Complete Guide to Effectively Managing Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide explores psoriasis in detail, covering its types, symptoms, causes, and advanced management options. It highlights personalized treatment approaches, including topical therapies, phototherapy, systemic medications, and lifestyle modifications, helping patients better control their condition and improve skin health and overall quality of life.

Complete Guide to Effectively Managing Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a persistent, autoimmune skin disorder that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by the development of thick, red, and scaly patches on the skin, psoriasis can significantly impact a person's quality of life. Understanding its various types, symptoms, causes, and available management strategies is essential for those affected. This comprehensive guide offers in-depth insights to help patients and caregivers navigate the condition effectively, ensuring better symptom control and skin health.
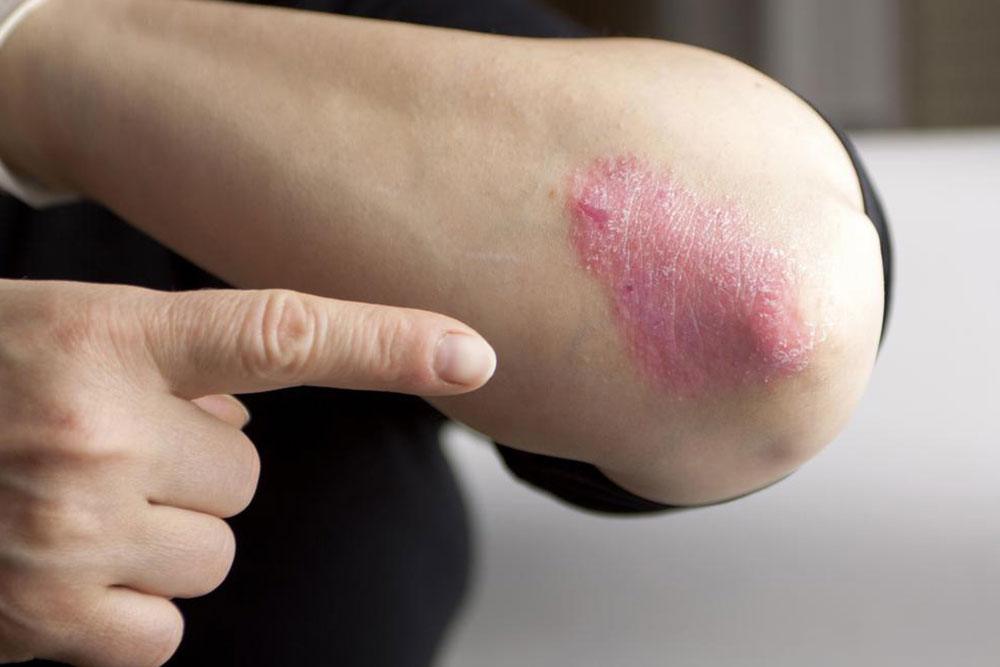
Psoriasis is not merely a superficial skin issue; it’s a complex autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This leads to accelerated skin cell production, resulting in the characteristic patches known as plaques. These plaques often appear on areas like the elbows, knees, scalp, and other regions, but they can develop anywhere on the body.
Types of Psoriasis and Their Characteristics
Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, presenting as raised, scaly patches. These areas are often itchy and uncomfortable. These plaques are typically covered with silvery-white scales and can vary in size.
Guttate Psoriasis: Appears as small, drop-shaped lesions, often triggered by infections like strep throat. It frequently affects children and young adults.
Inverse Psoriasis: Manifests as shiny, smooth, red patches in skin folds such as the underarms, groin, or around the genitals and buttocks.
Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules (blisters filled with non-infectious pus) surrounded by inflamed skin. It can be localized or widespread.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe, widespread form that causes extensive redness, pain, and skin shedding. It’s a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
Common Affected Areas and Manifestations
Psoriasis can affect virtually any part of the body, with certain areas being more prone to specific types:
Scalp: Mild cases involve fine scaling, but severe cases can have thick, crusted plaques covering large parts of the scalp, extending onto the forehead, ears, or neck. It may also cause hair thinning in affected regions.
Face: Psoriasis on the face appears around eyebrows, nasolabial folds, and forehead. Careful treatment is essential to prevent cosmetic concerns.
Hands, Feet, and Nails: These areas are prone to chronic irritation. Nail psoriasis is observed in up to 50% of cases, often leading to pitting, discoloration, or thickening, especially in individuals with psoriatic arthritis.
Genital Region: Inverse psoriasis predominantly affects this area, requiring delicate treatment to avoid irritation or discomfort.
Understanding Psoriasis Causes and Triggers
The exact origin of psoriasis remains elusive, but scientific research highlights the roles of genetics and immune system dysregulation. Several factors can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms:
Genetic Predisposition: Having a family history increases susceptibility. Specific genes related to immune response and skin cell growth are involved.
Immune System Dysfunction: Abnormal immune activity accelerates skin cell turnover, leading to lesions.
Environmental Triggers: Stress, infections, skin injuries, medications, smoking, and alcohol consumption can set off flare-ups.
Other Factors: Climate conditions, with cold and dry weather tending to worsen symptoms, are also influential.
Symptoms and How to Recognize Psoriasis
Recognizing the signs of psoriasis is crucial for early management. Typical symptoms include:
Red patches covered with silvery scales, often itchy and uncomfortable
Small, pinpoint scaling spots, especially in children
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed or become tender
Itching, burning, or soreness in affected areas
Thickened or ridged nails with abnormal growth
Joint stiffness, swelling, or pain if psoriatic arthritis develops
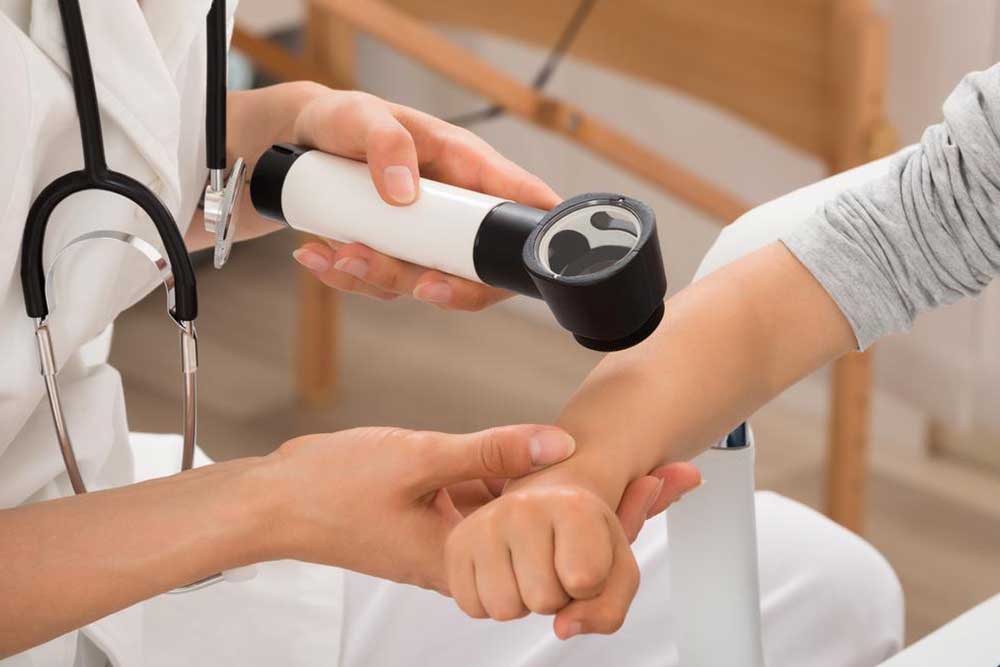
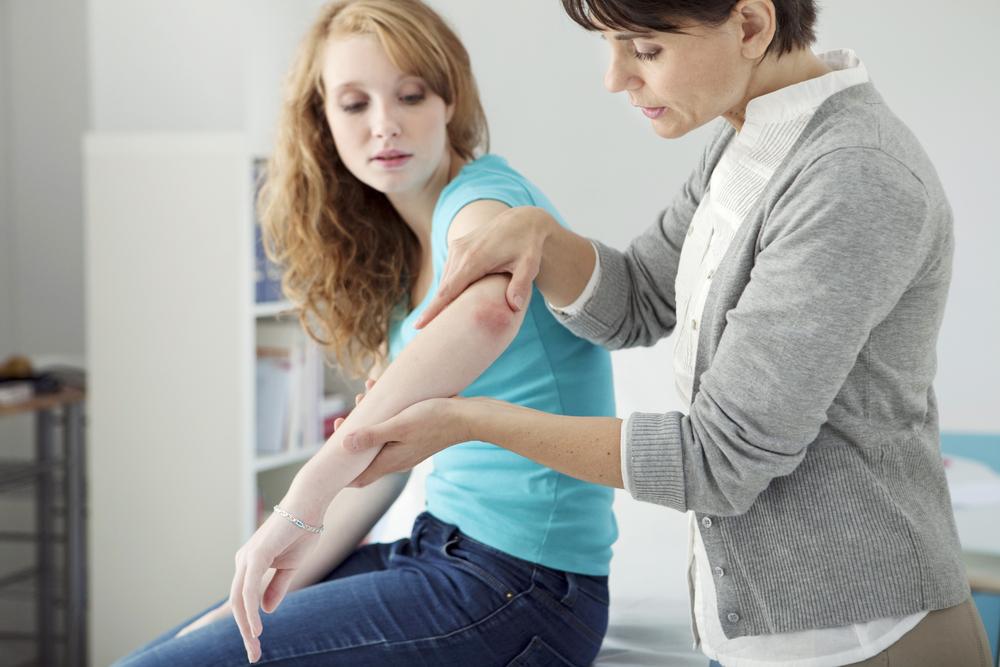
Diagnosis primarily involves visual examination by a dermatologist. In uncertain cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. Notably, psoriasis is a non-contagious condition, so it cannot be transmitted through skin contact.
Advanced Management Strategies for Psoriasis
While there is no definitive cure for psoriasis, numerous treatment options aim to control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve the quality of life for patients. An effective management strategy often involves a combination of therapies tailored to individual needs.
Topical Treatments
Many patients with mild to moderate psoriasis find relief through topical therapies. These include:
Corticosteroid creams: Reduce inflammation and itching. Used prudently to prevent skin thinning.
Vitamin D analogs: Such as calcipotriol, which slow skin cell growth.
Coal tar: Helps reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation.
Moisturizers: Regular use maintains skin hydration, preventing cracks and irritation.
Phototherapy and Light Therapy
Controlled exposure to natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light can significantly reduce psoriatic lesions. Phototherapy involves sessions of UVB light, performed under medical supervision, which can clear or diminish symptoms effectively.
Systemic Medications
Severe cases may require oral or injectable medications that modify immune responses. These include:
Biologic therapies: Target specific immune pathways (e.g., TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors).
Methotrexate, cyclosporine, or acitretin: Suppress immune system activity to control widespread psoriasis.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Additional strategies can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups:
Stress management techniques such as meditation and yoga
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods
Avoidance of known triggers like smoking and excessive alcohol
Regular skin hydration and gentle cleansing
Emerging and Alternative Treatments
Research continues into new therapeutic options, including herbal remedies, dietary supplements, and integrative medicine approaches. Patients should discuss these options with healthcare providers before initiation.
In conclusion, psoriasis is a multifaceted condition requiring a personalized approach to management. Awareness of its various forms, triggers, and therapeutic options empowers patients to lead healthier, more comfortable lives. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals is essential to adapt treatment plans as needed and prevent serious complications like psoriatic arthritis or infections.