
**Advanced Dermatological Therapies**: For cases that are resistant to standard treatments, dermatologists may recommend phototherapy, systemic immunosuppressants, or biologic agents—targeted therapies that modulate the immune response involved in eczema.
Strategies to Minimize Skin Damage and Prevent Flare-ups
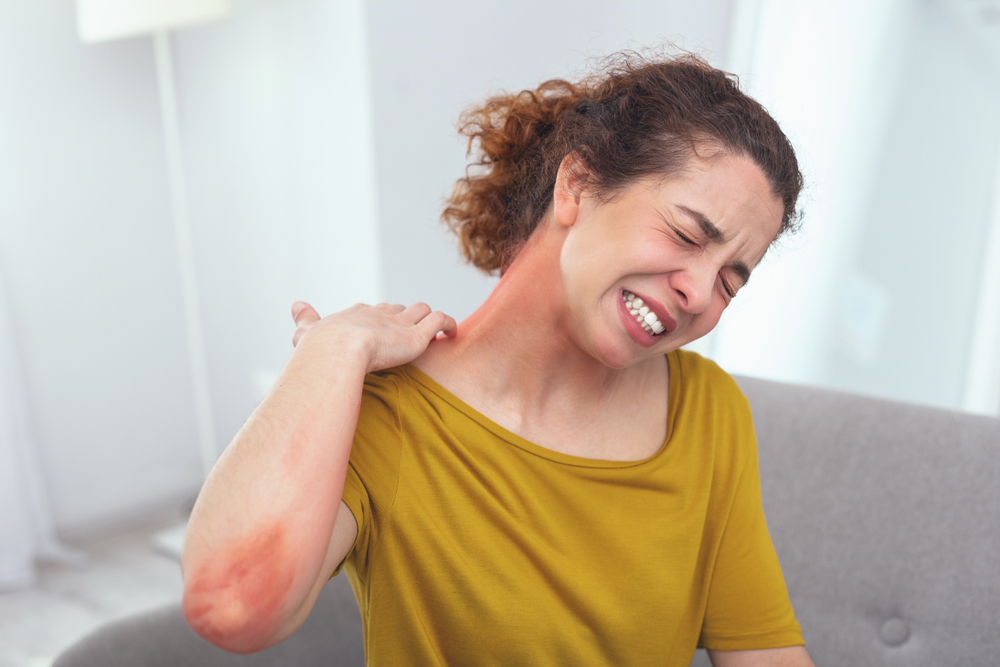
One of the most critical aspects of managing atopic dermatitis involves minimizing skin damage caused by scratching. When the skin is itchy, scratching may provide temporary relief but ultimately worsens the condition. It leads to thickening of the skin, creating a leathery texture, and can cause bleeding, scarring, or secondary infections. To combat this, several practical steps can be incorporated into daily routines:
Wearing loose, lightweight, and breathable clothing—preferably made from organic cotton or other hypoallergenic materials—to reduce irritation.
Avoiding scratching; instead, gently pat or rub the affected areas to stimulate relief without damaging the skin.
Keeping fingernails short, clean, and smooth to prevent unintentional scratching or skin tearing.
Implementing anti-scratch medications, such as antihistamines or calming creams, especially in infants or young children, to control the itching force.
Additionally, employing various distraction techniques, such as engaging in calming activities or mindfulness exercises, can reduce the psychological urge to scratch. Caregivers should also monitor for signs of infection, including increased redness, oozing, or warmth in affected areas, and seek prompt medical attention if needed.
Identifying and Avoiding Personal Triggers
Trigger management is fundamental to eczema control. Working closely with healthcare providers, patients should aim to identify specific factors that exacerbate their symptoms. Common triggers include certain fabrics, weather extremes, allergens, stress, and harsh skin care products. Strategies to reduce exposure encompass:
Wearing clothing made from soft, natural, and hypoallergenic fabrics like organic cotton or silk.
Maintaining a cool, humid environment—using air conditioning or humidifiers—to prevent overheating and excessive sweating, which can worsen eczema.
Switching to gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and detergents that do not strip natural skin oils or irritate sensitive skin.
Implementing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises, as stress is known to trigger flare-ups.
Patient education is key. Keeping a symptom diary can help identify specific irritants or environmental changes correlating with eczema outbreaks, paving the way for more personalized trigger avoidance strategies.
Role of Diet and Nutrition in Eczema Management
Dietary factors can influence atopic dermatitis in some individuals. Food allergies or sensitivities to common allergens like eggs, dairy, nuts, soy, and wheat may exacerbate symptoms. While not everyone with eczema needs dietary restrictions, identifying and eliminating triggering foods—under medical supervision—can lead to significant improvement.
It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before removing foods from the diet. They can help create a balanced nutritional plan that avoids allergens while ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients. For breastfeeding mothers, consulting a healthcare provider prior to changing their diet is crucial to avoid nutritional deficiencies and to monitor any impact on the infant.
Consistent Moisturization as a Cornerstone of Management
Regular and appropriate moisturizing is vital in controlling atopic dermatitis. Moisturizers help maintain the skin’s barrier function, reduce dryness, and prevent flare-ups. Various formulations are available, including ointments, creams, lotions, and oils. The choice of product depends on skin severity and personal preference:
**Ointments**: Highly effective in severe cases, providing a thick barrier that locks in moisture.
**Creams and Lotions**: Lighter and suitable for daytime use, especially on less affected areas.
Applying moisturizers immediately after bathing, while the skin is still damp, enhances absorption and efficacy. Using multiple types of moisturizers throughout the day, as guided by a dermatologist, can optimize skin hydration. If symptoms persist or worsen despite diligent moisturizer use, seeking professional advice is essential for exploring additional treatment options.
In conclusion, managing atopic dermatitis involves a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, trigger avoidance, and proper skin care. While the condition can be challenging, adopting these strategies improves skin health, reduces flare-ups, and enhances overall well-being.