Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Recognizing Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive article explores psoriasis in detail, covering its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and effective management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of lifestyle changes, stress management, and medical treatments in controlling flare-ups and improving quality of life for those affected by this chronic autoimmune skin disorder. Suitable for patients and caregivers, this guide provides valuable insights into understanding and managing psoriasis effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Recognizing Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
Psoriasis is a long-lasting autoimmune skin disorder that affects millions of people across the globe. In the United States alone, approximately 7.5 million individuals deal with this chronic condition, which can significantly impact their quality of life. Understanding the intricacies of psoriasis, from its symptoms and causes to available management options, is crucial for those affected and healthcare providers alike. This detailed guide aims to shed light on the condition, providing comprehensive insights to facilitate better awareness and effective control.
What is Psoriasis? An In-Depth Overview
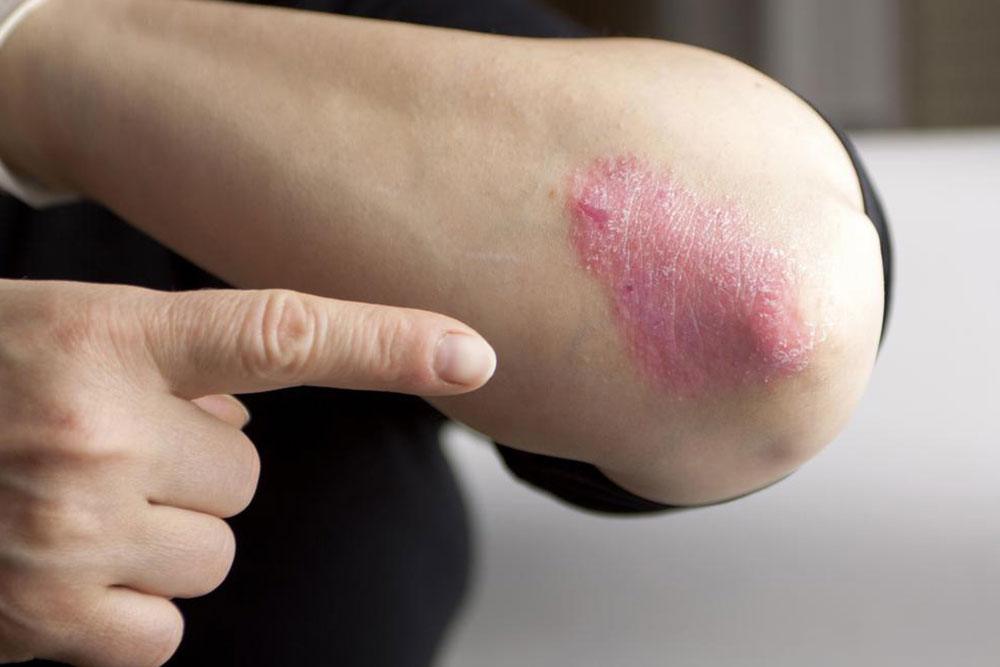
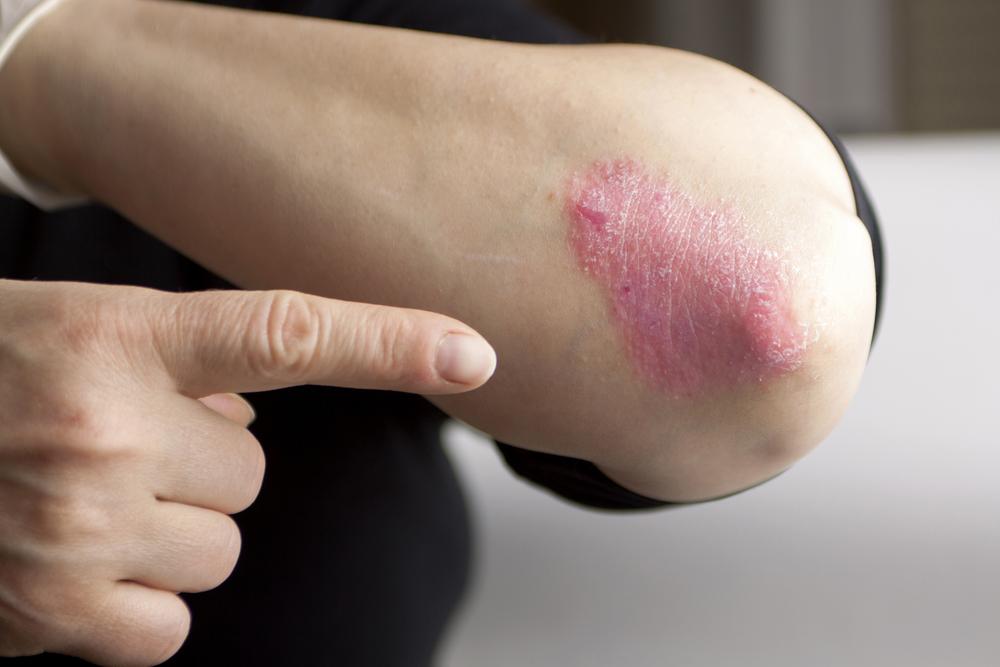
Psoriasis is classified as an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing rapid cell turnover. Normally, skin cells regenerate approximately every 28 days, allowing the skin to heal and renew gradually. However, in psoriasis, this process speeds up dramatically—completing in just a few days—leading to a buildup of dead skin cells that form thick, scaly patches known as plaques. These plaques can appear anywhere on the body, but commonly affect areas like the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The condition is characterized by periods of flare-ups and remission, often triggered by various internal and external factors.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Psoriasis
The presentation of psoriasis can vary based on the type, severity, and location. Common symptoms include:
Red, inflamed patches of skin covered with silvery or white scales
Itching, burning, or soreness in affected areas
Cracking, bleeding, or tenderness of the skin
Small, pitted, or discolored nails, sometimes with detachment from the nail bed
In some cases, the patches can merge into larger plaques or spread over significant areas of the body
Severe psoriasis forms may involve thickened skin and widespread lesions, which can be quite discomforting. Psoriatic arthritis, a related condition, can also develop in some individuals, leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, greatly affecting mobility and daily activities.
Understanding the Causes and Triggers of Psoriasis
Although the exact cause remains elusive, researchers widely believe that genetics and environmental factors play pivotal roles. Family history significantly increases the risk, indicating a hereditary component. The immune system's malfunction involves T-cells, which become overactive, leading to inflammation and accelerated skin cell production. Environmental triggers can set off flare-ups, including:
Skin injuries or trauma, such as cuts, scrapes, or sunburn
Psychological stress and emotional strain
Infections, especially streptococcal throat infections
Cold and dry weather conditions
Certain medications, such as beta-blockers and lithium
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
It’s vital to understand that psoriasis is not contagious. It cannot be transferred from one person to another through touch, sharing personal items, or close contact. This knowledge helps reduce stigma and social isolation often faced by sufferers.
Diagnosing Psoriasis: Approach and Techniques
If you notice persistent skin patches, itching, or scaling, seeking medical advice is essential. Self-diagnosis is not recommended because other skin conditions like eczema or fungal infections can mimic psoriasis. A healthcare professional will perform a thorough examination, focusing on common psoriasis sites such as the scalp, elbows, knees, and nails. Reviewing your medical history and family history is also critical in establishing a diagnosis.
In certain cases, a skin biopsy may be required. This involves removing a small sample of skin for microscopic examination, which helps differentiate psoriasis from other dermatological conditions. Accurate diagnosis ensures appropriate treatment planning and management.
Dietary and Lifestyle Strategies for Managing Psoriasis
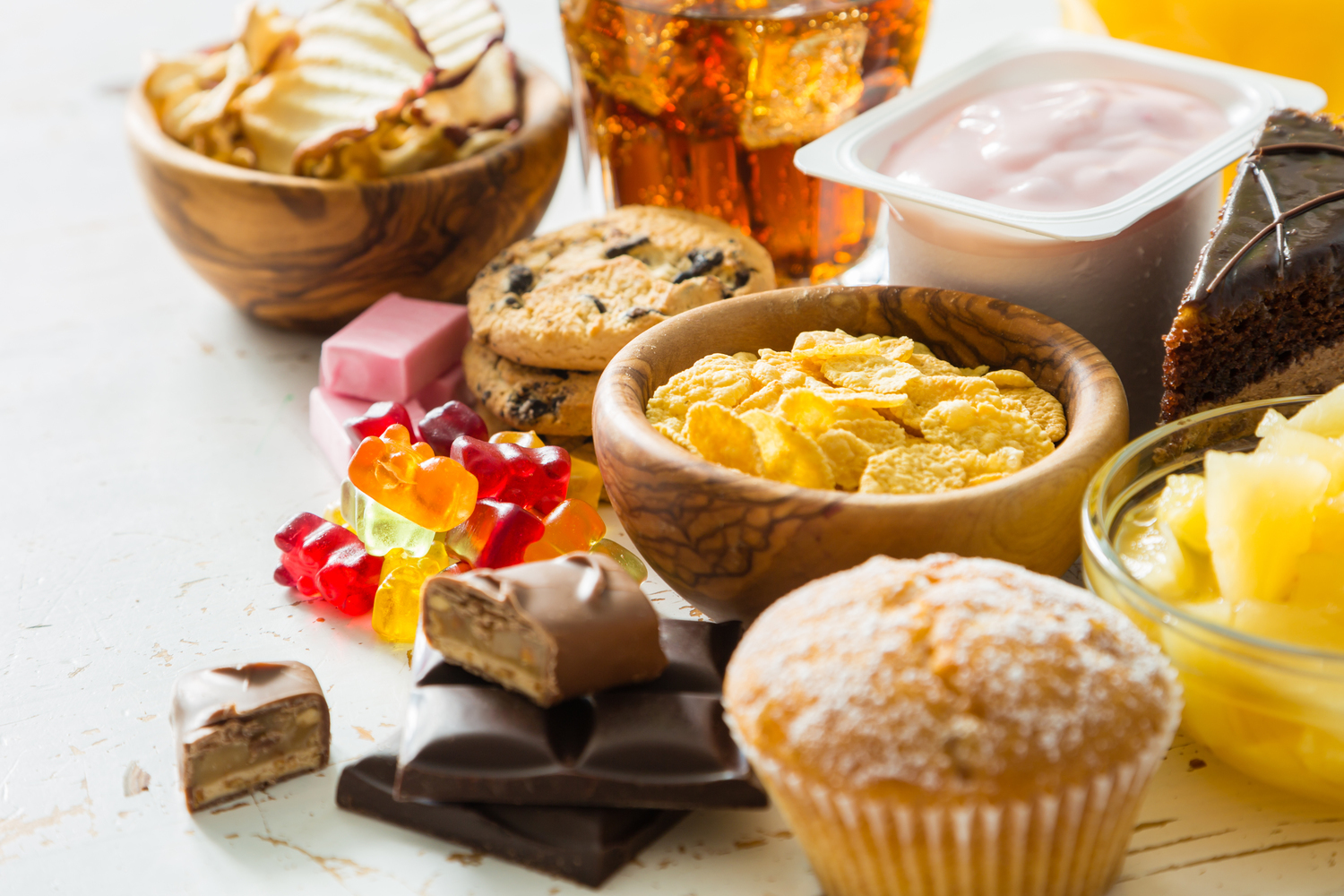
While no specific diet can cure psoriasis, certain nutritional and lifestyle modifications can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Maintaining a healthy weight is particularly beneficial, as obesity is linked to increased psoriasis severity. Consuming a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support overall skin health. Recommended dietary practices include:
Emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
Incorporating foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish like salmon and flaxseeds
Limiting or avoiding processed foods, red meats, dairy products, and foods high in added sugars
Additionally, staying well-hydrated and avoiding alcohol and smoking can positively influence disease management. Adopting a consistent skincare routine, moisturizing regularly, and avoiding harsh soaps also aid in alleviating symptoms.
Stress Management and Psychological Well-being
Psychological stress is a prominent trigger for psoriasis outbreaks. Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation and weaken the immune response. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity have been proven effective in stress reduction.
Seeking support from mental health professionals or joining support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional toll of living with a visible skin disorder. Developing healthy coping mechanisms enhances resilience and improves overall quality of life.
Addressing Emotional and Social Challenges
Psoriasis often impacts psychological health, leading to lowered self-esteem, social withdrawal, anxiety, and depression. Visible skin lesions can cause embarrassment and social stigma. It’s important for affected individuals to recognize these emotional challenges and seek help when needed. Engaging in counseling, joining peer support communities, and practicing self-compassion are critical steps toward emotional well-being.
Building a positive body image, setting realistic expectations, and focusing on self-care can significantly improve mental health. Support from family, friends, and healthcare providers plays an essential role in this process.
Available Treatment Options for Psoriasis
While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, a variety of treatments aim to control symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent flare-ups. The treatment plan depends on the severity, location, and impact on daily life. Common strategies include:
Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams, vitamin D analogs, coal tar preparations, moisturizers, and calcineurin inhibitors are frequently prescribed to alleviate mild to moderate symptoms.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly UVB, can slow down skin cell growth and reduce inflammation. This method requires medical supervision and is effective for widespread psoriasis.
Systemic Medications: For severe cases, healthcare providers may recommend oral or injectable medications like methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin, or biologic agents that target specific immune system pathways.
Emerging Therapies: Advances in biotechnology have led to the development of biologic drugs that precisely target immune system components involved in psoriasis, offering new hope for patients with resistant forms of the disease.
Combining medication with lifestyle modifications, skincare routines, and stress management usually yields the best results. Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals is essential to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.
In conclusion, understanding psoriasis comprehensively—from its symptoms and causes to management strategies—empowers individuals to effectively control their condition. While living with psoriasis can be challenging, adopting an integrated approach with proper medical care and lifestyle changes can significantly improve quality of life and skin health.