Comprehensive Guide to Medications for Managing Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive article explores effective medication options for managing type 2 diabetes, including insulin, pioglitazone, and acarbose. It highlights their mechanisms, benefits, side effects, and how they fit into a broader management strategy. Combining medication management with lifestyle changes is essential for optimal control and preventing serious complications of diabetes, ensuring a better quality of life for patients. The guide emphasizes the importance of medical supervision and personalized treatment plans for successful diabetes care.
Comprehensive Guide to Medications for Managing Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels resulting from insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. As one of the most common health conditions worldwide, managing T2DM requires a multifaceted approach that combines lifestyle modifications with pharmaceutical interventions. While adopting a balanced diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are foundational steps, medication management becomes essential when lifestyle changes alone are insufficient to control blood sugar levels.
Understanding the available medication options is crucial for patients to effectively manage their condition and prevent complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision loss. This comprehensive review explores the most effective and commonly prescribed medications for type 2 diabetes, highlighting their mechanisms, benefits, potential side effects, and considerations for use.
Insulin Therapy: The Cornerstone for Advanced Management
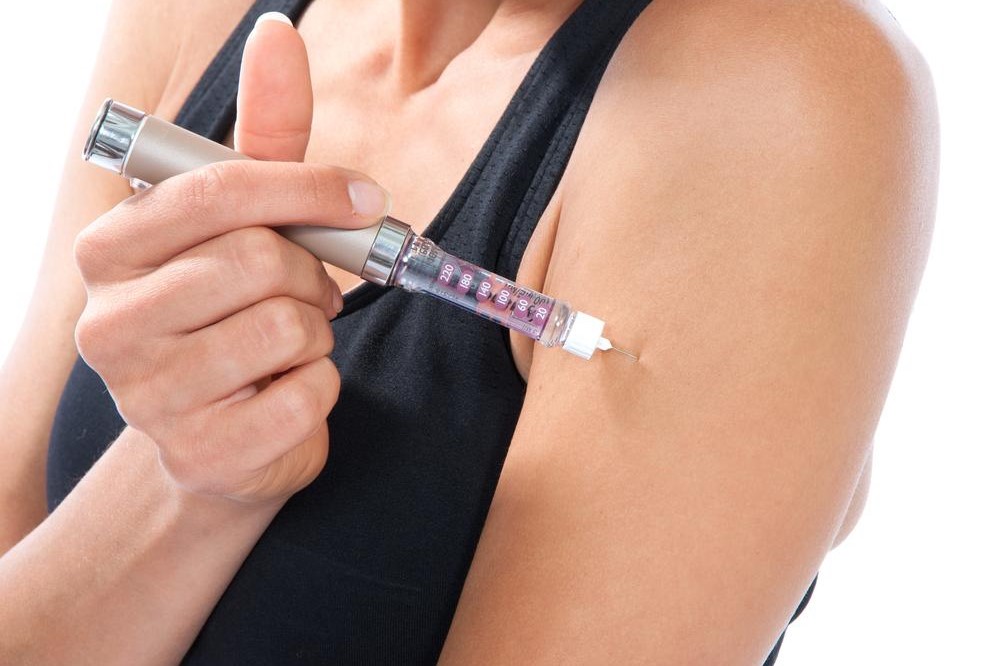
Insulin therapy remains a vital treatment option for many individuals with type 2 diabetes, particularly when oral medications fail to maintain optimal blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone primarily produced by the pancreas that facilitates glucose uptake into cells for energy. In people with T2DM, the body often becomes resistant to insulin's effects, or the pancreas produces insufficient insulin, necessitating supplementation.
Typically administered via subcutaneous injections, insulin therapy can be tailored to meet each patient's needs through various formulations, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulins. Proper administration and dosage adjustments require close monitoring and guidance from healthcare professionals to minimize risks such as hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood sugar) and undesired weight gain.
In some cases, insulin may be combined with other oral medications like metformin to enhance glycemic control. The decision to start insulin treatment involves careful assessment of blood glucose patterns, patient lifestyle, and potential side effects. Continuous monitoring and patient education are essential components of successful insulin therapy, ensuring safety and efficacy over time.
Thiazolidinediones: Boosting Insulin Sensitivity
Pioglitazone, belonging to the thiazolidinedione class of drugs, offers an alternative mechanism to control blood sugar by improving the body's response to insulin. Instead of increasing insulin production, pioglitazone enhances how effectively body cells respond to insulin, thereby reducing blood glucose levels. This medication is often prescribed in conjunction with other anti-diabetic drugs to achieve better glycemic control.
While pioglitazone is effective in managing blood sugar, it carries potential risks. Notably, it can exacerbate heart failure symptoms in susceptible individuals, given its role in fluid retention. Liver function should be regularly monitored during treatment, as there is a risk of liver toxicity. Patients with a history of heart disease or liver problems should consult their healthcare providers thoroughly before initiating pioglitazone therapy.
Common side effects include weight gain and edema. It is important to weigh these risks against the benefits, especially in patients with concurrent cardiovascular risk factors. Adherence to medical advice and regular follow-up appointments are key to safely incorporating pioglitazone into a diabetes management plan.
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: Modulating Carbohydrate Absorption
Acarbose represents a class of medications known as alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, which work by delaying carbohydrate digestion in the gut. This mechanism slows the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream after meals, helping to prevent postprandial blood sugar spikes—an important aspect of comprehensive diabetes management.
Used either alone or in combination with other medicines like metformin or insulin, acarbose can effectively stabilize blood sugar levels after meals. However, its use is often limited by gastrointestinal side effects, which include bloating, gas, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. These adverse effects result from the fermentation of undigested carbohydrates in the gut.
Patients prescribed acarbose should monitor their gastrointestinal symptoms and discuss any persistent issues with their healthcare provider. Starting with lower doses and gradually increasing can help minimize side effects. Proper dietary counseling is also recommended to optimize the effectiveness of acarbose therapy.
Your Comprehensive Management Plan
Effective management of type 2 diabetes involves selecting the right combination of medications tailored to an individual's health status, comorbidities, lifestyle, and response to treatment. Besides pharmacological interventions, lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes, weight management, regular exercise, and blood sugar monitoring are equally important.
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in guiding patients through medication choices, adjusting dosages, and monitoring for adverse effects. Patient education regarding medication administration, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
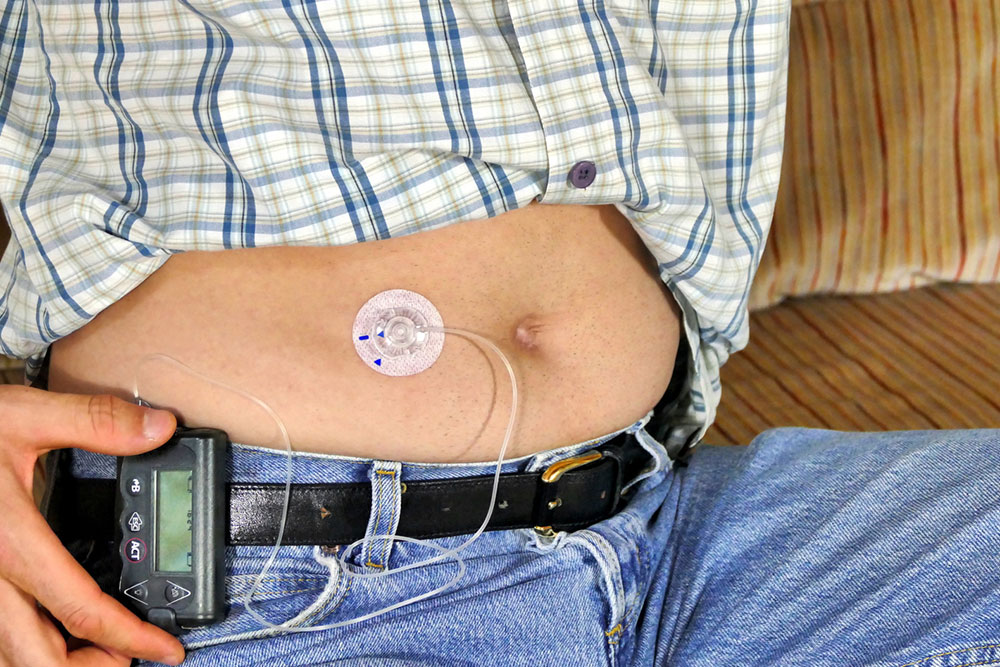
Technological advancements, including continuous glucose monitoring devices and insulin pumps, are revolutionizing diabetes care by providing real-time data that enable more precise management. Future developments in medication research aim to develop drugs with fewer side effects, better efficacy, and improved patient quality of life.
In summary, managing type 2 diabetes effectively requires a comprehensive approach that combines medication therapy with lifestyle modifications. Patients should work closely with their healthcare teams to develop personalized treatment plans, ensuring blood sugar levels are controlled to prevent long-term complications and maintain overall health.