Optimal Routine for Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels to Manage Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive guide explains how often individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood glucose levels, tailored to different types of diabetes and treatment plans. It highlights the importance of regular testing, optimal timing, and the use of advanced monitoring devices to ensure effective management and better health outcomes.
Understanding How Often You Should Check Your Blood Sugar Levels
Effective management of diabetes hinges on the regular and accurate monitoring of blood glucose levels. With the advancement of health technologies, patients now benefit from a variety of electronic monitoring devices that make self-testing more convenient and reliable. Developing an appropriate testing schedule is crucial and depends on your specific type of diabetes, your treatment regimen, and individual health needs.
When is the most appropriate time to measure blood glucose?
For individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, it is generally advised to monitor blood glucose levels around 5 to 7 times each day. This includes testing before meals, after meals, during or after physical activity, and at bedtime. This routine helps to understand how different factors like food intake, exercise, and insulin administration influence blood sugar fluctuations throughout the day.
Patients managing type 2 diabetes with insulin therapy should aim to test at least twice daily, often before breakfast and dinner or bedtime. The frequency might be increased or decreased based on their specific medication regimen and overall health condition. Those on oral medications or adopting lifestyle modifications may need less frequent testing, especially if their blood sugar levels are well controlled.
Monitoring schedules can be tailored further depending on the severity of the illness, age, and overall health. For example, pregnant women with gestational diabetes usually follow specialized testing routines, regularly checking blood sugar before and after meals to ensure the safety of both mother and baby. Consistency and timely monitoring are crucial for diabetes management, allowing for better adjustments in treatment and lifestyle to maintain blood glucose within target ranges.
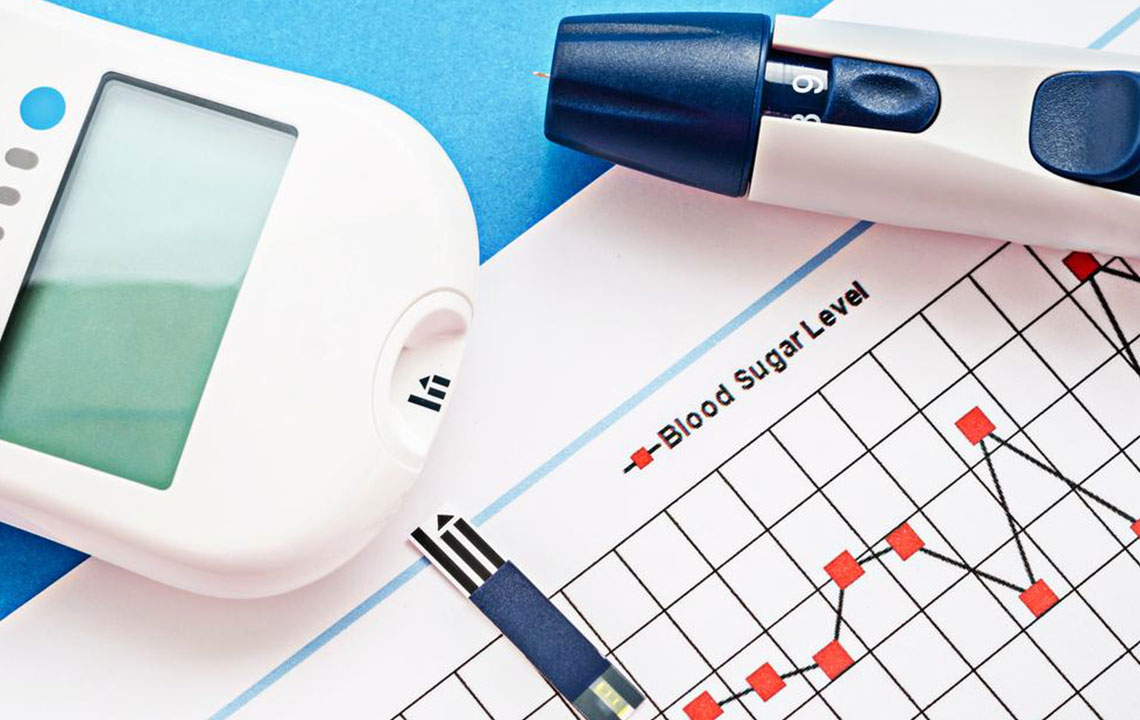
In all cases, consulting with healthcare professionals helps to design an ideal testing plan suited to individual needs, improving disease control and overall quality of life. As continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices become more popular, these allow for real-time tracking and reduce the need for frequent finger pricks. Still, traditional blood testing remains a fundamental element of diabetes management, emphasizing the importance of understanding the most effective and practical testing routines for each patient.