Comprehensive Guide to Blood Glucose Monitoring and Effective Charting for Better Diabetes Management
This comprehensive guide explores the importance of blood glucose monitoring and charting, emphasizing how tracking levels can significantly improve diabetes management. It covers the mechanisms of blood sugar regulation, the significance of maintaining target ranges, and provides practical advice on tools and lifestyle changes for optimal health. Learning to interpret blood glucose charts enables proactive health management, helping prevent long-term complications and improve overall well-being. Ideal for diabetics and health-conscious individuals alike, this guide offers valuable insights into effective blood sugar control.
Comprehensive Guide to Blood Glucose Monitoring and Effective Charting for Better Diabetes Management
Understanding your blood glucose levels is crucial for maintaining optimal health, especially for individuals managing diabetes or aiming to prevent it. Blood glucose, or blood sugar, indicates the amount of sugar present in your bloodstream at any given moment. This sugar serves as the primary energy source for your body's cells and is derived from the foods you consume daily. Proper regulation of blood glucose is vital to prevent health complications associated with elevated or low blood sugar levels.
Glucose is distinct from other sugars like sucrose or table sugar, which is composed of glucose and fructose. The body closely monitors and manages glucose levels through complex hormonal processes involving insulin and glucagon, ensuring they stay within healthy ranges. Understanding these mechanisms and how to track your blood sugar can empower you to make informed decisions about your diet, lifestyle, and medical care.
Throughout the day, blood glucose levels fluctuate naturally. They tend to be lowest before breakfast, rise after meals as the body absorbs sugars from food, and then gradually decrease during fasting periods. For healthy individuals, fasting blood sugar levels should typically be below 99 mg/dl. People with diabetes often experience greater variability, which makes regular monitoring essential to manage their condition effectively.
During blood sugar management, target ranges are established. The goal for most diabetics is to keep pre-meal (fasting) blood glucose levels below 130 mg/dl and post-meal levels under 180 mg/dl. Maintaining these levels helps prevent long-term complications such as nerve damage, kidney issues, vision loss, and cardiovascular problems.
What Is a Blood Glucose Chart?
A blood glucose chart is a structured document or digital record that tracks your blood sugar levels over days, weeks, and months. This chart is an invaluable tool in managing diabetes, providing visual insights into how different factors influence blood sugar. Regularly updating this chart allows individuals to recognize patterns, identify triggers for spikes or dips, and assess the effectiveness of their treatment plans.
By recording fasting levels, pre- and post-meal readings, and nighttime measurements, you can get a comprehensive view of your glycemic control. Insights gained from these charts assist healthcare providers in tailoring treatments, adjusting medications, and advising on dietary and lifestyle modifications to optimize health outcomes.
Why Is Tracking Blood Glucose Critical?
Monitoring blood glucose levels is as essential as keeping an eye on blood pressure or cholesterol. For healthy individuals, regular tracking helps maintain balance and prevent the development of diabetes. For diabetics, it is fundamental in preventing acute issues like hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and in avoiding long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, or retinopathy.
Consistent tracking offers early warnings of potential health issues, allowing for timely intervention. This ongoing vigilance promotes a better understanding of how lifestyle factors — diet, physical activity, stress, and medication adherence — influence blood sugar levels, empowering individuals to make proactive health decisions.
Tools and Tips for Effective Blood Sugar Monitoring
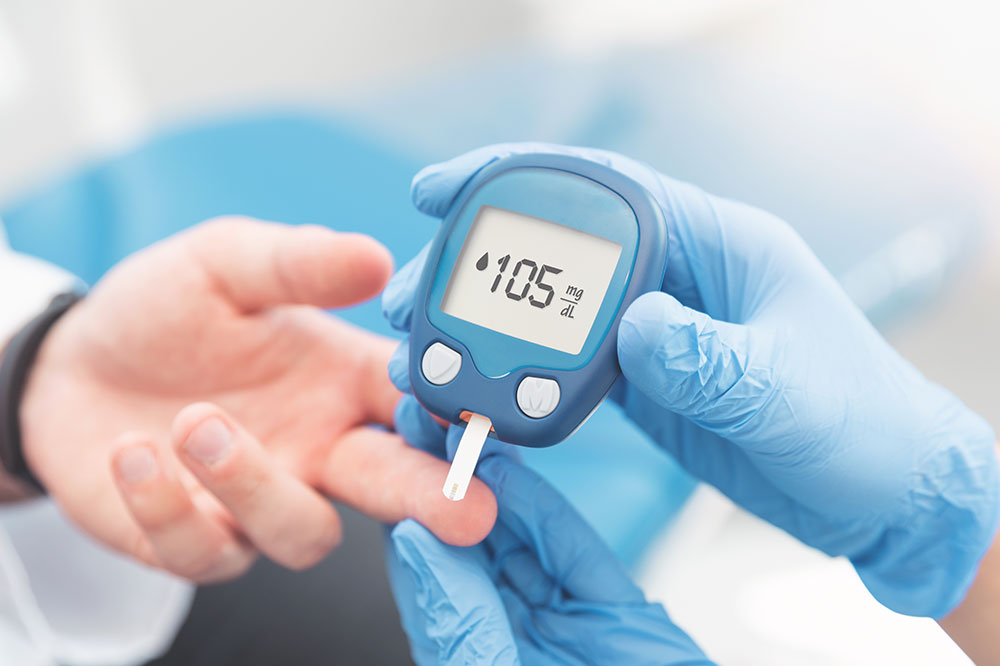
Various methods and devices are available for measuring blood glucose. The most common are glucose meters that require a small blood sample, typically obtained through a finger prick. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems have also gained popularity, providing real-time data and trend analysis without frequent finger pricks. However, it's crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before choosing a device to ensure it's suitable for your needs.
Key measurements to focus on include fasting blood sugar and post-meal levels. For healthy individuals, fasting levels should generally be under 100 mg/dl, and post-meal levels should be less than 140 mg/dl. For diabetics, the targets may vary based on individual circumstances but are often slightly higher.
In addition to measuring devices, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is vital. A balanced diet rich in fiber, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports stable blood sugar levels. Regular exercise, such as walking, jogging, or swimming, improves insulin sensitivity and promotes overall well-being. Adequate sleep, stress management techniques, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption further contribute to optimal glycemic control.
Keeping a detailed record of your blood sugar readings, food intake, physical activity, and medications can help identify patterns and inform your healthcare strategy. Use this data to work collaboratively with your healthcare team to refine your management plan, ultimately leading to fewer health risks and a better quality of life.