Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Blood Sugar Levels for Better Health
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies to maintain healthy blood sugar levels, emphasizing diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management. Practical tips include incorporating whole grains, green tea, hydration, and physical activity into daily routines. Managing blood glucose properly can prevent diabetes complications and enhance overall wellness. Ideal for individuals seeking to improve their metabolic health, this article provides actionable advice grounded in scientific research to promote stable blood sugar levels and a healthier lifestyle.

Strategies to Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels and Prevent Diabetes Complications
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing overall health, particularly for individuals living with diabetes or those at risk. Proper control of blood glucose not only reduces the likelihood of long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney issues but also enhances quality of life through better energy levels and wellbeing.
Understanding how to monitor and regulate blood sugar can empower individuals to take charge of their health. From dietary choices to lifestyle habits, there are multiple effective strategies to keep your blood glucose within a healthy range.
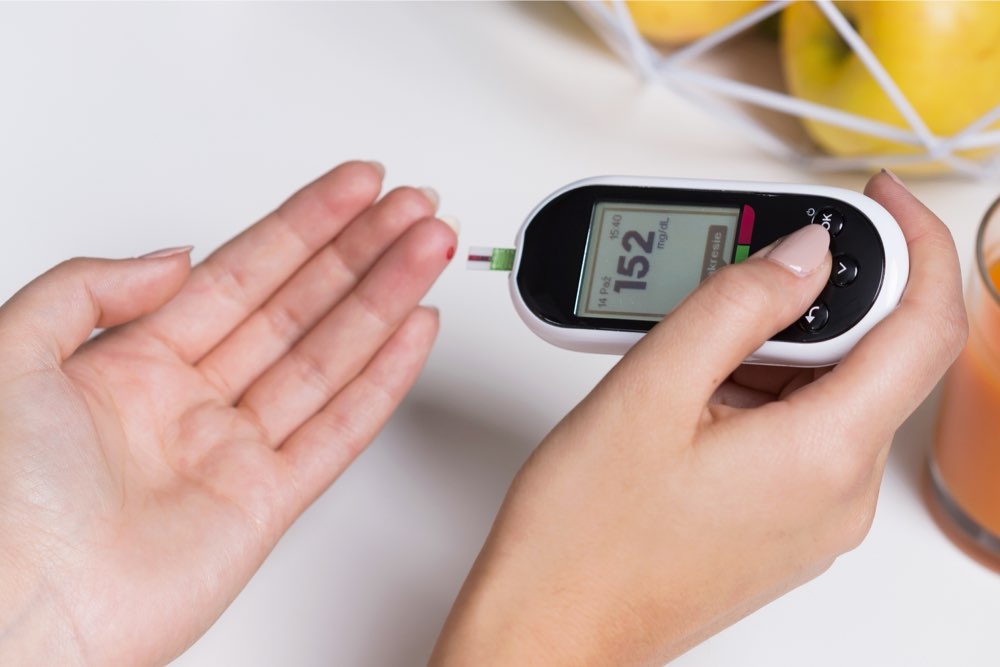
Understanding Normal Blood Sugar Levels
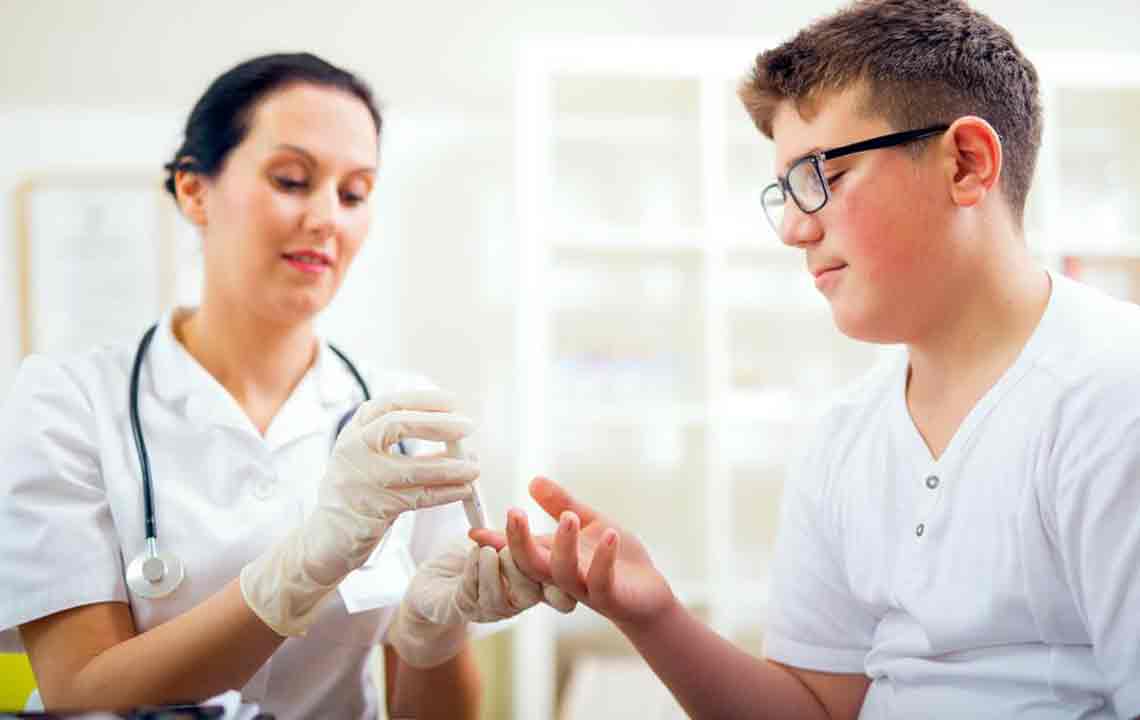
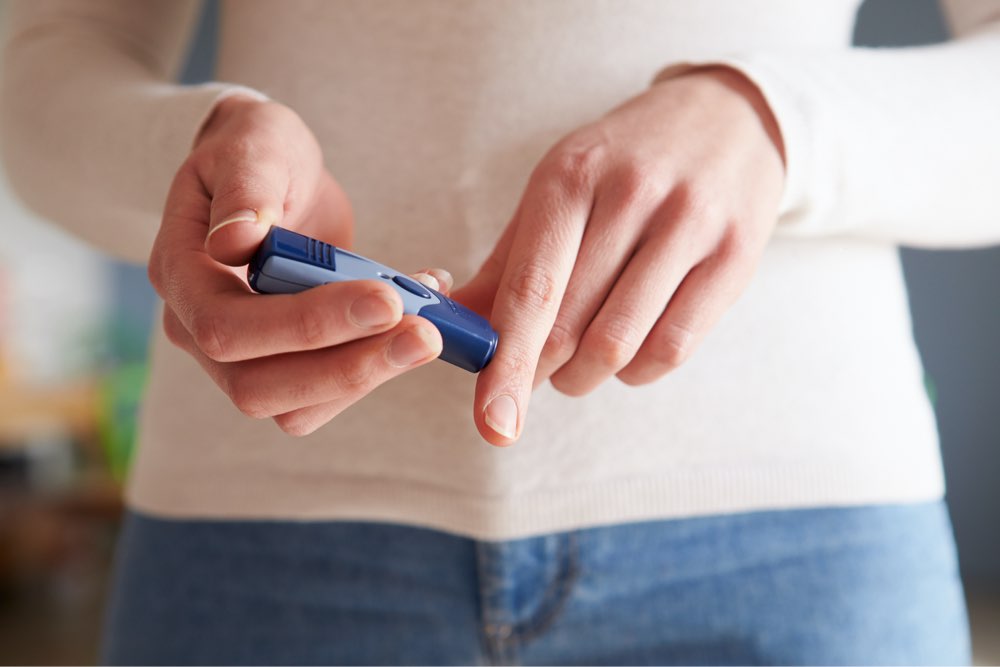
Maintaining awareness of your blood sugar readings is fundamental. Normal fasting blood sugar levels should ideally be between 70 to 130 mg/dL, while post-meal levels should stay below 140 mg/dL. Regular monitoring helps you identify patterns and make informed choices. Using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitoring device can provide real-time data, enabling proactive management.
It is important to understand that individual target ranges may vary based on age, health conditions, and medical advice. Always consult your healthcare professional to determine personalized goals and approaches for managing your blood sugar effectively.
Effective Practical Tips for Blood Glucose Control
Implementing consistent habits can significantly impact your blood sugar stability. Here are some scientifically-backed tips to help you maintain optimal levels:
1. Maintain Regular Meal Patterns
Skipping or delaying meals can cause fluctuations and spikes in blood glucose. Consuming balanced meals at consistent times, especially breakfast, helps regulate liver glucose production and reduces unnecessary surges. Consider portion control and mindful eating to support stable levels throughout the day.
2. Incorporate Whole Grains and Nutrient-Dense Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are essential for energy but need to be chosen wisely. Whole grains like oats, brown rice, quinoa, and minimally processed fruits and vegetables provide fiber that slows sugar absorption and prevents rapid spikes. Avoid refined carbs and sugary snacks which can lead to insulin resistance over time.
3. Regular Consumption of Green Tea
Green tea is renowned for its high antioxidant content, which promotes detoxification and supports metabolic health. Studies suggest that green tea may improve insulin sensitivity, aiding in blood sugar regulation and weight management. Drinking a cup or two daily can be an easy addition to your health routine.
4. Keep Hydrated With Adequate Water Intake
Proper hydration helps kidneys flush out excess glucose and prevents dehydration caused by high blood sugar. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily. Avoid sugary drinks which can exacerbate blood sugar spikes and contribute to weight gain.
5. Use Vinegar Strategically in Your Diet
Adding vinegar, particularly apple cider vinegar, to your meals or drinks can reduce post-meal blood sugar levels by up to 40%. A common practice is to dilute a tablespoon of vinegar in a glass of water and consume it before meals. However, moderation is key, especially for those on insulin or medications, to prevent adverse effects.
6. Prioritize Quality Sleep
Sleep deprivation affects hormone production, including insulin and cortisol, which can lead to increased blood sugar levels. Strive for 7-9 hours of restful sleep per night. Establishing a calming bedtime routine and maintaining consistent sleep schedules support hormonal balance and metabolic health.
7. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Exercise plays a vital role in lowering blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and boosting metabolism. Even light activities like walking, stretching, or cycling for 30 minutes daily can make a crucial difference. Incorporate strength training and aerobic exercises for comprehensive benefits.
8. Include Leafy Green Vegetables in Your Diet
Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, chard, and collard greens are rich in iron, magnesium, and fiber, which support blood health and glucose regulation. Adding these vegetables to your meals enhances nutrient intake and promotes satiety with fewer calories.
9. Flavor Water with Fruits and Herbs
Infusing water with natural flavors like lemon, cucumber, mint, or orange slices can make hydration enjoyable and encourage increased water consumption. These additions also contain antioxidants and vitamins that support overall health and detoxification.
10. Boost Your Dietary Fiber Intake
Dietary fiber, especially soluble fiber, plays a significant role in stabilizing blood sugar levels. Aim for 25-30 grams daily by including foods like beans, lentils, oats, berries, and vegetables. Fiber slows carbohydrate digestion, preventing rapid glucose absorption and reducing insulin spikes.
11. Manage Stress Through Relaxation Techniques
Chronic stress produces cortisol, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. Incorporate stress-reduction practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or hobbies that promote relaxation. Managing stress effectively supports hormonal balance and helps maintain steady glucose levels.
In conclusion, managing blood sugar effectively requires a multifaceted approach combining dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and mindfulness practices. By staying vigilant and adopting these habits, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes complications and improve overall health. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals is essential for personalized guidance and ongoing support.