Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Symptoms, Types, and Management
A detailed, comprehensive guide to psoriasis, covering symptoms, types, management strategies, and lifestyle tips. Learn how to identify psoriasis early and explore various treatment options to improve quality of life. This article is essential for patients and caregivers seeking in-depth understanding of this chronic skin condition.
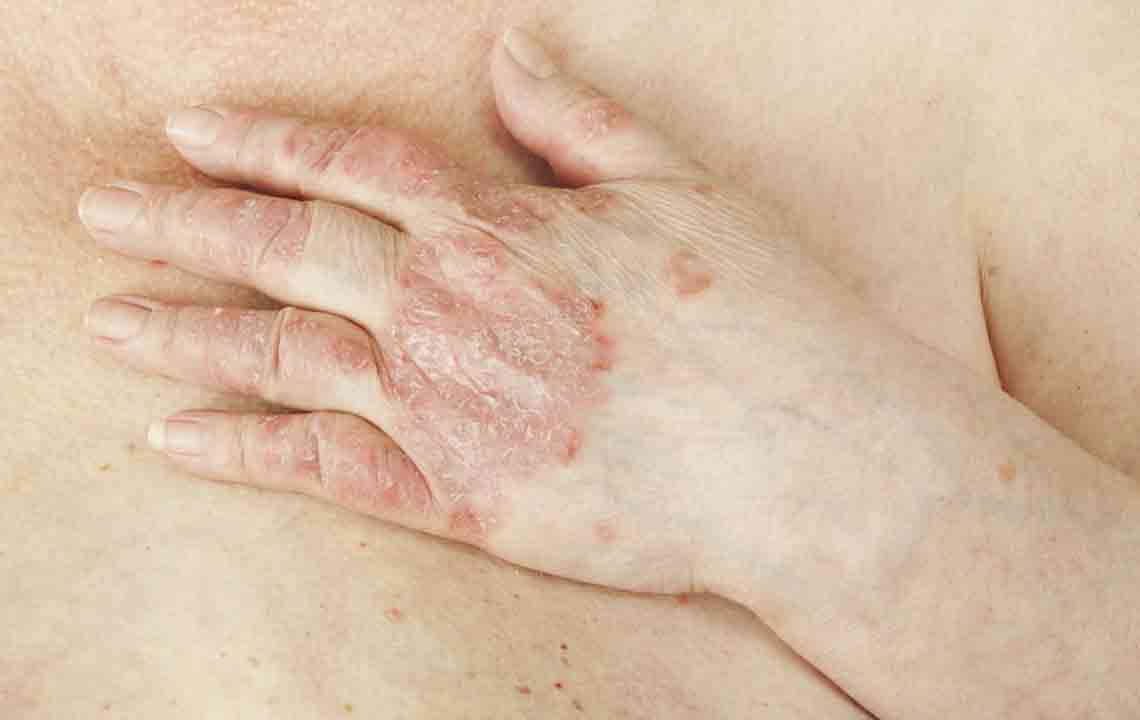
Understanding Psoriasis: An In-Depth Look at Symptoms and Different Types
Psoriasis is a complex, chronic autoimmune skin disorder that impacts millions worldwide. It is characterized by abnormal immune system activity that leads to rapid skin cell proliferation, resulting in thickened, inflamed patches of skin. Often appearing as red, itchy, and scaly plaques, psoriasis can significantly affect quality of life, causing discomfort, embarrassment, and emotional distress. Although commonly diagnosed in young adults, psoriasis can affect individuals of all ages, making awareness crucial for early management and treatment.
Understanding the diverse manifestations of psoriasis is essential for effective management. The disease involves an abnormal immune response that triggers skin cell overproduction, leading to characteristic patches that can be itchy, painful, or cracked. The severity varies widely—from minor localized patches to widespread plaques covering large portions of the body. Recognizing early signs and differentiating between the various types of psoriasis is vital for initiating appropriate treatment and improving patient outcomes.
The Symptoms of Psoriasis: Recognizing the Signs
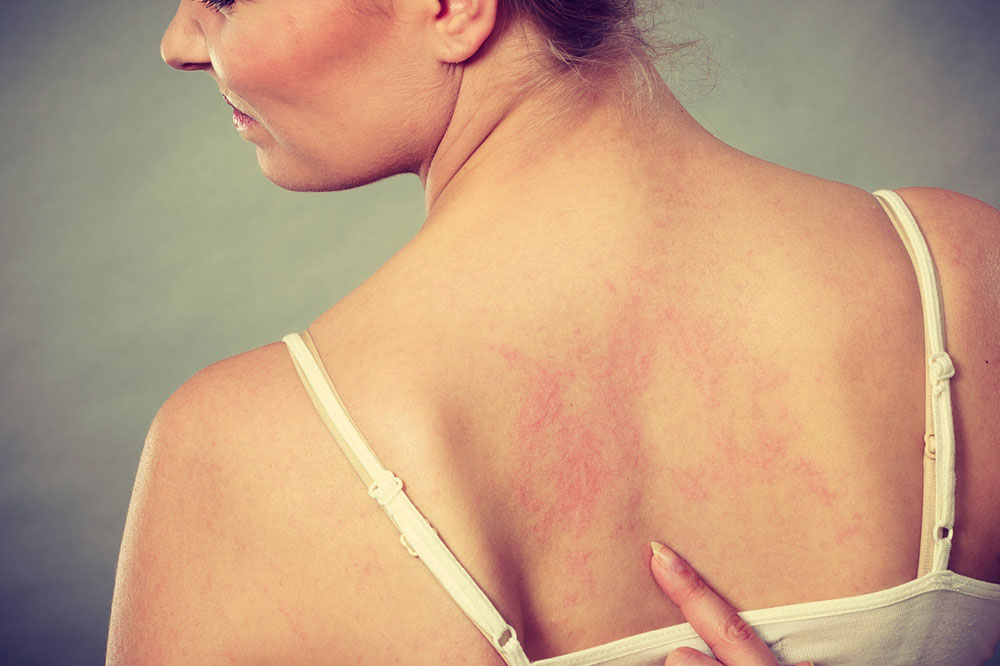
Symptoms of psoriasis can be quite distinctive but may sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions. Typically, affected areas exhibit red or pink patches topped with silvery-white scales. These patches may be itchy, burning, or sore, leading to discomfort and potential secondary infections if scratched extensively. In addition to skin symptoms, psoriasis can involve other parts of the body:
Thickened, ridged, or ridged nails, sometimes with detachment or pitting
Inflammation and swelling in the joints, known as psoriatic arthritis
Cracking or bleeding skin in severe cases
Itching and burning sensations that can be intense
Early identification of these signs allows for timely medical intervention. Healthcare professionals can distinguish psoriasis from other dermatologic conditions like eczema or dermatitis through clinical examination and, if necessary, skin biopsies. Managing psoriasis effectively requires a combination of therapies tailored to the severity and type of the disease.
Different Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is not a singular condition but encompasses several distinct types, each with unique characteristics and implications for treatment:
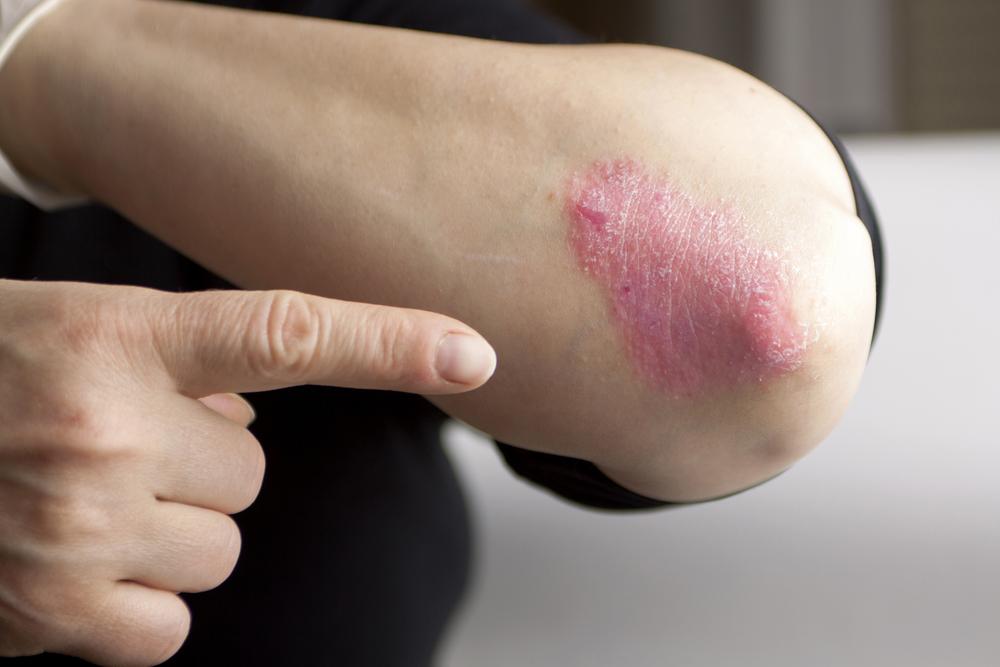
Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris): The most common form, presenting as raised, red patches with silvery scales typically found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
Guttate Psoriasis: Characterized by small, drop-shaped lesions, often triggered by infections or stress. It frequently appears on the trunk, arms, and legs.
Pustular Psoriasis: Presents as white pustules (blisters filled with non-infectious pus) surrounded by inflamed skin, often impacting the palms and soles.
Inverse Psoriasis: Occurs in skin folds such as underarms, groin, or around genitals, marked by shiny, smooth, and inflamed patches without significant scaling.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe, rare form involving widespread redness, pain, and shedding. This type can be life-threatening and requires urgent medical attention.
Understanding these variants allows physicians to create customized treatment regimens. Each type’s triggers, symptoms, and response to therapy can differ, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis.
Treating and Managing Psoriasis
While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, numerous treatments exist to help manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve quality of life. A comprehensive approach often involves topical therapies, systemic medications, phototherapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, moisturizers, and coal tar preparations are used to soothe inflamed skin, reduce scales, and prevent flares.
Systemic Medications: For moderate to severe cases, drugs like methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologic agents targeting immune pathways can be prescribed.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can help slow skin cell growth and decrease inflammation.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies: Stress management, avoiding known triggers, maintaining skin hydration, and adopting a healthy diet can significantly impact disease severity.
Effective management requires coordination with healthcare providers, ongoing monitoring, and adherence to prescribed treatments. Patients are encouraged to educate themselves about their condition and participate actively in their care plan.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Preventive Care
Living with psoriasis involves more than medical treatment. Lifestyle changes can dramatically influence disease progression and ease discomfort. Strategies include:
Avoiding known triggers such as stress, infections, smoking, and certain medications
Keeping skin moist with emollients and moisturizing creams to prevent cracking and scaling
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, yoga, or counseling
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids
Regularly consulting healthcare providers for check-ups and treatment adjustments
Early intervention and consistent management can help reduce symptom severity, minimize flare-ups, and improve overall well-being.
The Importance of Medical Consultation
Since psoriasis can mimic other skin conditions and vary greatly among individuals, professional medical diagnosis is essential. Dermatologists can identify the specific type of psoriasis, evaluate severity, and recommend personalized treatment options. Patients should seek medical advice if they notice persistent or worsening symptoms, or if they experience joint pain, which could indicate psoriatic arthritis.
Recognizing the symptoms early and applying appropriate treatments can substantially improve life quality and prevent complications. With ongoing research and emerging therapies, many patients find effective relief from this chronic condition.