Complete Guide to Blood Glucose Monitoring for Diabetes Management
This comprehensive guide explores blood glucose monitoring, emphasizing its importance, testing methods, optimal timing, and target levels for effective diabetes management. Regular blood sugar testing is vital for preventing complications, adjusting treatments, and understanding individual responses to lifestyle and medication. The article provides practical tips for accurate testing and interpreting results, empowering patients to take control of their health. Tailored recommendations for different types of diabetes ensure personalized management strategies, making this guide an essential resource for diabetics seeking to improve their blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Complete Guide to Blood Glucose Monitoring for Diabetes Management
Keeping track of blood glucose levels is a cornerstone of effective diabetes care. Regular monitoring allows individuals to understand how their body responds to food, physical activity, medication, and other factors that influence blood sugar. This comprehensive guide provides detailed information on how to perform blood glucose testing accurately, interpret results, and utilize this information to optimize health outcomes.
At-home blood sugar testing is straightforward and accessible with the use of modern glucose meters. These compact devices enable individuals to perform quick, reliable tests and maintain tight control over their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Why Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring Matters
Monitoring blood glucose is crucial for people living with diabetes, whether Type 1, Type 2, or gestational diabetes. It serves as a vital feedback mechanism to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment regimens, lifestyle choices, and dietary modifications. Furthermore, frequent testing helps detect sudden changes or dangerous fluctuations in blood sugar—whether spikes or drops—that could threaten health if left unaddressed.
Regular testing also provides valuable insight into how various factors—such as stress, illness, or physical activity—affect blood sugar levels. This understanding empowers patients to make informed decisions about their daily routines and helps prevent acute episodes like hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Consistent blood sugar monitoring enables individuals to assess how well their current treatment plan is working. It allows for timely adjustments to medication or lifestyle, thereby optimizing overall health and preventing long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, or vision problems. Early detection of irregular blood glucose patterns can facilitate prompt medical intervention, potentially saving lives.
Ideal Timing for Blood Glucose Testing
The timing for blood glucose testing is typically personalized and guided by healthcare professionals, based on the type of diabetes and the individual's specific needs. For instance, people with Type 1 diabetes often need to check their blood sugar multiple times daily for precise management. Tests are usually performed before meals (fasting), after meals (postprandial), before bedtime, and sometimes during the night or during episodes of illness or hypoglycemia.
In contrast, those with insulin-dependent Type 2 diabetes might test two to three times daily, often before and after meals, to better understand how insulin and diet influence their blood sugar levels. For individuals managing diabetes through lifestyle and diet alone, routine testing may be less frequent but still essential to maintain good control.
Healthcare providers tailor testing schedules to each patient's condition, ensuring they gather enough data to make effective treatment decisions.
Understanding Target Blood Glucose Levels
Maintaining blood glucose within target ranges is crucial for diabetes management. These ranges vary among individuals based on factors such as age, duration of diabetes, pregnancy status, and presence of other health conditions. Generally, the goals are to keep fasting blood sugar levels between 80 to 130 mg/dL and post-meal levels below 180 mg/dL.
For younger, healthier adults under 60 years old without other illnesses, optimal ranges often fall between 80 and 120 mg/dL. Conversely, older individuals or those with comorbidities like heart, kidney, or lung diseases may have slightly higher target levels—such as 100 to 140 mg/dL—due to increased risks associated with hypoglycemia.
Prolonged deviations from these target ranges can increase the risk of complications. Elevated blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) can lead to nerve, kidney, and eye damage, while low levels (hypoglycemia) can cause fainting, seizures, or even loss of consciousness. Therefore, achieving and maintaining ideal blood glucose levels is fundamental to a comprehensive diabetes management strategy.
Steps to Test Blood Sugar Effectively
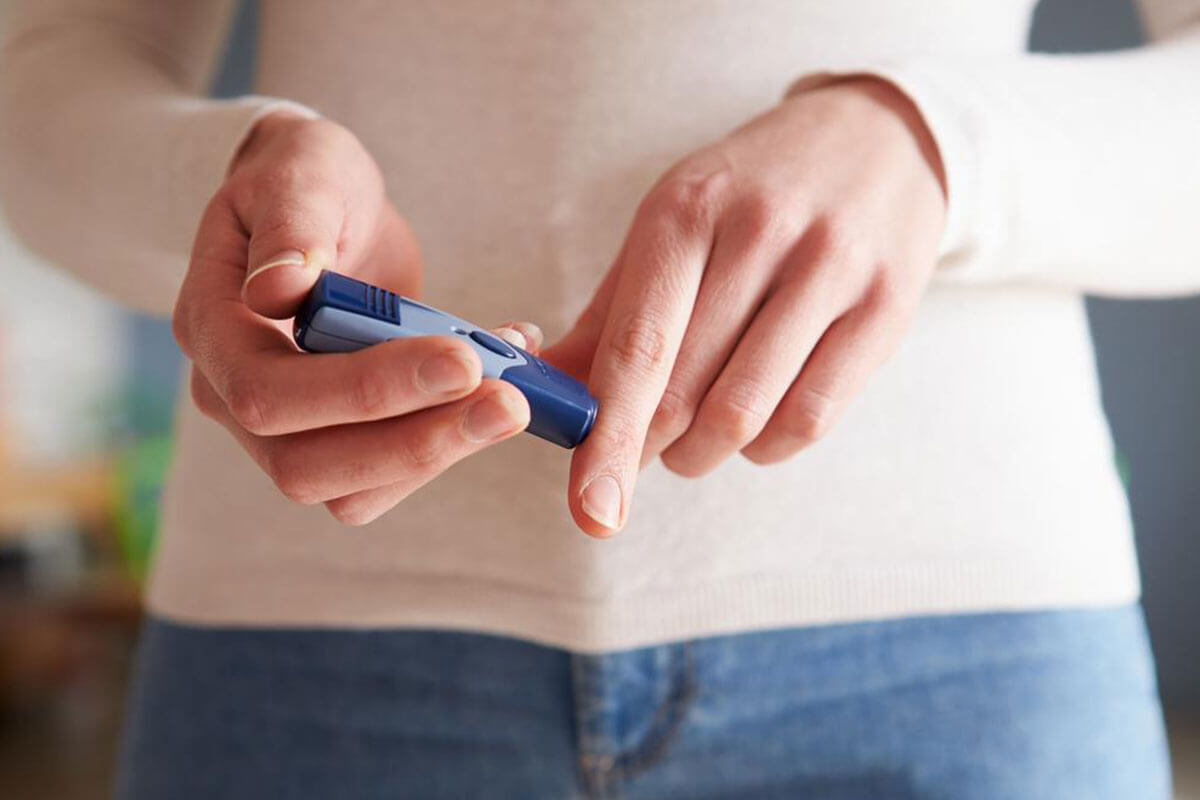
Performing an accurate blood glucose test involves a few straightforward steps. First, wash your hands thoroughly to remove any residues that might affect the reading. Next, prepare your glucose meter and test strip as per the manufacturer's instructions. Prick the side of your fingertip with a sterile lancet to obtain a small blood sample. Apply this blood drop onto the test strip inserted into the glucose meter. Within seconds, the device displays your blood glucose level.
To ensure consistency and accuracy, it's vital to calibrate your glucometer regularly and use the proper testing techniques. Avoid testing immediately after intense physical activity or while experiencing stress, as these can temporarily influence readings. Always record your results, along with the time of day and any relevant notes like medication doses or dietary intake, to share with your healthcare provider.
Consistent testing and accurate measurement are essential for effective diabetes management. By understanding your blood sugar patterns, you can make informed decisions and communicate more effectively with your medical team.
In conclusion, systematic blood glucose monitoring is a cornerstone of successful diabetes care. With proper techniques, regular testing, and specialist guidance, individuals can maintain optimal control over their blood sugar levels, thus safeguarding their health and quality of life.