Comprehensive Guide to Managing Blood Sugar Levels for Diabetes Patients
This comprehensive guide offers valuable insights into managing blood sugar levels in diabetes. It covers how to measure levels accurately, interpret results, and adopt lifestyle changes to maintain healthy glucose levels. Emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring, record-keeping, and professional support, the article aims to help individuals control their condition and prevent complications. Whether newly diagnosed or managing long-term diabetes, this guide provides essential tips for effective blood sugar management and overall health improvement.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Blood Sugar Levels for Diabetes Patients
Diabetes is a chronic health condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, which, if left unmanaged, can lead to severe health complications. Understanding how to effectively monitor and control blood glucose is essential for individuals living with diabetes or those at risk. This detailed guide provides valuable insights into blood sugar management, including how to measure levels accurately, interpret readings, and adopt lifestyle habits that promote stable blood glucose levels. Maintaining proper blood sugar regulation is crucial to preventing complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
The Growing Global Impact of Diabetes
The worldwide incidence of both type-1 and type-2 diabetes continues to rise alarmingly. According to recent epidemiological data, millions of people across the globe are affected by these conditions, emphasizing the importance of effective blood sugar management strategies. The rise in urbanization, unhealthy diets, sedentary lifestyles, and genetic factors contribute to this trend. As such, understanding blood glucose control is not only a personal health issue but a significant public health concern that requires awareness and intervention at individual and community levels.
Effective blood glucose management begins with understanding your body's specific target ranges. Maintaining a consistent blood sugar chart is essential for tracking your progress over time. Keeping accurate records can help you and your healthcare provider identify patterns, recognize triggers that cause blood sugar spikes, and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
How to Measure Blood Sugar Levels
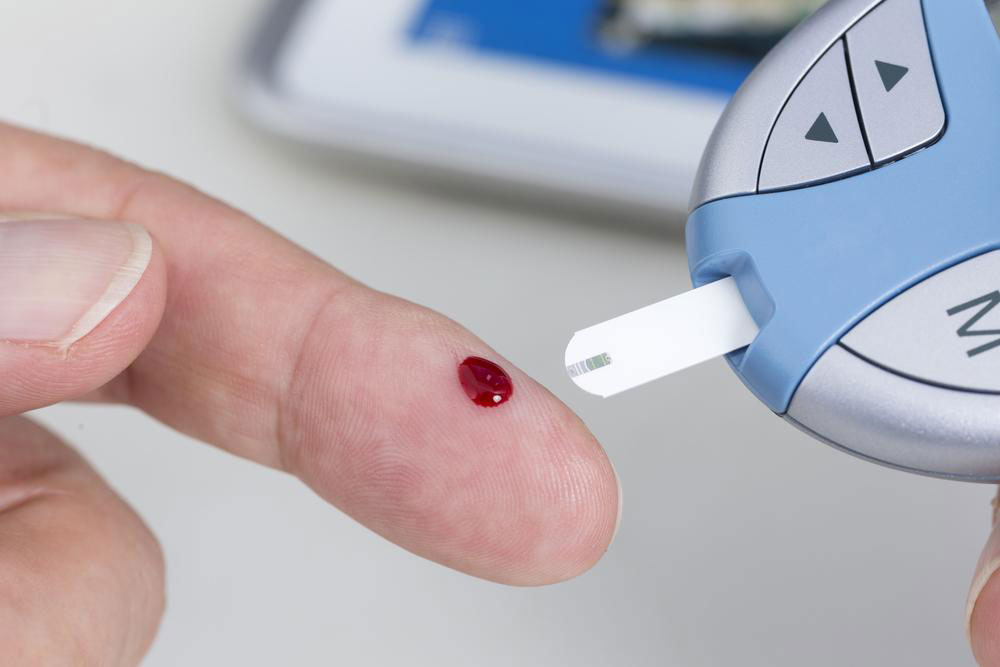
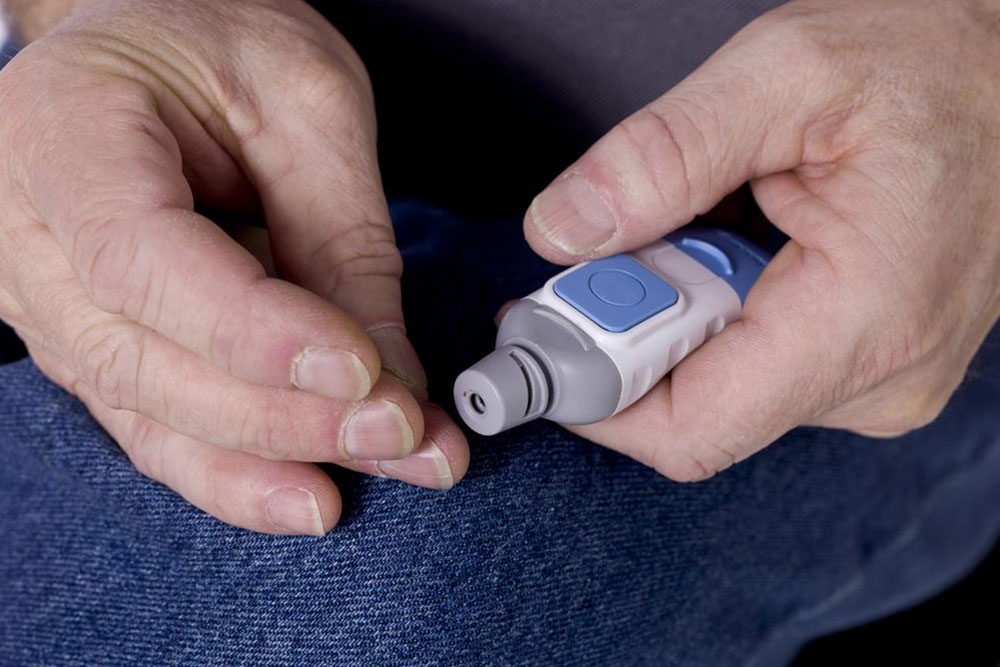
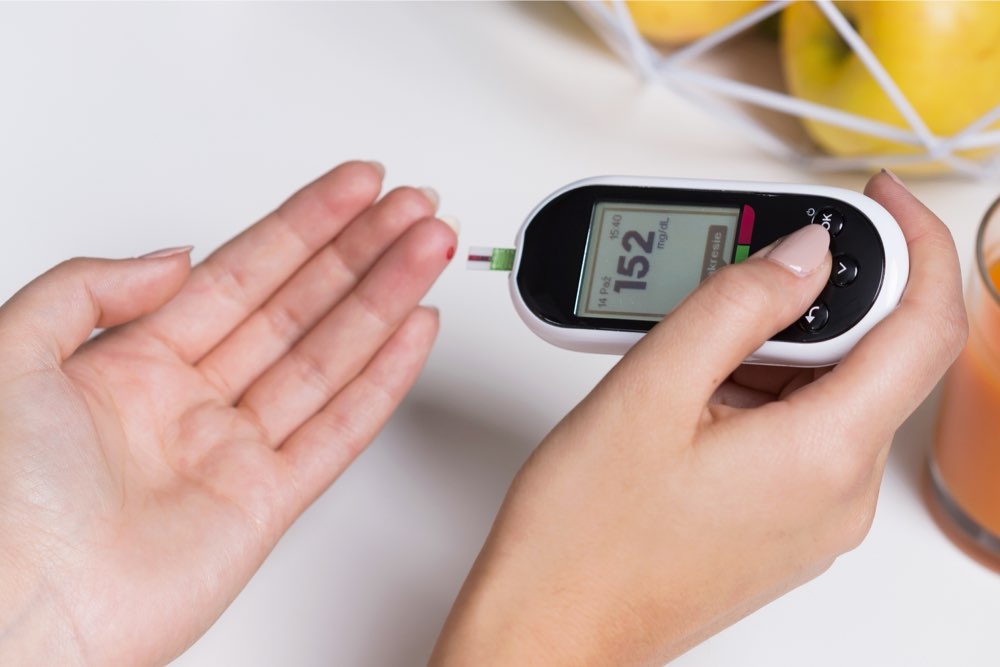
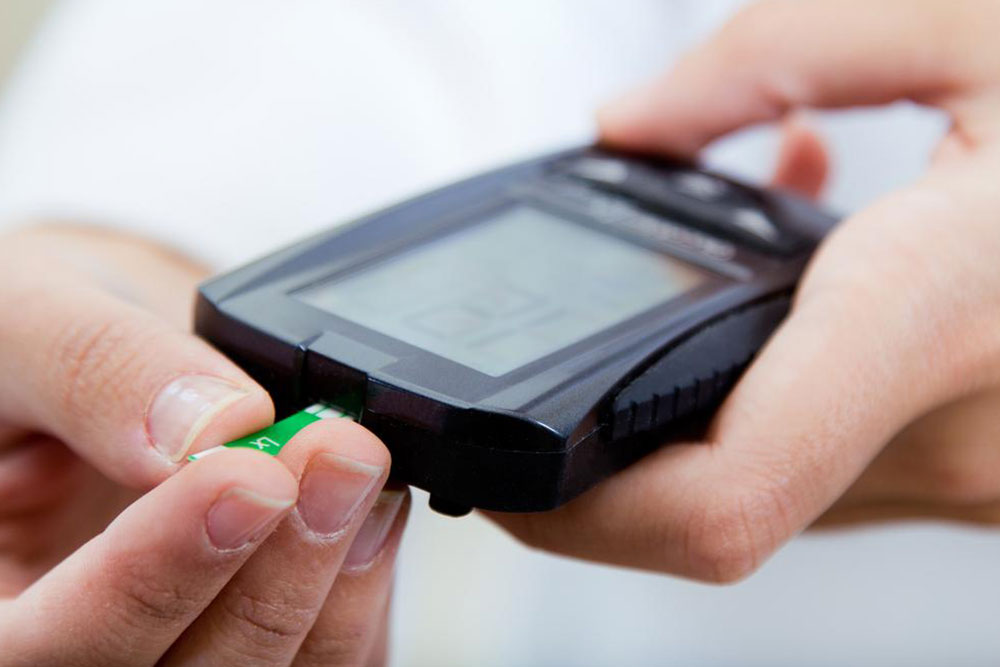
The most common method to monitor blood glucose is through a glucose meter paired with test strips, allowing convenient testing at home or on the go. To use a glucose meter, you prick your fingertip with a lancet, place a small blood sample on the test strip inserted into the device, and obtain a reading within seconds. Regular monitoring provides critical data to manage diet, activity, and medication effectively. It’s advisable to test your blood sugar at specific times daily, including fasting, post-meal, and pre-bed, to get a comprehensive picture of your glucose control.
Where to Obtain Testing Supplies and Support
Many government clinics, hospitals, and community health centers offer free or affordable blood sugar testing kits, making it easier for patients to regularly monitor their levels. Understanding normal blood sugar ranges helps in making informed health decisions. Typically, fasting blood sugar should be below 100 mg/dL. Postprandial (after meals) levels should stay under 180 mg/dL to reduce the risk of complications. For insulin-dependent individuals, target ranges vary slightly: pre-exercise levels should be at least 100 mg/dL, and before bedtime, levels should ideally be between 100 and 140 mg/dL. If your readings consistently fall outside these ranges, consult your healthcare provider promptly for guidance.
Maintaining Detailed Medical and Lifestyle Records
Keeping detailed records of your blood sugar levels, medication schedules, dietary habits, and physical activity helps your healthcare team make better-informed decisions about your treatment plan. This ongoing documentation aids in identifying trends and assessing the effectiveness of your current management strategies, facilitating timely adjustments to medication or lifestyle modifications.
Adopting a Healthy Lifestyle for Better Blood Sugar Control
Lifestyle plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can significantly improve blood sugar stability. Avoiding refined sugar, processed foods, and excessive carbohydrate intake can prevent spikes in blood glucose. Regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or resistance training, enhances insulin sensitivity and helps lower blood sugar levels. Weight management, stress reduction, and adequate sleep are additional lifestyle factors that influence diabetes control. If blood sugar levels remain high despite lifestyle efforts, seeking professional medical advice about medications or natural remedies is essential. Proper management minimizes the risk of long-term health complications, including cardiovascular diseases, kidney damage, nerve issues, and vision impairment.
Consistent blood testing, combined with lifestyle modifications and medical treatments, forms the foundation of effective diabetes management. Educating oneself about the condition, understanding individual health data, and working closely with healthcare providers can empower patients to live healthier, more comfortable lives with diabetes.