Effective Strategies for Managing Type 1 Diabetes and Maintaining Optimal Health
This article provides detailed strategies for managing type 1 diabetes effectively, emphasizing insulin therapy, balanced diet, regular exercise, lifestyle habits, and preventive health care. It offers practical tips to help individuals control blood sugar levels and maintain overall well-being, minimizing the risk of complications and leading a healthy lifestyle.

Effective Strategies for Managing Type 1 Diabetes and Maintaining Optimal Health
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to a complete or partial deficiency of insulin. Insulin is essential for regulating blood glucose levels, and its absence results in elevated blood sugar levels, which can cause a variety of health complications over time. This condition often manifests in childhood or young adulthood, but it can also develop later in life, affecting individuals regardless of age.
If you have been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, it is important to remember that with proper management and lifestyle adjustments, you can lead a healthy, active, and fulfilling life. The key is understanding the condition and implementing effective strategies that help control blood sugar levels and prevent long-term complications.
Discover comprehensive tips for managing type 1 diabetes effectively. Proper insulin therapy, diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits form the cornerstone of optimal health management for individuals with this condition. Learning how to monitor blood sugar, care for your eyes and feet, and minimize lifestyle risks will help you maintain well-being and prevent complications.
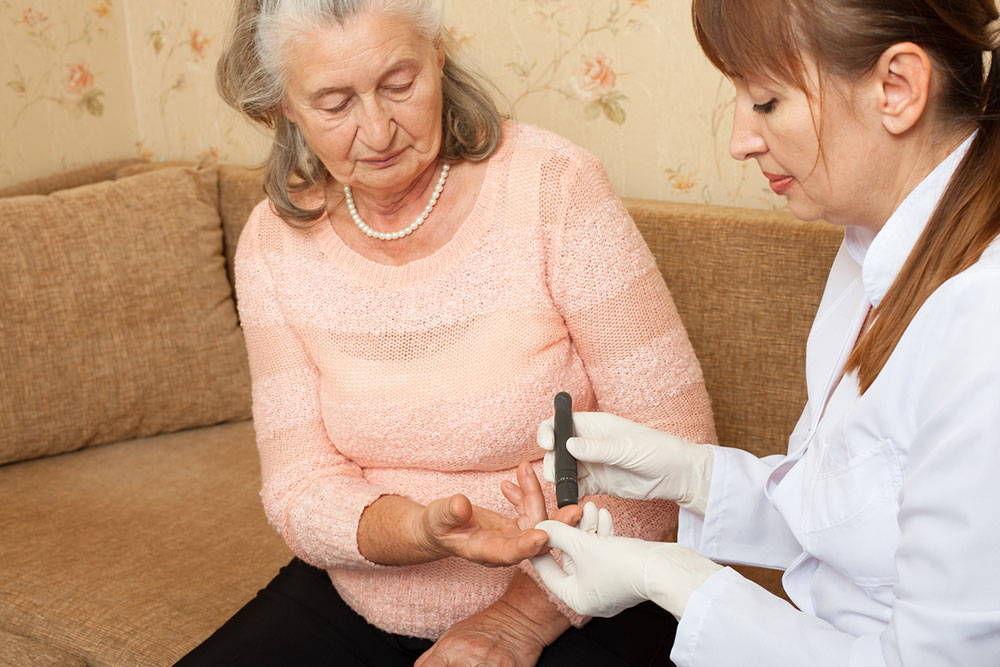
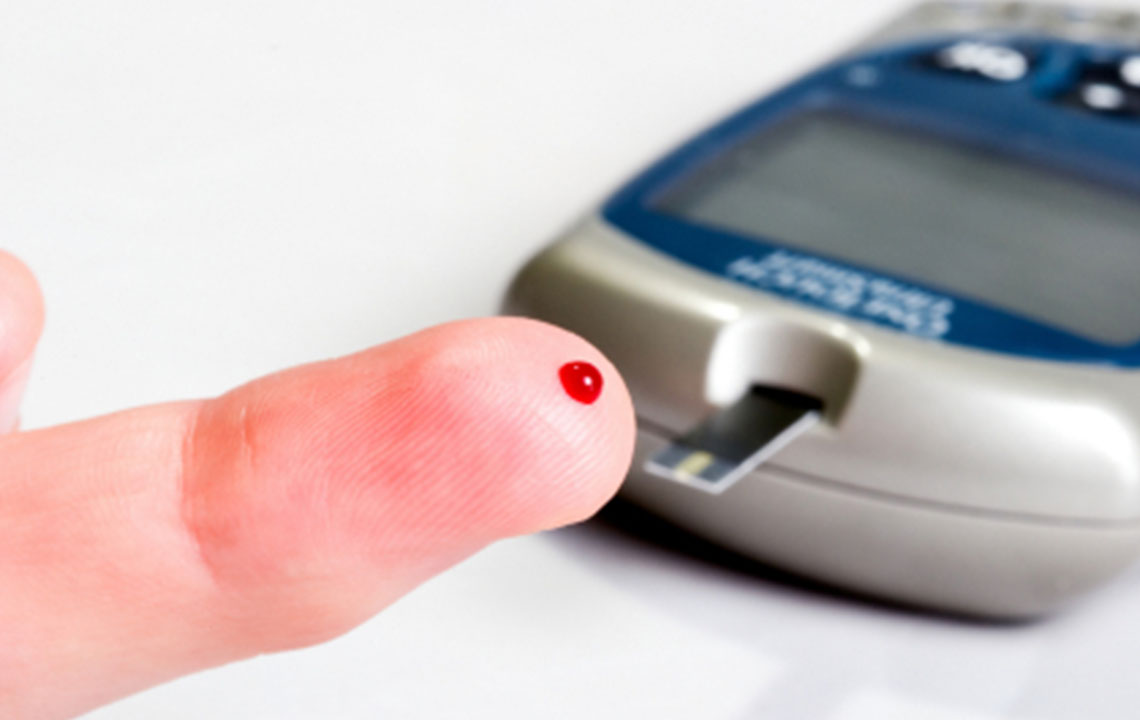
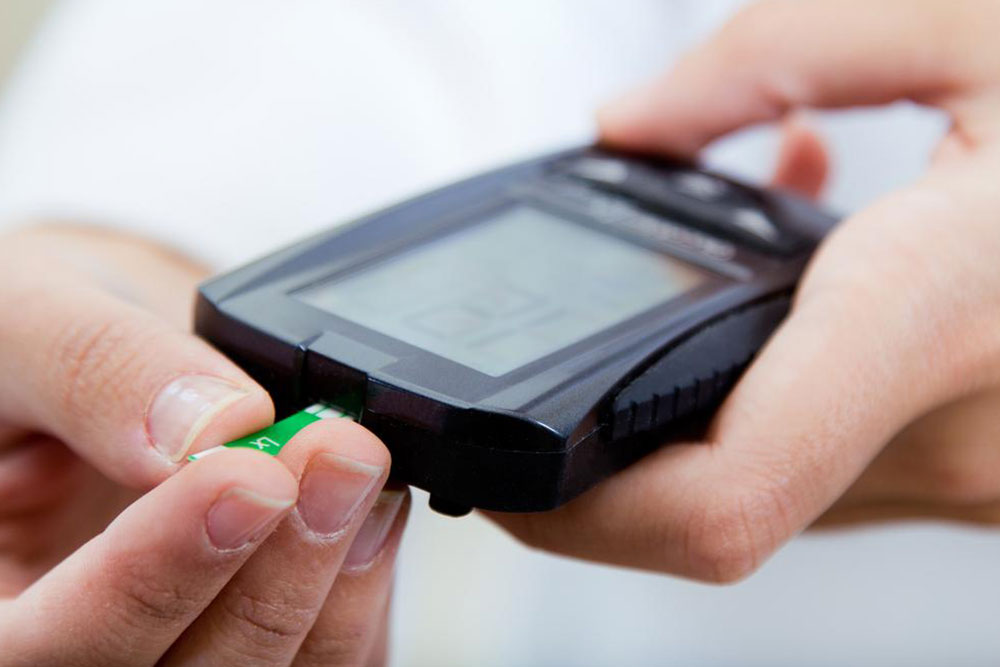
Insulin Therapy and Blood Sugar Monitoring Since individuals with type 1 diabetes cannot produce insulin naturally, daily insulin injections or the use of insulin pumps are essential for survival. Healthcare providers tailor these treatments based on your unique needs, lifestyle, and blood sugar patterns. Regular blood glucose monitoring via glucometers or continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMS) is vital to maintaining stable levels and avoiding both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Keeping detailed records of your blood sugar readings helps your healthcare team optimize your treatment plan. In some cases, additional medications such as medications to manage cholesterol or blood pressure may be prescribed to mitigate associated health risks.
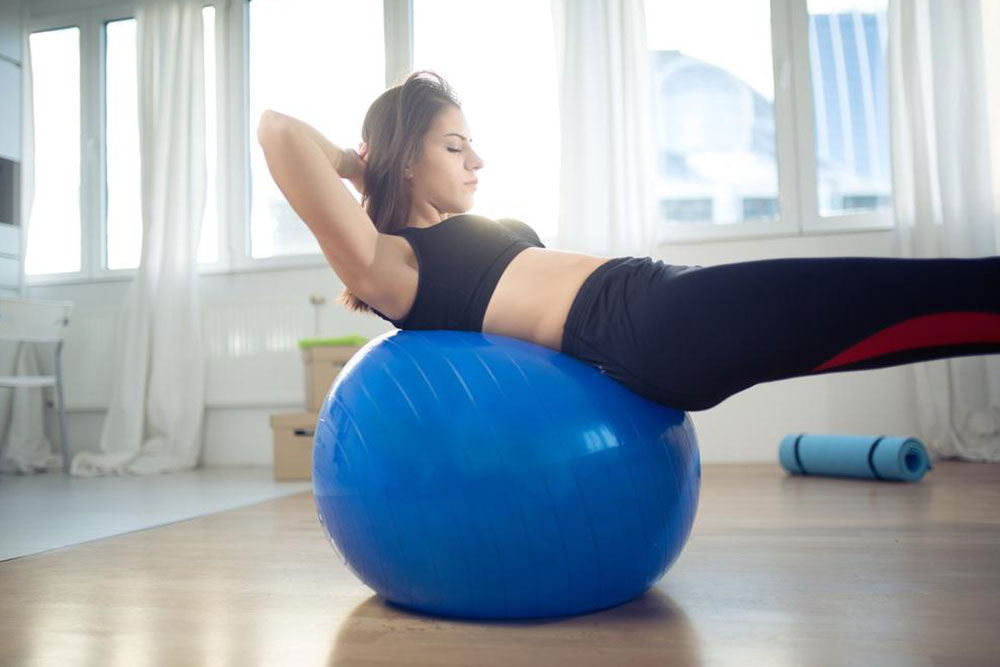
Nutrition and Physical Activity A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in controlling blood glucose. Emphasize nutrient-rich foods like fresh vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods high in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbs, which can cause rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Establishing regular meal times and carbohydrate counting helps maintain consistent glucose levels. Regular physical activity, including 30 to 60 minutes of moderate exercise—such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or jogging—improves insulin sensitivity and aids in blood sugar management. Always coordinate your activity level with your insulin dose and carbohydrate intake to prevent unexpected blood sugar changes.
Adopting a Healthy Lifestyle Your daily habits significantly impact your diabetes management. Quitting smoking reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications, which are more prevalent among people with diabetes. Limiting alcohol intake helps prevent blood sugar spikes and reduces liver strain. Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or engaging hobbies supports emotional stability and reduces cortisol levels, which can affect glucose control. Seeking mental health support when needed and maintaining a positive outlook are important aspects of holistic diabetes care. Staying socially connected and well-rested enhances your resilience and overall health.
Vision and Foot Health Care Diabetes can lead to complications such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, or cataracts, affecting your eyesight. Regular eye examinations with an ophthalmologist are essential for early detection and treatment of eye issues. Foot health is equally crucial because diabetes can cause neuropathy, poor circulation, and ulcers, increasing the risk of infections and amputations. Daily foot inspections, proper footwear, and prompt treatment of cuts or blisters help prevent severe complications. Regular visits to healthcare providers for foot assessments should be a part of your routine to ensure optimal foot health.
In summary, managing type 1 diabetes effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes insulin therapy, blood sugar monitoring, healthy eating, physical activity, lifestyle modifications, and proactive health checks. Education about your condition and working closely with your healthcare team empower you to take control and enjoy a high quality of life despite the chronic nature of diabetes.