Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Health Implications
This detailed guide explores psoriasis, a chronic skin condition, covering its symptoms, causes, triggers, and health risks. Learn about various treatment options, lifestyle adjustments, and recent developments in managing this complex autoimmune disorder to improve quality of life.
Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Health Implications
Psoriasis is a persistent and chronic skin disorder characterized by the abnormal proliferation of skin cells. This rapid cell turnover results in the buildup of dry, scaly patches that are often visible on various parts of the body. Although the exact cause of psoriasis remains somewhat elusive, research indicates that immune system dysfunction plays a pivotal role in its development. Specifically, abnormalities within immune cells such as an imbalance of neutrophils and overactive T-cells contribute significantly to the pathogenesis of the condition. Understanding these immune mechanisms provides insight into why psoriasis manifests and how it can be managed effectively.
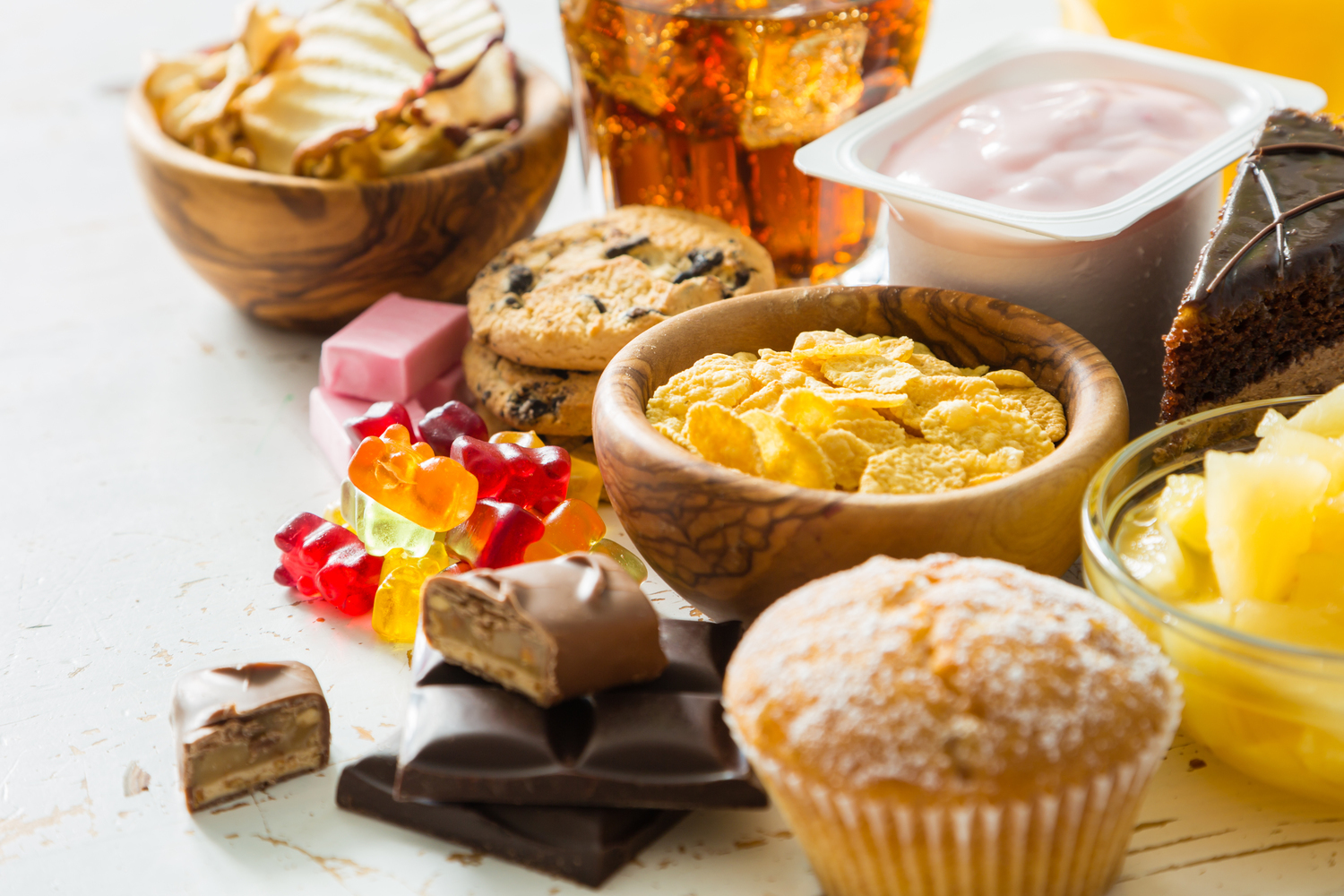
It is widely understood that certain triggers can induce or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. These triggers include physical skin injuries like cuts or sunburns, infections, ongoing stress, lifestyle choices such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, vitamin D deficiency, and the use of specific medications. Additionally, a family history of psoriasis or other autoimmune diseases increases an individual’s risk of developing the condition. Environmental and genetic factors interweave, making psoriasis a complex disorder with multifactorial origins.
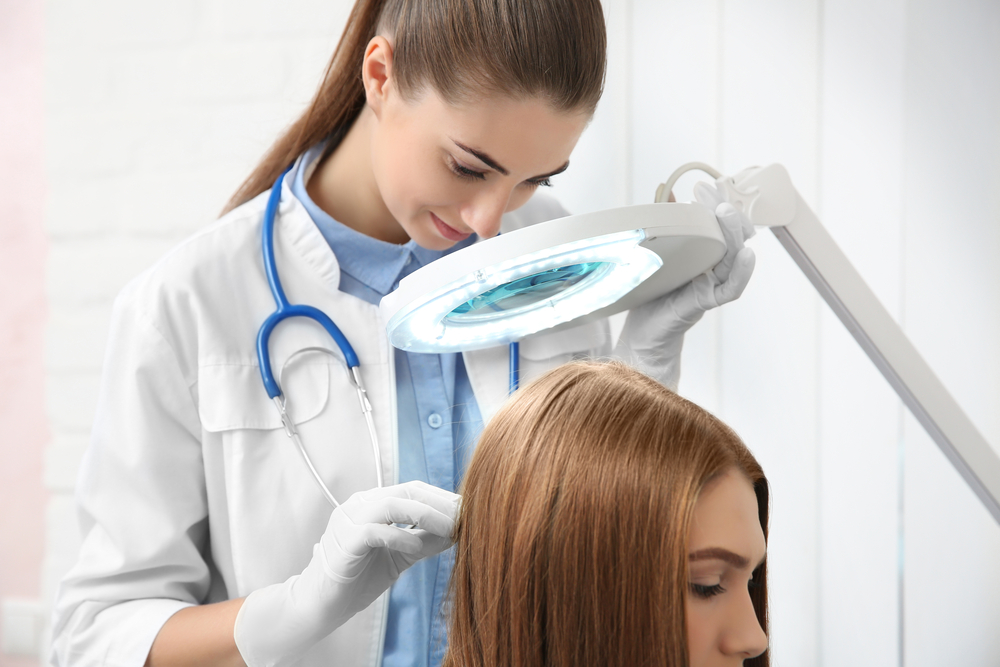
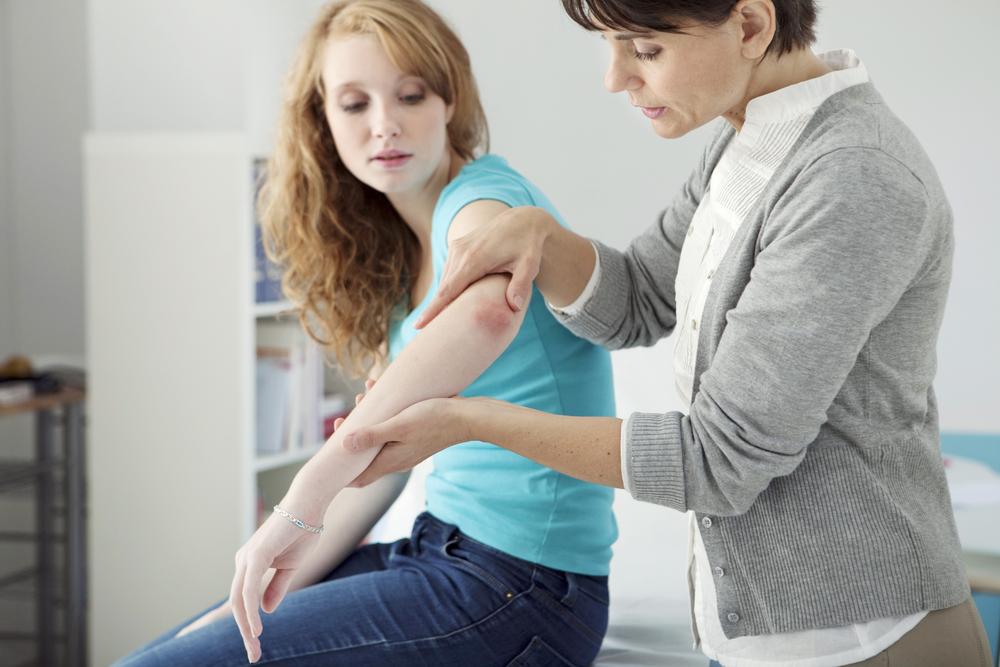
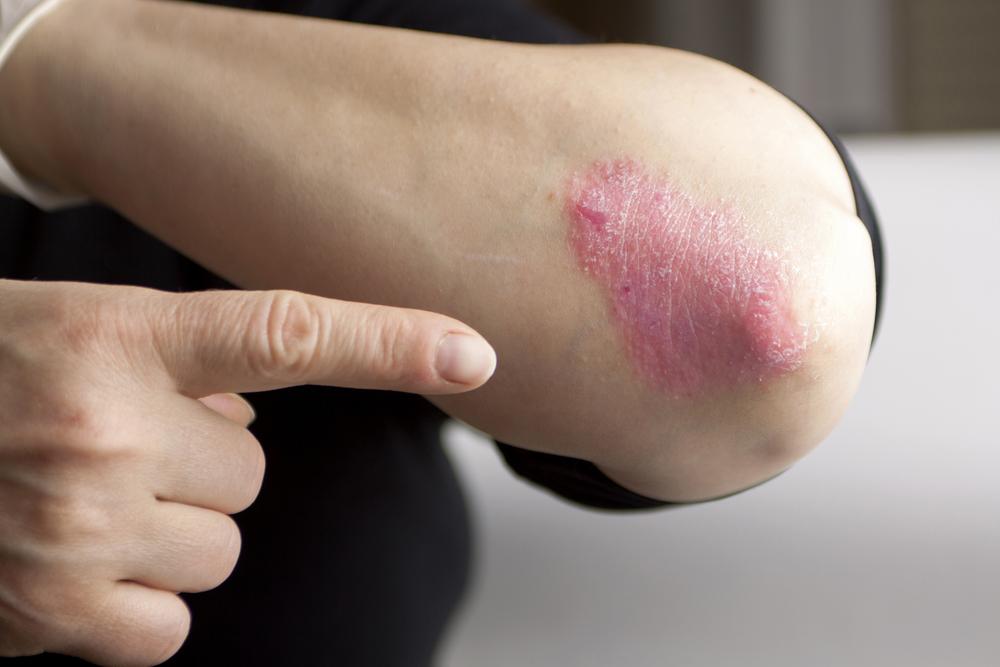
Clinically, psoriasis often presents as dry, raised, and inflamed skin lesions covered with a silvery or white scale. These lesions can vary in size and severity, depending on the type of psoriasis and individual factors. One common form, plaque psoriasis, can appear anywhere on the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Apart from skin involvement, psoriasis may also impact joints, leading to psoriatic arthritis, a condition characterized by joint pain and stiffness.
Beyond the visible skin symptoms, psoriasis can influence overall health and quality of life. Emotional distress, including anxiety and depression, is frequently associated with the condition due to its chronic and visible nature. Moreover, research has linked psoriasis with increased risks of other health issues such as kidney problems, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndrome.
Typical symptoms include skin inflammation, redness, swelling, scaling, and in some cases, nail alterations like pits or ridges. Psoriasis primarily affects adults, with onset commonly occurring between the ages of 18 and 25, although it can develop at any age. The chronic nature of psoriasis requires a comprehensive management approach tailored to each patient’s severity and circumstances.
Management strategies encompass a range of treatments. Topical therapies, including corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and moisturizers, are often first-line options for mild to moderate psoriasis. Phototherapy, involving controlled exposure to ultraviolet light, can help reduce lesions in more extensive cases. Systemic medications, such as biologics and immunosuppressants, are reserved for severe cases due to their potential side effects but are highly effective in controlling symptoms. Lifestyle modifications, including diet adjustments, stress reduction, and avoiding known triggers, play a supportive role in managing the disease.
In recent years, alternative therapies have gained popularity as complementary options for relief. These include herbal remedies, acupuncture, and new biologic agents that specifically target immune pathways involved in psoriasis. Ongoing research continues to shed light on innovative treatments and personalized approaches to improve long-term outcomes for patients.
Understanding psoriasis as a multifaceted condition is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. With advancements in medical research and a broader array of treatment options, individuals living with psoriasis can achieve better skin health and overall well-being.