Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Atopic Dermatitis for Better Skin Health
Effective management of atopic dermatitis involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and environmental adjustments. Regular dermatologist visits, proper skin hydration with creams, avoiding triggers, and stress management are essential. Emerging therapies like biologics offer hope for severe cases. This comprehensive guide provides practical strategies to control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve quality of life for those affected by eczema. Prioritizing gentle skincare routines and trigger avoidance is vital for long-term skin health and comfort.

Effective Strategies for Managing Atopic Dermatitis
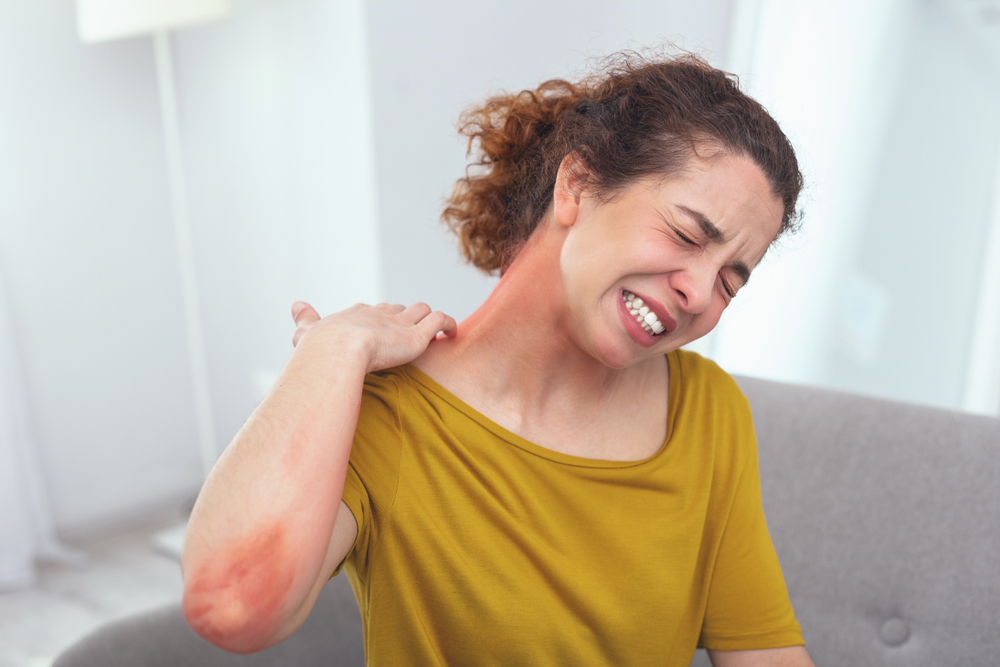
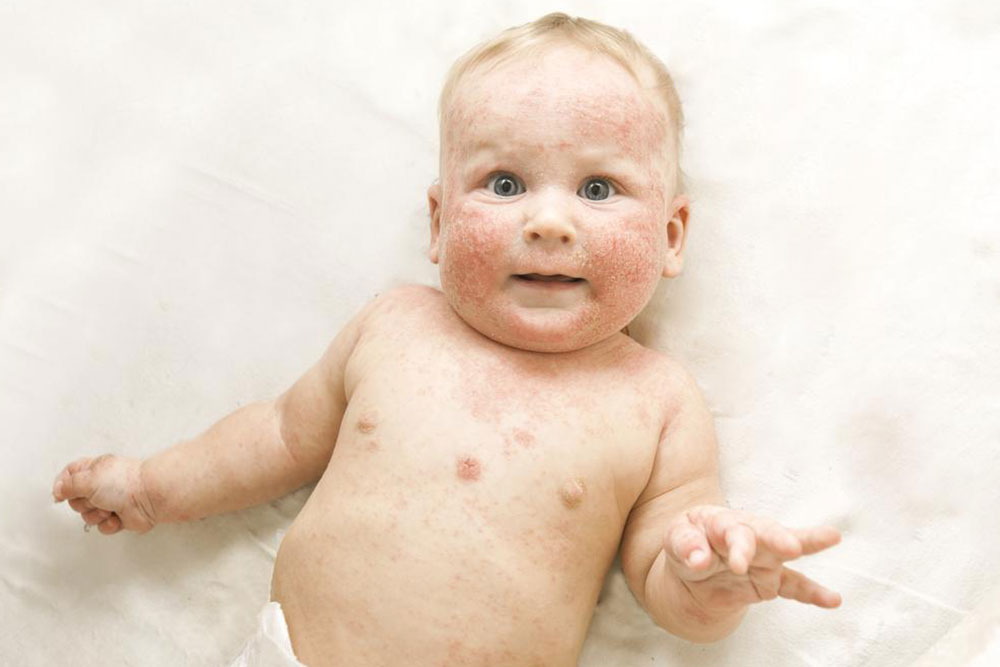
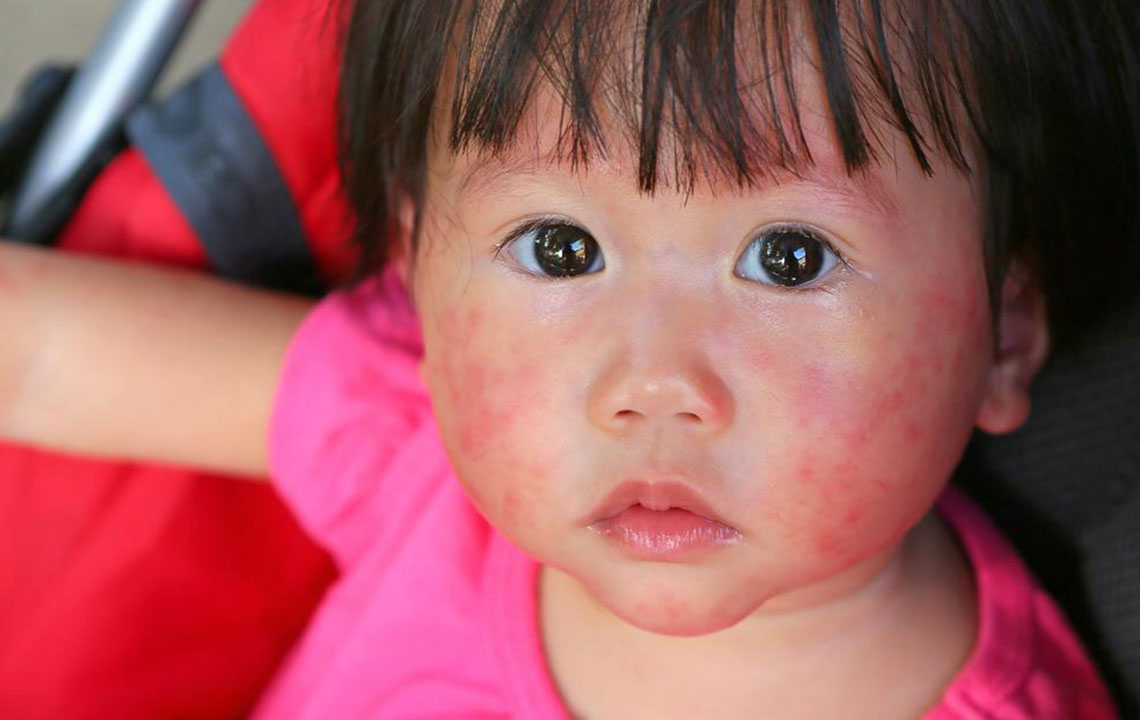
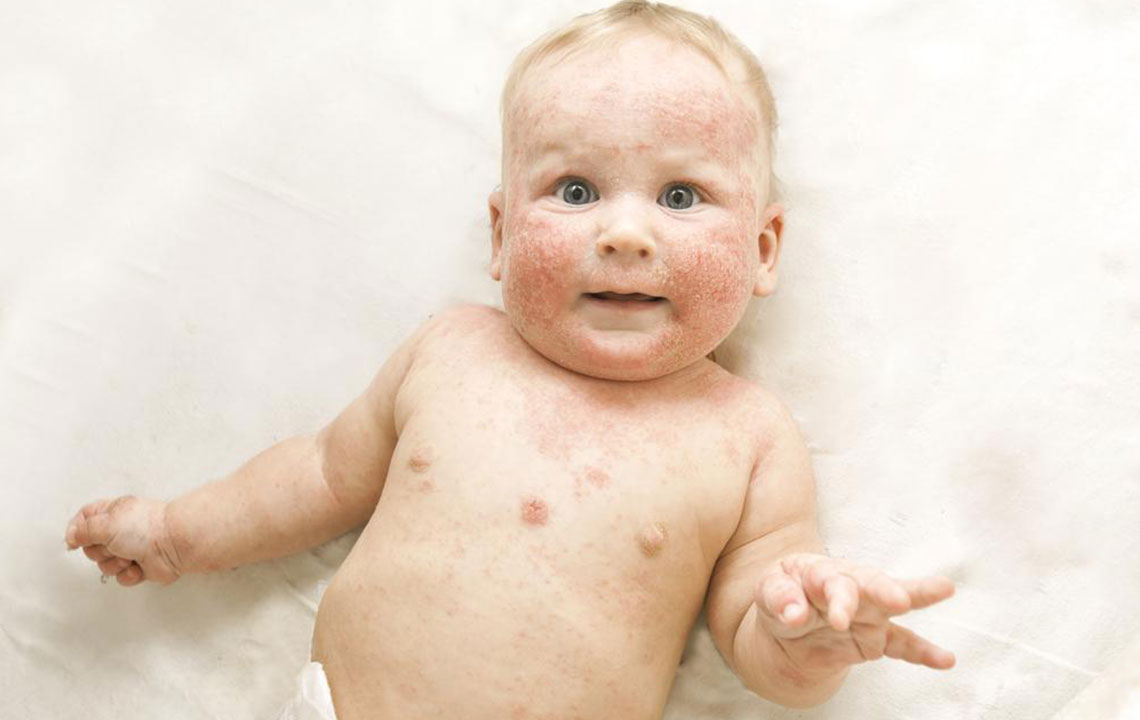
Atopic dermatitis, often referred to as eczema, is a complex, chronic inflammatory skin disorder that affects millions worldwide. It is characterized by episodes of inflamed, extremely dry, itchy, and irritated skin patches that can significantly diminish a person's quality of life. Though no definitive cure exists as of now, adopting proper management techniques allows individuals to control symptoms effectively and lead more comfortable, healthier lives. It’s important to understand that while atopic dermatitis itself is not contagious, its symptoms and flare-ups can cause physical discomfort and emotional distress, affecting both mental health and social interactions.
Understanding the nature of atopic dermatitis is the first step toward effective management. The condition involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors that predispose individuals to compromised skin barrier functions and immune responses. This makes the skin more vulnerable to irritants, allergens, and microbial invasions, thus leading to chronic inflammation. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals, especially dermatologists, is crucial for ongoing assessment, personalized treatment plans, and timely adjustments to therapy.
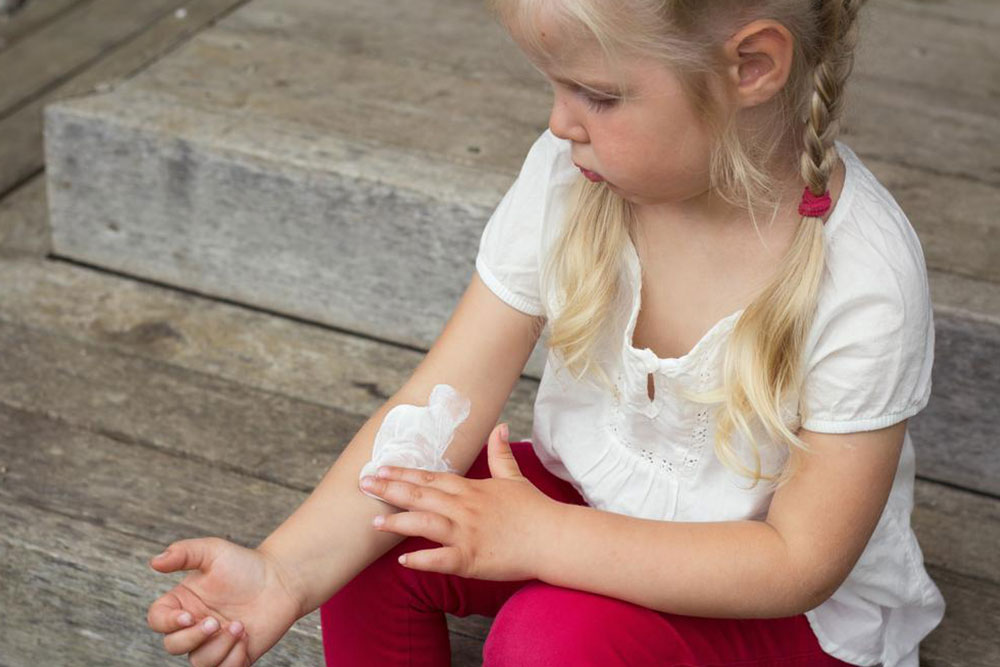
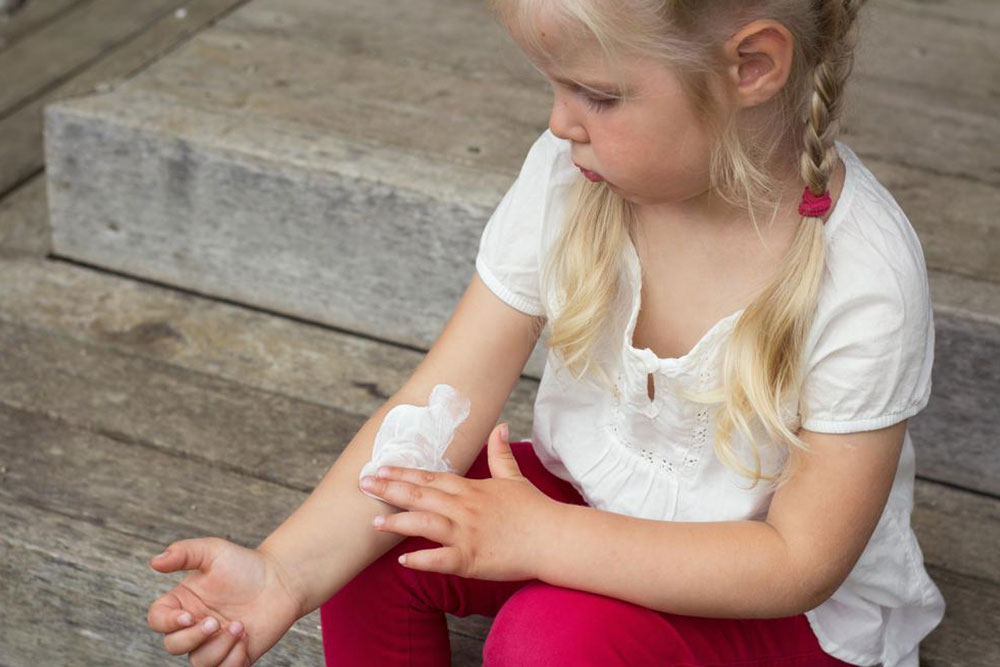
One of the key cornerstones of managing atopic dermatitis is the consistent use of prescribed topical treatments, such as corticosteroid or non-steroid anti-inflammatory ointments. These medications help reduce inflammation during flare-ups and prevent severe skin damage. Additionally, emollients or moisturizers are fundamental in restoring skin barrier function. Thick creams, ointments, and petroleum jelly are highly recommended to maintain hydration, especially after bathing, when the skin is most receptive to moisture absorption.
Beyond medical treatments, lifestyle modifications play a vital role. Patients should identify and avoid known triggers that exacerbate symptoms. Common triggers include harsh soaps, synthetic fabrics, pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and certain foods like eggs, peanuts, and soy, which can trigger allergic reactions. Using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and bathing in lukewarm water helps prevent skin irritation. Keeping baths and showers brief minimizes skin drying, while patting the skin dry and applying moisturizers immediately can lock in moisture effectively.
Skin care routines should be gentle and consistent. Avoid scratching the affected areas, as this can worsen inflammation and lead to skin infections. For children, it's especially important to keep nails trimmed and discourage scratching through distraction or using soft gloves at night. Wearing loose, breathable clothing made of natural fibers reduces irritation and allows skin to breathe. Regular humidification of indoor air, especially in dry climates or during winter months, can prevent skin from becoming excessively dry and itchy.
Diet also influences atopic dermatitis management. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support skin health. However, some individuals may have food allergies that trigger flare-ups; hence, food elimination diets should be conducted under medical supervision to identify specific sensitivities. Additionally, managing stress levels through relaxation techniques, adequate sleep, and stress-reduction strategies can decrease the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Emerging therapies and ongoing research continue to improve the understanding and treatment of atopic dermatitis. New biologic medications targeting specific immune pathways have shown promising results, particularly for severe cases unresponsive to traditional therapies. Patient education about skin care, trigger avoidance, and adherence to treatment regimens remain essential components of effective management.
In conclusion, while atopic dermatitis can be a challenging skin condition, comprehensive and proactive management strategies—combining medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and environmental controls—can lead to substantial improvements. Consistent skin care routines, avoiding triggers, and regular dermatological consultations ensure that individuals can minimize flare-ups and enjoy healthier, more comfortable skin. Awareness and early intervention are key to controlling this persistent condition and enhancing overall well-being.