Cutting-Edge Insulin Delivery Technologies to Optimize Type 1 Diabetes Management
Explore advanced insulin delivery systems transforming type 1 diabetes management. Learn how insulin pumps, especially modern tethered and patch types integrated with continuous glucose monitors, are improving blood sugar control and quality of life. Discover the technology behind these devices, their operation, and benefits for personalized treatment, providing a comprehensive guide to the latest innovations in diabetes care.
Cutting-Edge Insulin Delivery Technologies to Optimize Type 1 Diabetes Management
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the body's inability to produce insulin, a vital hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This condition often manifests during childhood or adolescence but can develop at any age in adulthood. Managing type 1 diabetes requires a lifelong commitment to maintaining blood glucose within a healthy range. Advances in medical technology have revolutionized treatment options, with innovative insulin delivery systems playing a crucial role in improving quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
Understanding Insulin Therapy and Its Importance
Insulin therapy remains the cornerstone of managing type 1 diabetes. Since the pancreas no longer produces sufficient insulin, patients rely on external sources to regulate their blood sugar levels. Historically, insulin injections via syringes or pens were the primary method, but today, technological advancements have introduced devices that make insulin administration more efficient, consistent, and unobtrusive. These innovations aim not only to control blood sugar levels effectively but also to reduce the burden and complexity of daily management for patients.
What Are Insulin Pumps?
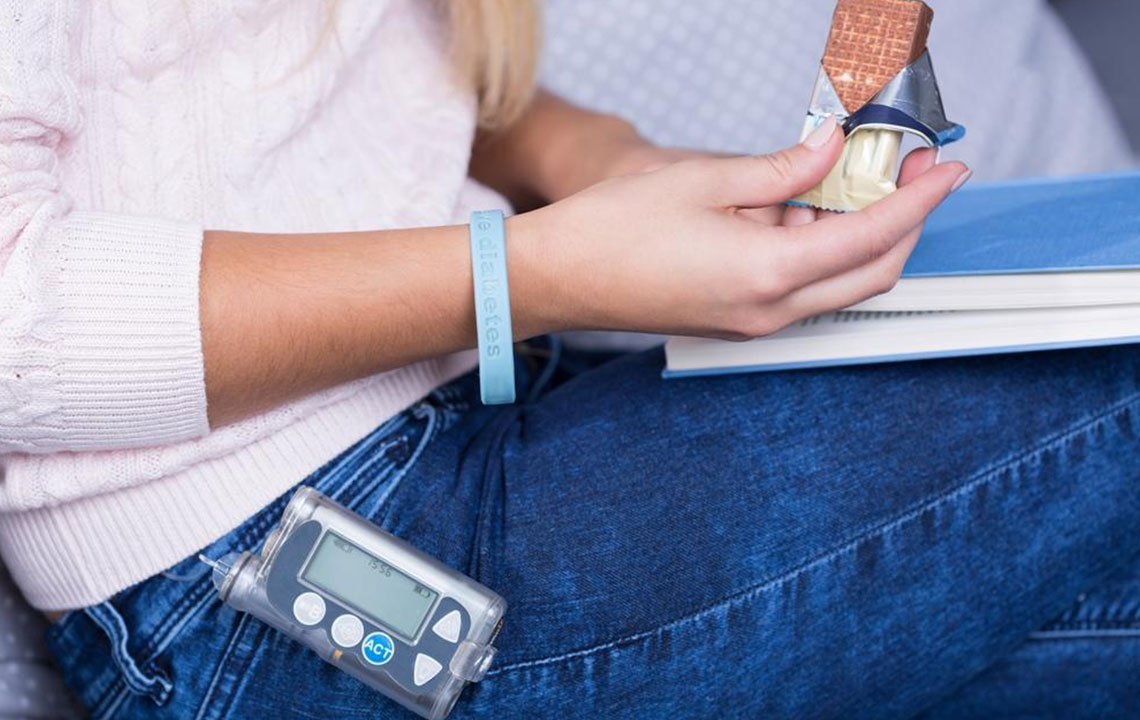
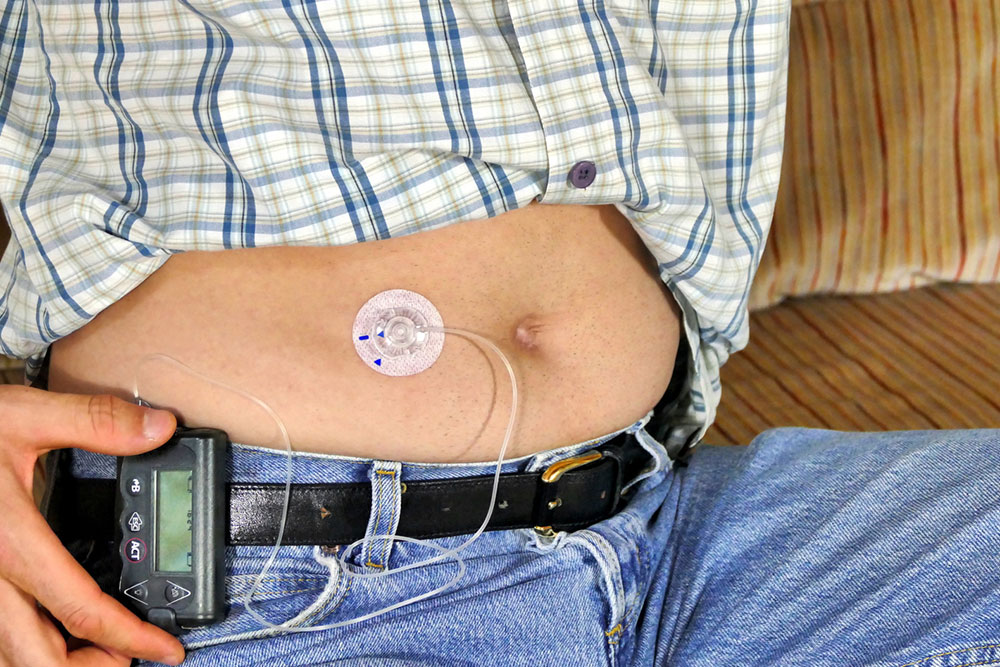
Insulin pumps are advanced, miniature devices designed to deliver precise doses of insulin continuously throughout the day. These wearable gadgets are about the size of a small smartphone or a deck of cards, making them discreet and portable. They mimic the natural functioning of the pancreas by providing a steady basal infusion of insulin and allowing users to administer additional doses, known as boluses, during meals or when blood sugar levels spike unexpectedly. Insulin pumps have become a pivotal tool in modern diabetes management, offering enhanced control and flexibility.
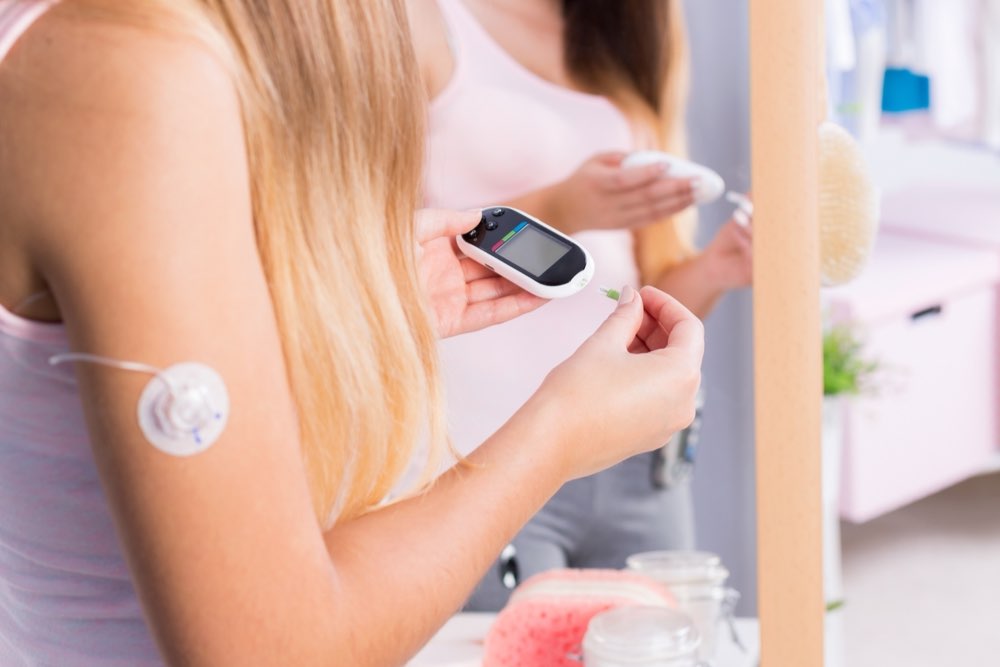
Recent developments incorporate integrated continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology into insulin pumps, enabling automated adjustments of insulin delivery based on real-time blood glucose data. This seamless integration enhances user convenience, reduces the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and promotes tighter glucose control, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for users.
How Do Insulin Pumps Work?
Designed to emulate the natural insulin release of the pancreas, modern insulin pumps are programmable devices that deliver both basal and bolus doses. The basal rate is set to provide a continuous background infusion of insulin, tailored to the user’s needs based on time of day, activity level, and metabolic response. Users can manually adjust basal rates or rely on automated features that adapt to changing conditions. For bolus doses, the user inputs current blood glucose levels and carbohydrate intake, and the pump calculates the precise insulin amount required, streamlining the process and reducing calculation errors.
Some insulin pumps are equipped with algorithms that automatically determine insulin requirements based on CGM data. This closed-loop system, often termed a 'artificial pancreas,' adjusts insulin delivery dynamically, minimizing hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia episodes, thereby offering safer and more efficient diabetes management.
Types of Insulin Pumps: Tethered vs. PatchInsulin pumps mainly fall into two categories according to their design and attachment method: tethered (tubed) pumps and patch (tubeless) pumps. Each type offers unique advantages and drawbacks suited to different user preferences and lifestyles.
Tethered (Tubed) Insulin Pumps
Tethered pumps are the traditional form of insulin delivery devices. They involve a small, battery-operated pump connected to a catheter, which is inserted under the skin via a cannula. The device features a display screen for monitoring insulin levels, adjusting settings, and inputting meal or activity information. The reservoir within the pump typically holds enough insulin to last two to three days before needing a refill. These devices are versatile and customizable, allowing users to fine-tune their insulin doses based on daily routines. During activities like showering, swimming, or exercise, users can disconnect the tubing if their pump is waterproof—a convenience that helps maintain lifestyle flexibility.
Patch (Tubeless) Insulin Pumps
Patch pumps are compact, disposable devices that combine the insulin reservoir and cannula in a single adhesive patch attached directly to the skin. Controlled wirelessly via external devices such as smartphones or dedicated pump controllers, these pumps are highly convenient and eliminate the need for tubing. They are made to be waterproof, allowing users to engage in water activities without disconnecting. Once the insulin reservoir is empty, a new patch can be attached at a different site, providing continuous insulin delivery with minimal disruption. Patch pumps are especially popular among active individuals due to their convenience and ease of use.
Advantages of Contemporary Insulin Delivery Devices
Modern insulin pumps bring a multitude of benefits for individuals managing type 1 diabetes. Firstly, they enable precise, programmable insulin dosing, allowing for personalized adjustments based on daily carbohydrate intake, physical activity, and stress levels. This flexibility significantly enhances metabolic control, reducing complications associated with fluctuating blood sugar levels. The integration of continuous glucose monitoring further elevates these benefits by providing real-time feedback, which supports prompt and accurate insulin adjustments.
Furthermore, insulin pumps improve quality of life by minimizing the discomfort and inconvenience of frequent injections. They empower users with more control over their condition, promoting a more normal lifestyle free from constant needle punctures. The detailed data logs generated by these devices can be easily shared with healthcare professionals to enable better treatment planning and adjustments. As technology advances, features such as remote monitoring, automated insulin adjustments, and improved waterproofing are anticipated to enhance user experience even further.
Ultimately, these advanced insulin delivery systems are transforming the landscape of diabetes management—making it safer, more effective, and more adaptable to individual needs. They are a testament to how technological innovation can significantly improve health outcomes and patient autonomy.