In-Depth Comprehensive Guide to Managing Chronic Psoriasis for Better Skin Health
This comprehensive guide delves into chronic psoriasis, exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis and personalized therapies, including topical treatments, phototherapy, and advanced biologic drugs. The article offers practical advice on lifestyle modifications and skin care routines to improve quality of life for psoriasis patients, highlighting recent developments in the management of this autoimmune skin disorder.
Understanding, Diagnosing, and Effectively Treating Chronic Psoriasis
Chronic psoriasis is a complex autoimmune skin condition that affects millions worldwide, presenting with persistent symptoms such as itching, redness, flaking, and scaling of the skin. Recognized as a long-term disorder, psoriasis not only impacts physical appearance but also significantly affects an individual's quality of life, mental health, and daily activities. This detailed guide aims to provide comprehensive insights into this condition, exploring its causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, and cutting-edge treatment options to empower patients and caregivers in managing this challenging disease effectively.
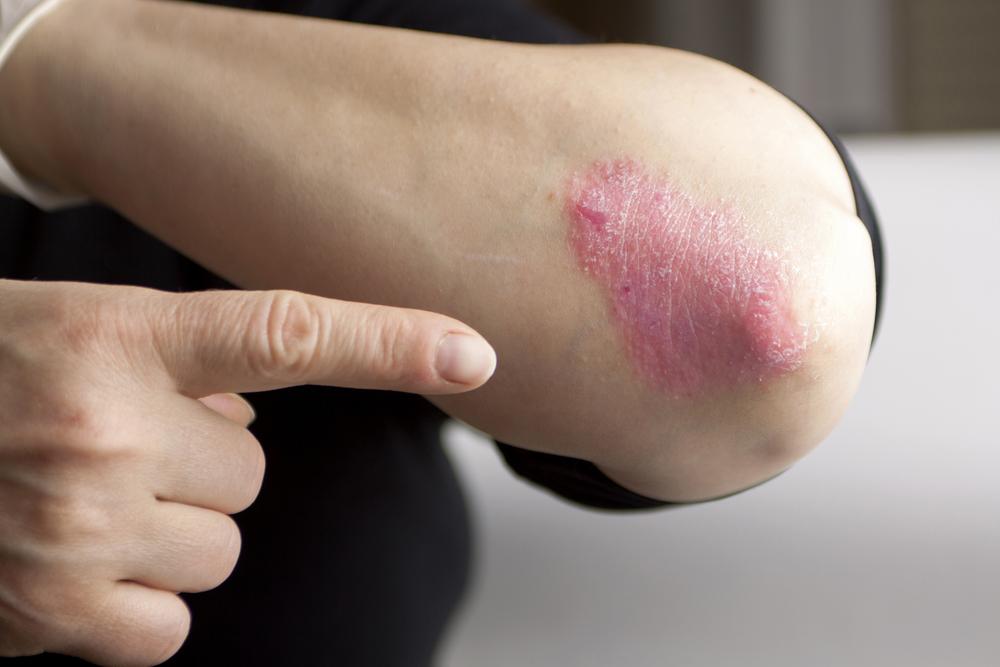
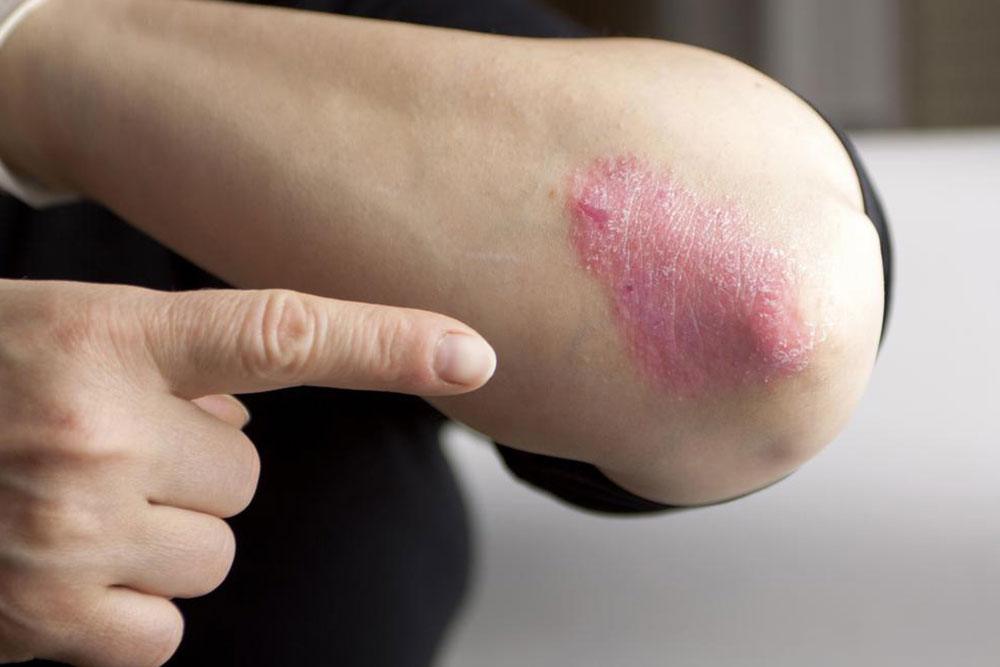
Understanding psoriasis starts with recognizing its hallmark features: inflamed, scaly patches that can vary greatly in size, shape, and location. While the precise cause remains largely unknown, it is understood as an autoimmune response where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid skin cell turnover and subsequent buildup. Factors such as genetic predisposition, stress, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices may all contribute to the onset and exacerbation of psoriasis.
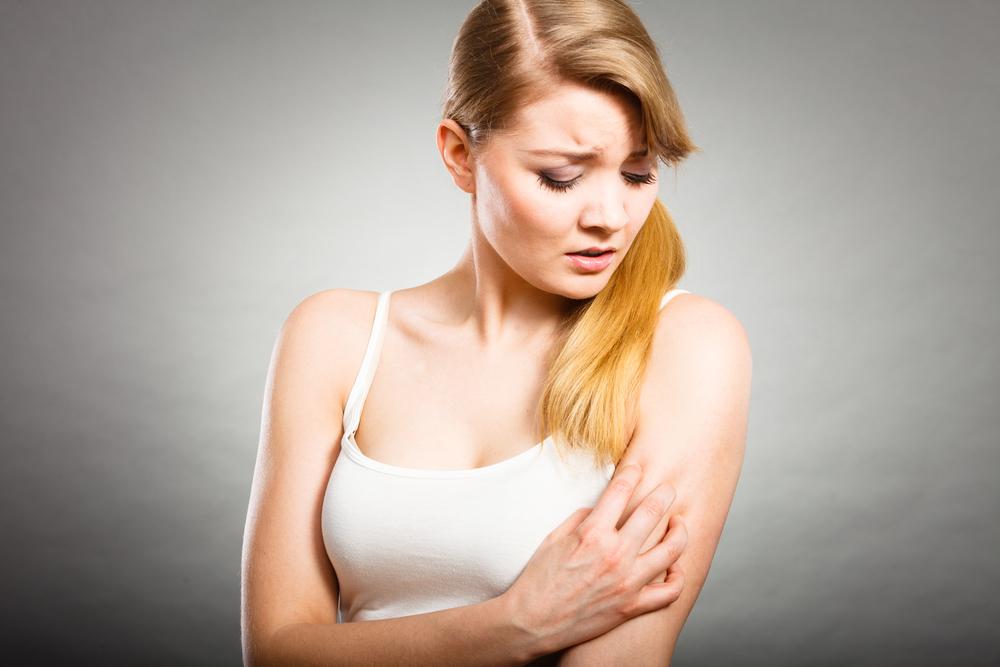
The symptoms of psoriasis extend beyond superficial skin changes; they often involve underlying biological processes that lead to physical discomfort and emotional distress. Common signs include:
Bright red, inflamed patches that may be raised
Silvery or white scaling that flakes off easily
Intense itching and irritation
Possible pain or burning sensation in affected areas
Joint pain, swelling, or stiffness, indicating psoriatic arthritis
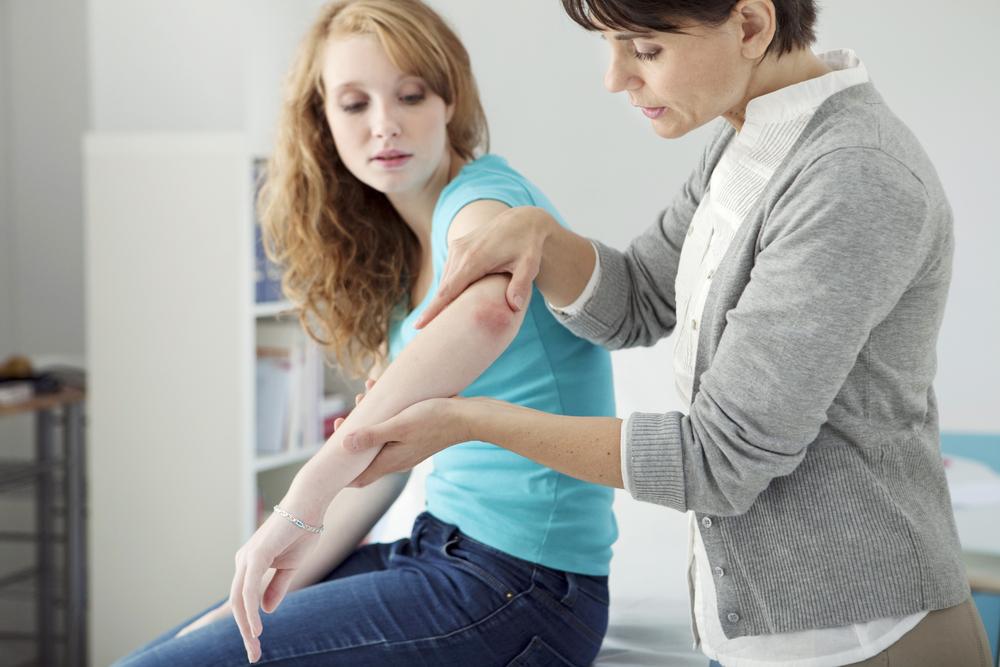
Diagnosing psoriasis involves a thorough physical examination, patient history, and sometimes skin biopsies, to distinguish it from other skin conditions. Accurate diagnosis is essential because psoriasis manifests in various forms, each requiring tailored treatment strategies. Typically, psoriasis is classified into seven main types based on appearance, location, and severity:
Plaque psoriasis (psoriasis vulgaris) – The most common type, characterized by raised, red patches covered with a silvery scale, frequently seen on elbows, scalp, knees, and lower back.
Guttate psoriasis – Presents as small, drop-shaped, pink-red spots, often triggered by streptococcal infections, common in children and young adults.
Pustular psoriasis – Features white pustules (pus-filled blisters) on a red, inflamed background, sometimes widespread, necessitating urgent medical intervention.
Inverse psoriasis – Occurs in skin folds like underarms, groin, or behind knees, characterized by shiny, smooth, and bright red patches that lack scales, often worsened by sweating or friction.
Erythrodermic psoriasis – A severe, rare form involving widespread redness, peeling, and systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, and possible infections, requiring immediate medical care.
Nail psoriasis – Manifests as pitting, discoloration, and separation of nails, which may be linked with or may influence joint inflammation.
Psoriatic arthritis – An inflammatory joint condition accompanied by skin symptoms, causing pain, stiffness, swelling, and potential joint damage if untreated.
Management of psoriasis hinges on precise diagnosis of its type and severity. Treatment options are diverse and may include topical agents, phototherapy, systemic drugs, or biological therapies. The goal is to control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve the patient's overall well-being.
For plaque psoriasis, corticosteroid creams remain a frontline treatment, complemented by moisturizers and phototherapy such as UVB light therapy to slow down skin cell proliferation. Guttate psoriasis treatments emphasize managing infections triggering the episodes, usually antibiotics, alongside symptomatic management. Inverse psoriasis responds well to potent topical steroids and measures to reduce friction and sweating in affected folds. Pustular psoriasis sometimes requires systemic corticosteroids or biologic agents, especially when widespread. Although the underlying causes are not fully understood, ongoing research into immune pathways and genetic factors continues to open new avenues for targeted therapies.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications such as stress management, smoking cessation, weight control, and avoiding known triggers play vital roles in long-term disease control. Emerging treatments like biologic drugs, aimed at specific immune components, have revolutionized psoriasis management, offering relief to severe cases and decreasing reliance on systemic steroids. Skin care routines that include gentle cleansing, hydration, and protection from environmental irritants are also crucial for maintaining skin integrity.
Living with psoriasis demands a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatment with lifestyle changes and emotional support. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers, patient education, and participation in support groups can significantly enhance coping strategies and overall quality of life. Advances in research continue to improve our understanding of this complex disease, promising more effective, personalized therapies in the future.