The Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Managing Psoriasis Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers detailed insights into psoriasis, a common autoimmune skin condition affecting millions worldwide. It covers causes, symptoms, and various treatment options including topical therapies, systemic medications, and light therapy. The article emphasizes the importance of professional diagnosis and personalized management strategies to control symptoms effectively. Learn how to distinguish psoriasis from other skin conditions and explore lifestyle tips to improve quality of life. Ideal for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals seeking an in-depth understanding of this chronic disease.

In-Depth Knowledge of Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
Comprehensive Understanding of Psoriasis
Living with skin conditions like psoriasis can be challenging, not only physically due to discomfort but also mentally due to social stigma and misconceptions. Many people mistakenly believe that all skin diseases are contagious, which leads to misjudgments and social isolation for those affected. Moreover, attempting to treat psoriasis without professional medical guidance can exacerbate symptoms or delay effective management. Therefore, awareness, accurate information, and consulting healthcare professionals are essential for managing this chronic skin disorder effectively. This article provides a detailed overview of psoriasis, its underlying causes, symptoms, and available treatment options to help patients and caregivers better understand and control the condition.
Psoriasis affects millions worldwide, with estimates suggesting around 7.5 million individuals in the United States alone live with this chronic autoimmune disorder. It significantly impacts daily life, causing physical discomfort and emotional distress. Understanding its causes and exploring the best management strategies are crucial for improving patients' quality of life.
What is psoriasis?
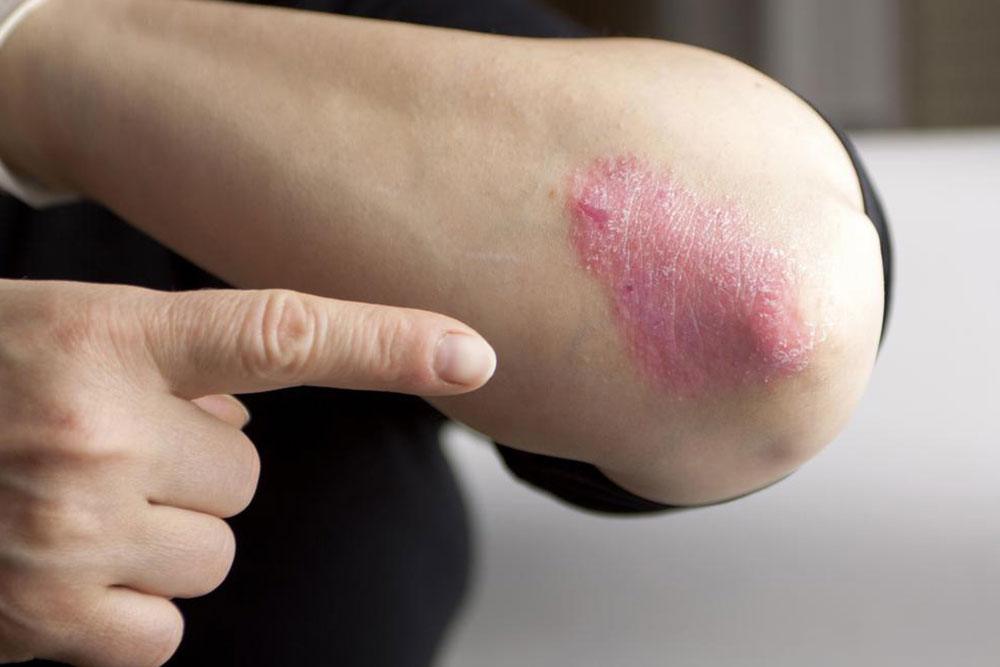
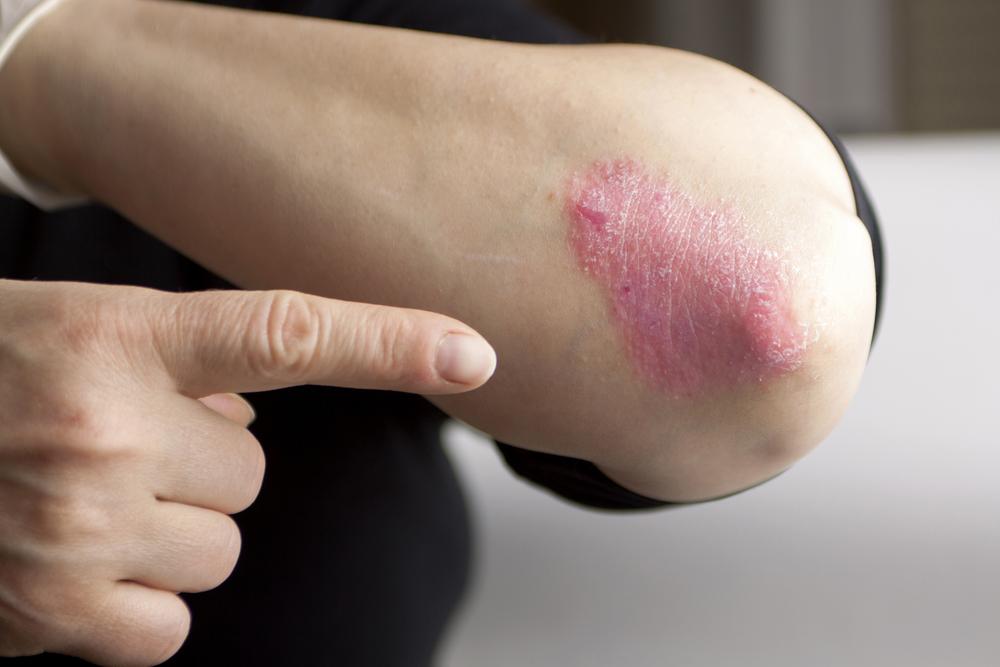
Psoriasis is a long-term autoimmune disease characterized by abnormal immune responses that accelerate skin cell production, leading to thickened, scaly patches on the skin.
Typically manifesting as silvery-white scales overlaying red, inflamed patches, psoriasis can occur on various parts of the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, hands, feet, face, nails, mouth, and genital areas. The core issue lies in a rapid turnover of skin cells—normally, skin cells regenerate every 28 to 30 days, but in psoriasis, this process speeds up to just a few days. This rapid cell buildup results in visible plaques and lesions, which are often accompanied by discomfort and itching.
Common symptoms associated with psoriasis
Symptoms can differ depending on the type of psoriasis but generally include red, raised patches with silvery scales, soreness, cracking, dry skin, intense itching, burning sensations, joint discomfort, and possible nail abnormalities such as pitting or discoloration.
Understanding the causes of psoriasis
Although the precise cause remains unknown, current research points to a combination of genetic factors and immune system dysfunction as primary contributors.
Genetic predisposition: Family history plays a significant role, with estimates indicating that 2-3% of those with psoriasis inherit specific genetic markers that increase their susceptibility.
Immune system involvement: The disease manifests when immune cells mistakenly recognize healthy skin cells as threats, leading to inflammation, accelerated cell production, and plaque formation.
Treatment options for psoriasis: Managing a chronic condition
While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, many therapies exist that help keep symptoms under control and improve patients' quality of life.
Topical therapies: For mild to moderate psoriasis, corticosteroid creams, salicylic acid, coal tar, calcipotriol, moisturizers, and vitamin D analogs can effectively reduce inflammation, scaling, and itching.
Systemic medications: Severe cases may require systemic treatments such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin, or biologic agents like TNF-alpha inhibitors, which modulate immune responses more broadly.
Phototherapy: Light therapy, involving exposure to natural sunlight or controlled ultraviolet B (UVB) light, can slow down immune activity and reduce plaque formation.
Recognizing the importance of tailored treatment plans, stress management, lifestyle changes, and regular medical checkups are vital elements of effective psoriasis management. Patients should work closely with dermatologists to identify the most suitable therapies for their specific condition, monitor progress, and adjust treatments as needed.
In conclusion, psoriasis is a complex autoimmune skin disorder that requires a comprehensive approach encompassing medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and psychological support. With increased awareness and proper management, individuals living with psoriasis can lead healthier, more comfortable lives.