Ultimate Guide to Psoriasis: Causes, Types, and Effective Treatments
This comprehensive article explores the causes, types, and treatments of psoriasis, providing detailed insights into symptom recognition and management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of professional diagnosis and personalized care to effectively control this chronic skin condition. Learn about the different psoriasis types, symptoms, and lifestyle tips to improve quality of life for sufferers. Whether you're newly diagnosed or seeking better management options, this guide offers valuable information to help understand and cope with psoriasis more effectively.
In-Depth Exploration of Psoriasis: Symptoms, Variations, and Management Strategies
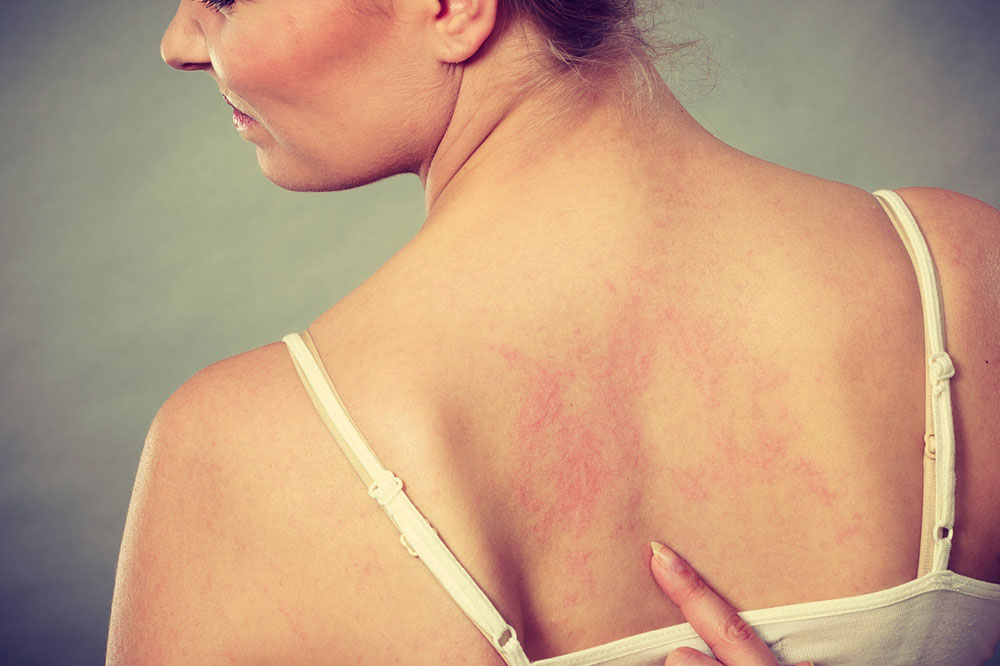
It’s completely natural to experience the urge to scratch an itch, but persistent scratching can worsen skin conditions like psoriasis, leading to redness, lesions, and inflammation. Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide, resulting in discomfort, sleep disturbances, and difficulty concentrating. Though there is currently no complete cure for psoriasis, numerous treatments are available that help in effectively controlling and managing its symptoms, improving quality of life for sufferers.
What is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is a common autoimmune disease that causes rapid skin cell turnover, leading to inflammation and the appearance of thickened, scaly patches on the skin. It is a complex condition that involves immune system dysregulation, causing the body to attack healthy skin cells. This results in the characteristic patches of inflamed, itchy, and often painful skin that are hallmark symptoms of the condition.
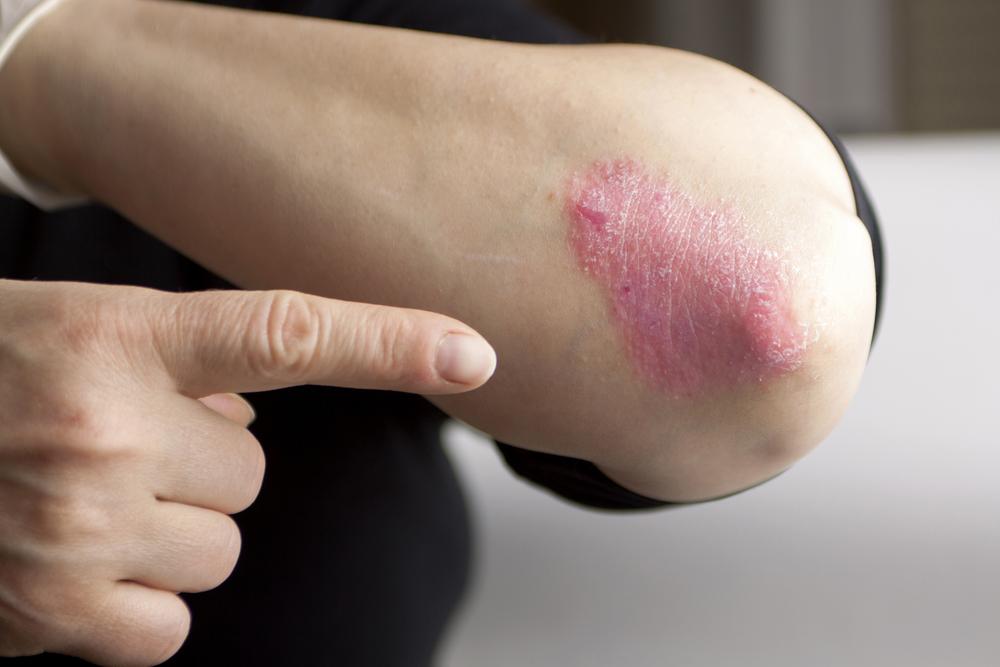
Psoriasis typically manifests as red patches covered with silvery-white scales, and sometimes it can lead to sores filled with pus. The areas most commonly affected include the elbows, knees, and scalp, but the condition can also appear on the torso, palms, soles of the feet, and other parts of the body. The severity and pattern of psoriasis vary widely among individuals, making it a highly individualized condition to manage.
Types of Psoriasis The different forms of psoriasis can present with unique features and involve different parts of the body. Understanding these variations is crucial for effective management and treatment planning. The primary types include:
Guttate Psoriasis: This type is often seen in individuals under 30 and is characterized by small, drop-shaped spots of red skin, usually appearing on the trunk and limbs. It is frequently triggered by infections such as streptococcal throat infections (strep throat), which initiate immune responses that lead to these distinctive lesions.
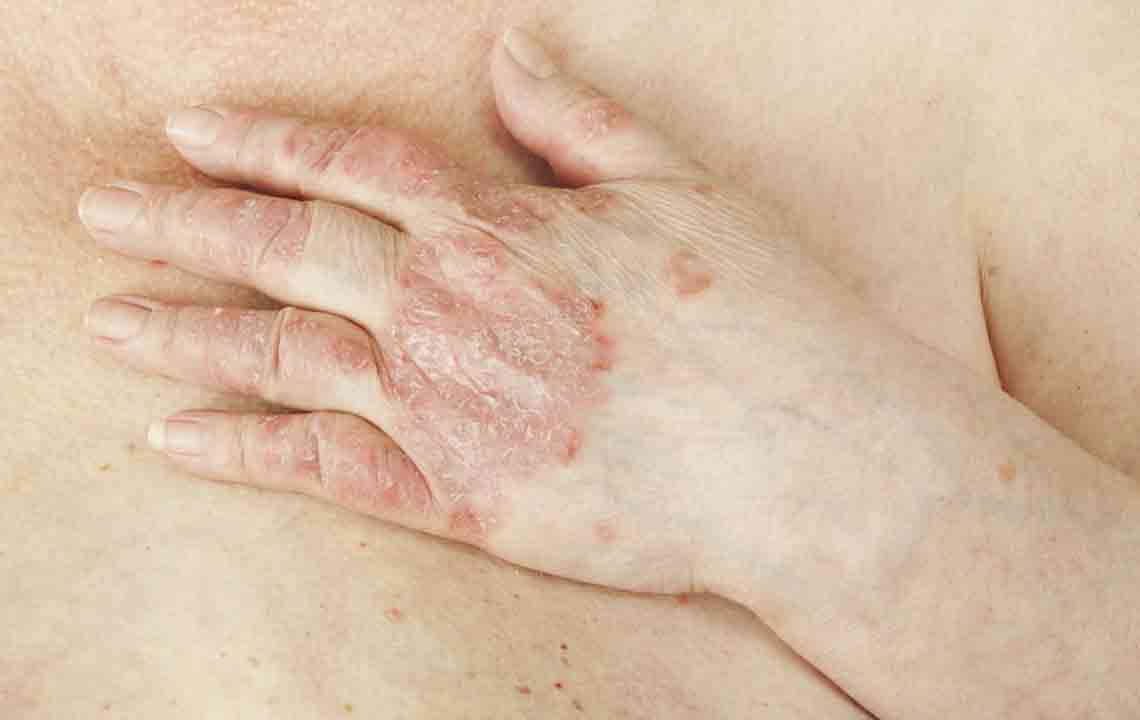
Inverse Psoriasis: Also known as flexural psoriasis, this form manifests as shiny, red patches that are smooth and gloss-like. It typically affects skin folds such as the groin, under the breasts, around the genitals, and behind the knees. Sweating and friction can exacerbate inverse psoriasis, making it more uncomfortable in hot or humid environments.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis: This is a severe and potentially life-threatening variant that causes widespread redness, scaling, and skin shedding over large areas of the body. It often results from the worsening of other psoriasis types or from reactions to certain medications, infections, or abrupt withdrawal of psoriasis treatments. Immediate medical intervention is required due to the risk of dehydration, infection, and systemic complications.
Recognizing Psoriasis Symptoms The symptoms of psoriasis can vary depending on its type and severity, but common signs include:
Persistent red, inflamed patches that itch or burn, especially in affected areas
Silver-white or yellowish scales or plaques that often flake off
Dry, cracked skin that might bleed
Presence of pus-filled blisters or sores
Joint pain and swelling, indicating psoriatic arthritis in some cases
Irregular immune responses leading to systemic symptoms in severe cases
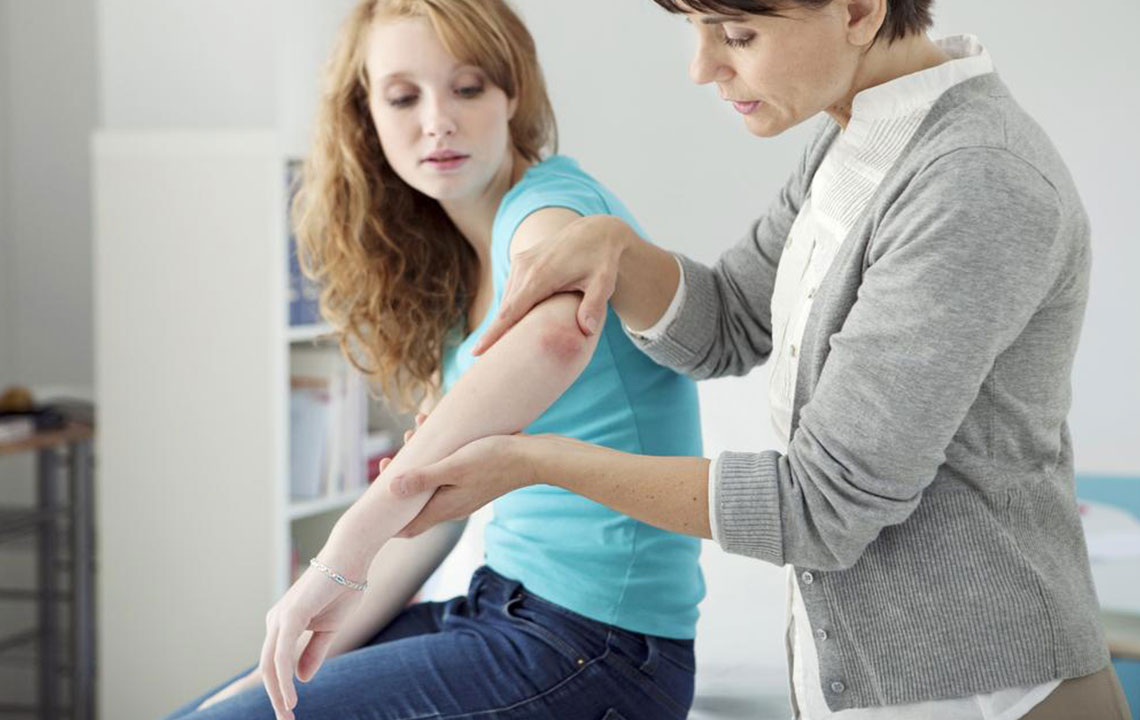
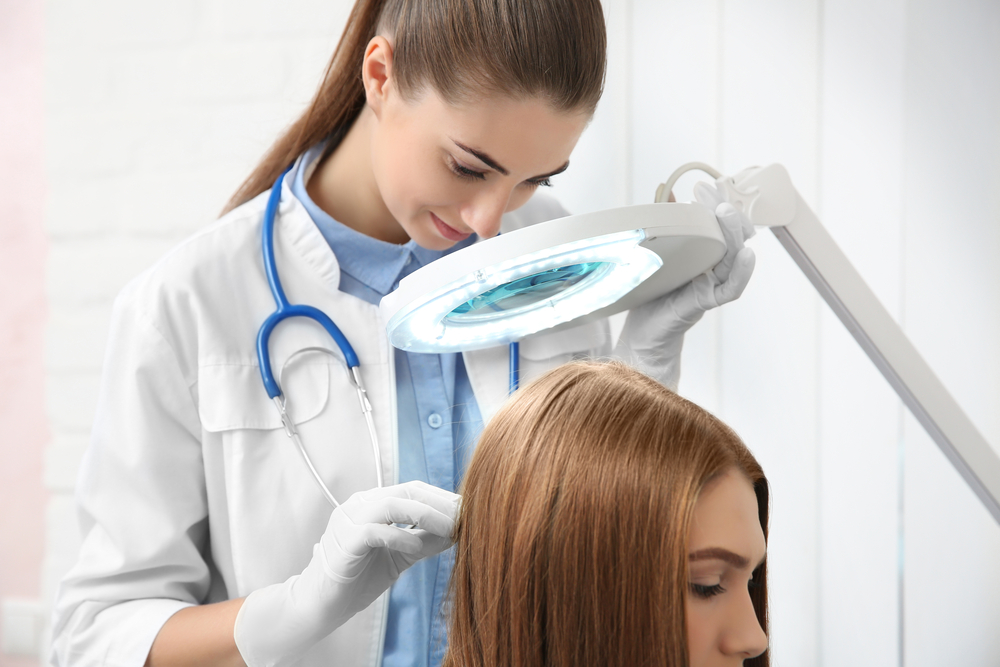
Diagnosing Psoriasis Diagnostic procedures involve a combination of clinical examination and, if necessary, laboratory tests. Typical diagnostic steps include:
Visual Examination: A trained dermatologist evaluates the skin for characteristic symptoms and reviews the patient's medical and family history to identify patterns and triggers.
Skin Biopsy: If the diagnosis is uncertain, a small skin sample may be taken under local anesthesia for microscopic examination. This helps differentiate psoriasis from other skin conditions such as eczema, fungal infections, or skin cancers.
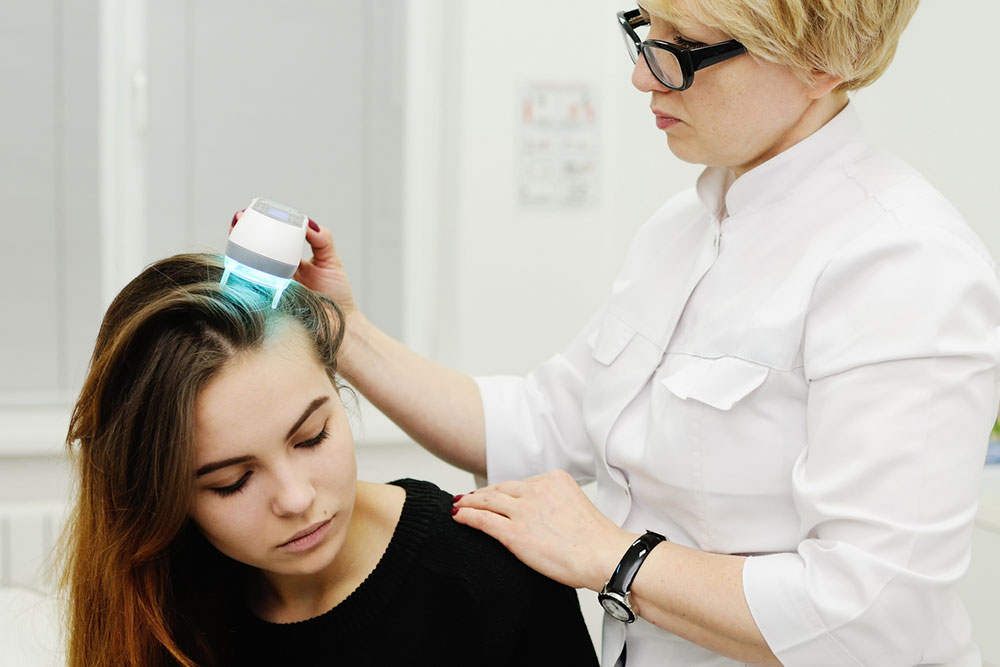
Managing Psoriasis Symptoms Effectively Although a cure for psoriasis remains elusive, various strategies and treatments can significantly alleviate symptoms and reduce flare-ups. A personalized approach often combines medical therapies with lifestyle modifications, providing relief and improving patients’ overall quality of life. Effective management tips include:
Minimize scratching to prevent further skin damage and infection
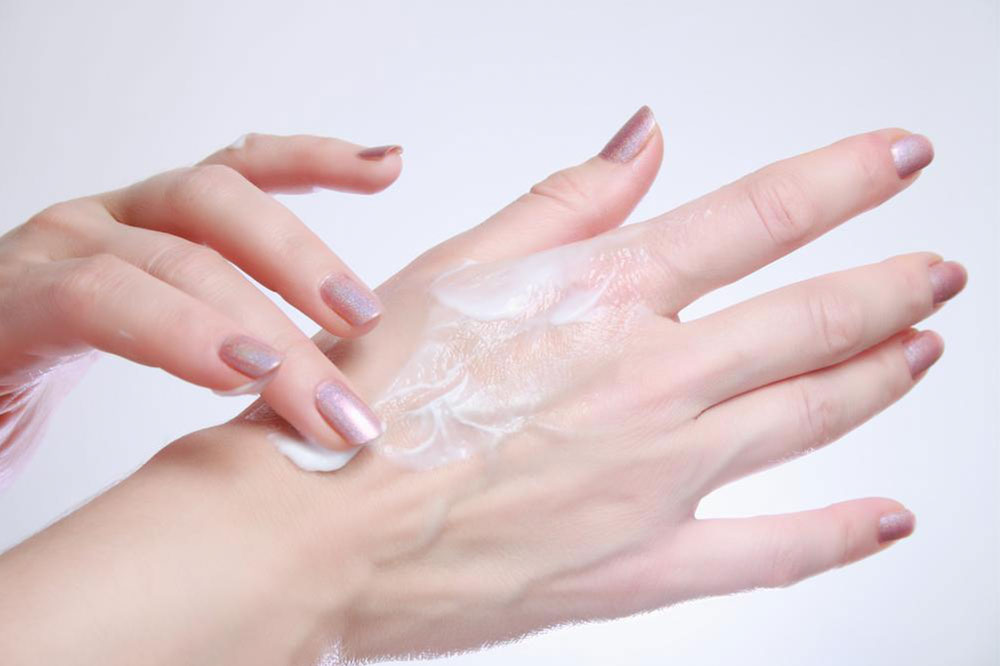
Use soothing moisturizers regularly to maintain skin hydration and reduce inflammation
soak in warm saltwater baths to soften scales and remove buildup
Avoid excessive sun exposure; moderate sunlight can be beneficial but too much UV radiation can worsen symptoms
Apply topical treatments such as coal tar preparations, corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or salicylic acid to reduce scales and inflammation
Adopt a diet that promotes skin health: focus on consuming heart-healthy foods rich in nuts, seeds, and plant-based proteins
Limit intake of red meats, processed foods, and dairy products, which are known to increase inflammation
Avoid alcohol consumption, as it can trigger flare-ups and interfere with treatments
Take warm, not hot, baths and immediately apply moisturizers to lock in hydration
Implement stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises to help reduce flare-ups triggered by stress
Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric into your diet; turmeric contains curcumin, which helps reduce inflammation in the body
It’s essential for individuals with psoriasis to stay informed about their condition and work closely with healthcare providers to develop tailored treatment plans. Self-treatment without professional guidance may lead to complications or ineffective management. Regular follow-up appointments, adherence to prescribed therapies, and lifestyle adjustments can greatly improve living with psoriasis.