Comprehensive Guide to Blood Glucose Monitoring: Importance, Key Components, and Effective Practices
This comprehensive guide covers the importance of blood glucose monitoring, key components of blood sugar control, and best practices for effective management. It emphasizes the significance for both diabetics and health-conscious individuals, providing insights on devices, target ranges, and lifestyle strategies to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Comprehensive Guide to Blood Glucose Monitoring: Importance, Key Components, and Effective Practices
Understanding blood glucose levels is fundamental to managing overall health, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk. Blood glucose, often referred to as blood sugar, indicates the amount of sugar present in your bloodstream at any given moment. This measurement is vital because it reflects how well your body regulates sugar intake from food and how effectively your body utilizes this energy source to fuel cellular functions. Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is essential for overall well-being, preventing complications, and ensuring the body's systems operate smoothly.
The sugar found in your blood is primarily glucose—a simple carbohydrate derived from the digestion of foods rich in carbohydrates, such as bread, rice, pasta, fruits, and sweet treats. Glucose is transported via the bloodstream to various tissues and organs, providing the necessary energy for muscles, brain function, and other vital processes. Understanding the dynamics of blood glucose helps in making informed decisions about diet, lifestyle, and medication if needed.
Blood sugar levels are not static; they naturally fluctuate throughout the day due to various factors such as meals, physical activity, stress, and hormonal changes. Typically, healthy individuals experience low fasting blood sugar levels early in the morning—usually below 99 mg/dl—before breakfast. After consuming a meal, blood glucose levels spike but generally stabilize within a safe range if the body regulates it properly, staying under 130 mg/dl pre-meal and below 180 mg/dl post-meal. For individuals with diabetes, these ranges often become harder to maintain, necessitating careful monitoring to prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, which can lead to severe health complications.
What is a Blood Glucose Chart?
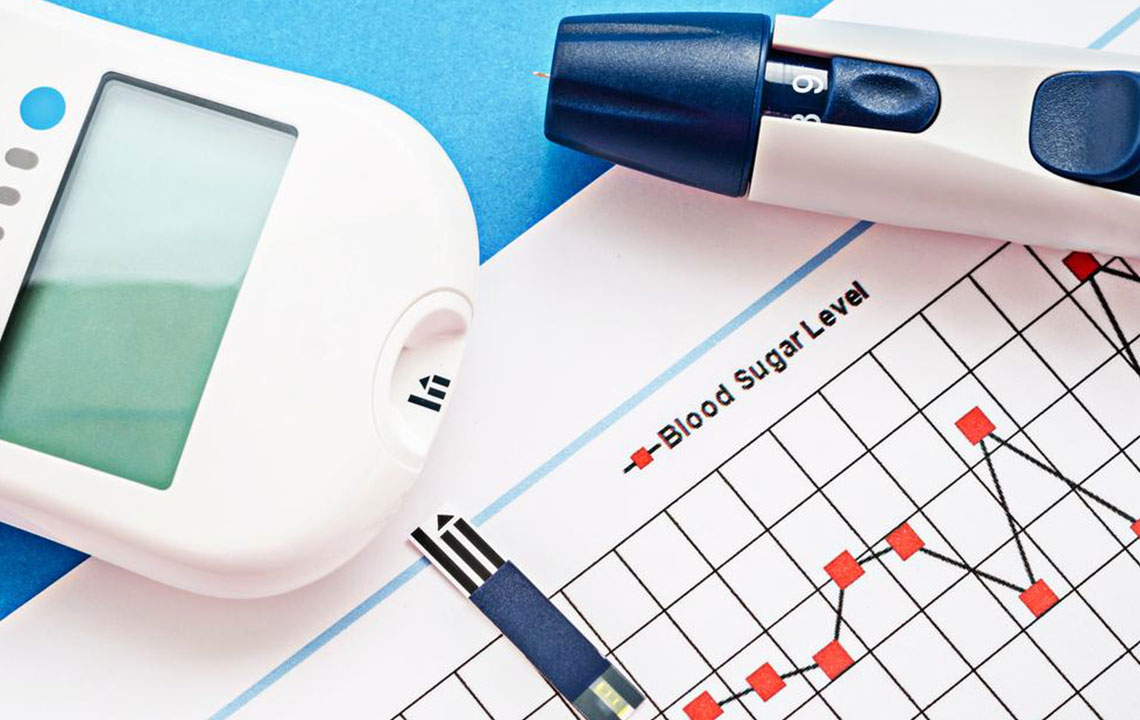
A blood glucose chart or log is a vital tool used to record and track blood sugar levels over time. This simple yet powerful record-keeping method allows individuals and healthcare providers to observe patterns, identify triggers, and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans. Because blood glucose can vary significantly throughout the day, consistent monitoring provides a clearer picture of how lifestyle, diet, medications, and other factors influence blood sugar control.
Having a detailed record of fasting and post-meal blood glucose readings helps to prevent or delay diabetes-related complications, such as kidney damage, vision problems, and cardiovascular issues. Moreover, it empowers patients to take control of their health by understanding how their behaviors impact their blood sugar levels and adjusting their routines accordingly.
Why Is Monitoring Blood Sugar Important?
Monitoring blood glucose levels is similar in significance to tracking blood pressure or cholesterol. It offers a snapshot of your metabolic health and provides early warning signs of potential issues. For diabetics, maintaining blood sugar within targeted ranges is crucial to avoiding long-term damage to vital organs and tissues. Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, and vision loss. Conversely, very low levels—hypoglycemia—can cause dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness.
Regular blood glucose monitoring enables timely adjustments to diet, physical activity, and medications, promoting better glucose control. This proactive approach reduces the risk of acute complications and enhances long-term health outcomes. Moreover, by understanding the relationship between lifestyle factors and blood sugar levels, individuals can adopt healthier habits, such as balanced nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep—factors all pivotal in maintaining stable blood glucose.
Choosing and Using Blood Glucose Monitoring Devices
There is a wide variety of blood glucose monitoring devices available today, ranging from traditional blood glucose meters to continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. These tools are invaluable for managing diabetes effectively but require proper usage and interpretation. Before selecting a device, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable option based on your health status and lifestyle.
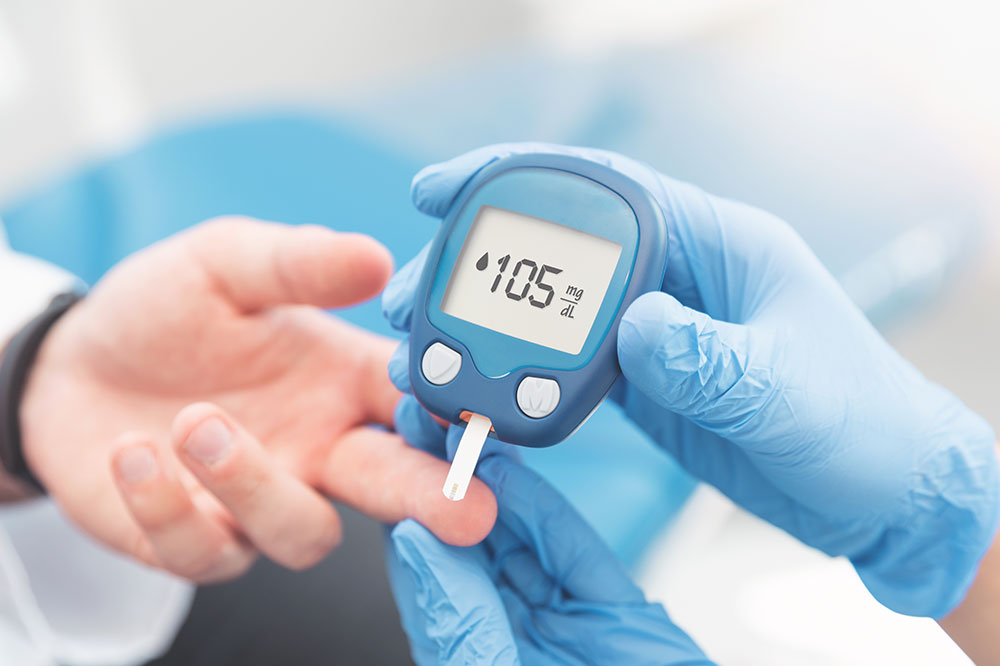
Most glucose meters are straightforward to operate: insert a test strip, prick your finger with a lancet to obtain a small blood sample, and place it on the strip to get a reading. Modern devices often feature LCD displays, memory storage, and even Bluetooth connectivity to sync data with smartphones or computers. For optimal management, diabetics should record fasting blood sugar levels and post-meal readings regularly, comparing these values against target ranges to evaluate treatment effectiveness.
Maintaining blood sugar levels within the normal range—less than 100 mg/dl fasting and below 140 mg/dl after meals—is crucial. Achieving this entails a comprehensive approach including a balanced diet rich in fiber, low in refined sugars, and controlled carbohydrate intake. Regular physical activity, stress reduction techniques, adequate hydration, sleep hygiene, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are all integral to stable blood glucose.
Furthermore, understanding how daily routines influence blood sugar levels helps individuals make proactive adjustments. For instance, engaging in moderate exercise after meals can help lower post-meal spikes. Managing stress through relaxation techniques or mindfulness can prevent cortisol-induced increases in blood sugar. Overall, consistent monitoring combined with lifestyle modifications plays a pivotal role in achieving optimal blood glucose management and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.