Proven Methods to Effectively Manage Blood Sugar Levels for Better Health
Discover comprehensive, science-backed strategies for effective blood sugar management. This detailed guide covers dietary choices, exercise routines, lifestyle habits, and regular health monitoring to help individuals with diabetes or prediabetes maintain stable glucose levels. Through consistent, sustainable practices, you can improve your overall health, reduce complications, and enjoy a more balanced, active life. Learn practical tips on nutrition, physical activity, hydration, sleep, and stress management to achieve long-term blood sugar control and enhance your well-being.
Proven Methods to Effectively Manage Blood Sugar Levels for Better Health
Managing blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect for individuals living with diabetes or prediabetes. Proper regulation of glucose in the bloodstream not only helps in preventing immediate symptoms but also reduces the risk of long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision issues. Achieving optimal blood sugar management involves a comprehensive approach that combines dietary choices, physical activity, lifestyle modifications, and regular health monitoring. In this extensive guide, we delve into effective, science-backed strategies to help you keep your blood glucose within a healthy range, enhance your overall well-being, and lead a more active, balanced life.
Proper management of blood sugar isn't about temporary measures; it's about integrating sustainable habits into your daily routine. The key is consistency and making informed decisions that support your body's needs. From nutritional adjustments to exercise routines and sleep hygiene, these strategies are designed to empower you to take control of your health with confidence and clarity.
Maintain Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in consistent exercise is one of the most effective ways to enhance insulin sensitivity — the body's ability to respond to insulin more efficiently. Regular physical activity helps muscles absorb glucose from the bloodstream, reducing blood sugar levels naturally. Incorporate activities like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, dancing, or even yoga into your weekly routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, divided across multiple sessions. Besides controlling blood sugar, regular exercise helps with weight management, boosts cardiovascular health, and improves overall energy levels.
Select Nutrient-Dense, Low-Glycemic Index Foods
Your dietary choices play a pivotal role in blood sugar regulation. Focus on foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins while reducing processed foods high in refined carbs. Opt for whole grains like oats, quinoa, barley, and brown rice instead of refined white flour products. Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) release glucose slowly, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar. Incorporate plenty of vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds into your meals. Small, consistent dietary adjustments can lead to significant improvements over time, making managing your sugar levels more achievable and sustainable.
Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals
Instead of large, infrequent meals, aim for smaller portions spread evenly throughout the day. Eating 4-6 small meals can help maintain steady blood glucose levels by reducing fluctuations. This approach minimizes the risk of hyperglycemia post-meal spikes and prevents hypoglycemia during fasting periods. Consistency in meal timing also helps regulate insulin release and supports your body's natural rhythm. Pair carbs with proteins or healthy fats to slow digestion and stabilize glucose absorption.
Incorporate Barley and Whole Grains Into Your Diet
Barley is renowned for its high dietary fiber content, especially soluble fiber, which helps modulate blood sugar levels and suppresses appetite. Regular consumption of barley has been associated with improved glycemic control and lowered cholesterol levels, contributing to cardiovascular health. Whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice have similar benefits, providing sustained energy release and nutrient-rich profiles. These foods form a vital part of a balanced diet aimed at controlling blood glucose and enhancing overall health.
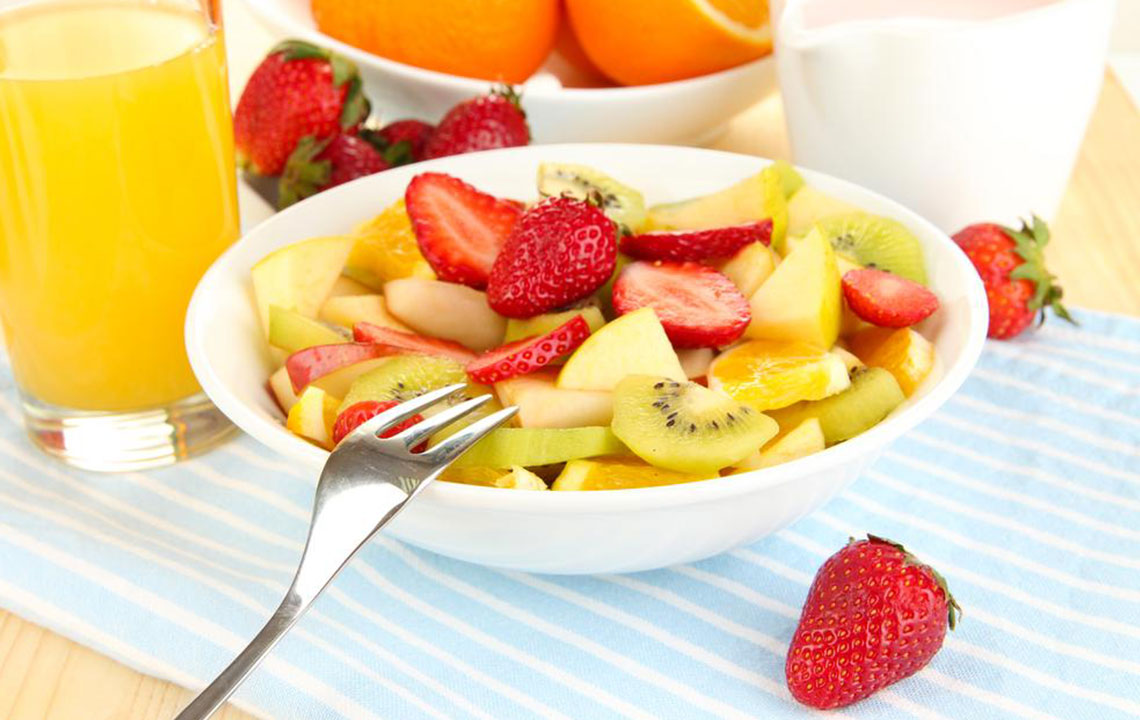
Choose Whole Fruits Over Fruit Juices
Whole fruits are packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a healthier choice for blood sugar management. Fruit juices, even 100% natural ones, often contain concentrated sugars, leading to rapid glucose absorption and spikes in blood sugar levels. Incorporate fruits like berries, apples, pears, and oranges into your diet, and consume them in moderation. The fiber in whole fruits not only aids digestion but also slows down sugar absorption, helping to maintain more stable blood glucose levels.
Ensure Sufficient Vitamin D Levels
Adequate vitamin D is essential for insulin production and sensitivity. Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Sunshine exposure for about 15-20 minutes daily, along with dietary sources like fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and supplements if recommended by your doctor, can help maintain optimal vitamin D levels. Regular monitoring of vitamin D status, especially for people at higher risk, can support better glucose regulation and overall metabolic health.
Control Your Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates are the primary macronutrient that directly impacts blood sugar levels. Managing the quantity and quality of carbs consumed is fundamental. Focus on complex carbs with high fiber content and low GI to prevent sudden glucose surges. Limit intake of sugary snacks, desserts, white bread, and processed foods. Instead, opt for balanced meals incorporating lean proteins and healthy fats to slow carbohydrate digestion and absorption. Proper carbohydrate management helps maintain more consistent blood glucose readings and reduces the risk of complications.
Stay Well-Hydrated
Water is vital for optimal metabolic functions, including blood sugar regulation. Proper hydration supports kidney function, helping to flush excess glucose from your bloodstream through urine. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, or more if you're physically active or in a hot climate. Limit sugary beverages and sodas that can significantly increase your calorie intake and adversely affect blood sugar levels. Adequate hydration is a simple, yet essential, part of their diabetes management toolkit.
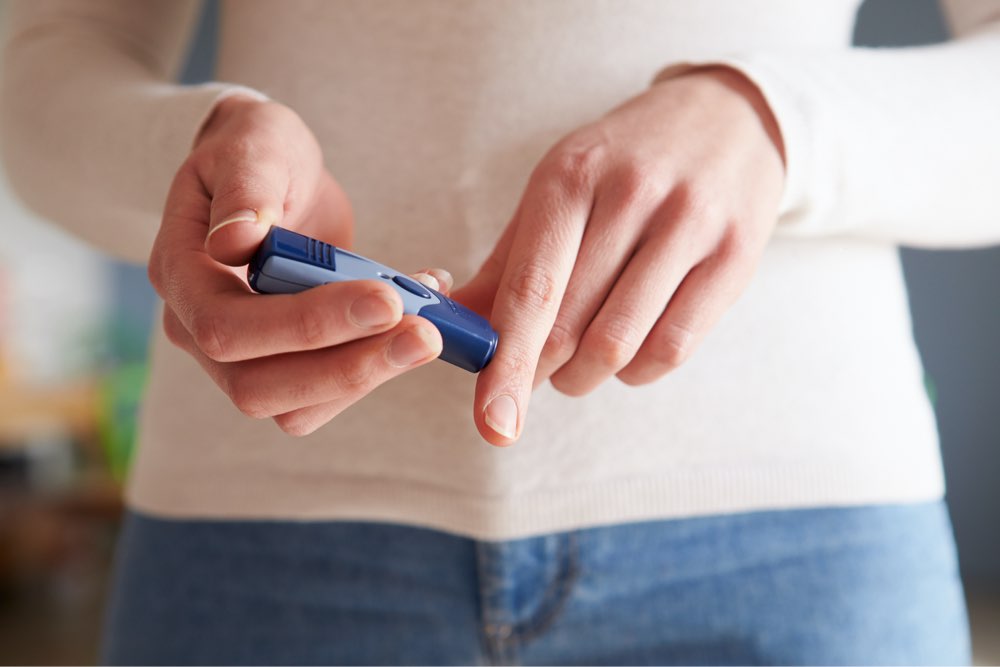
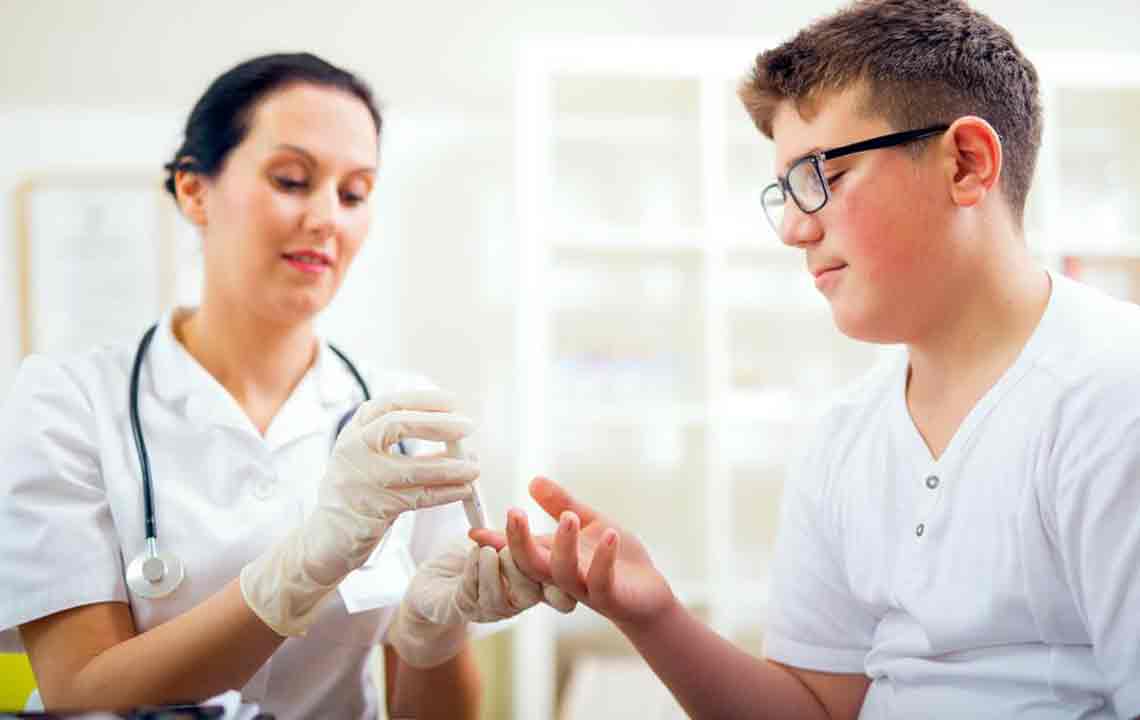
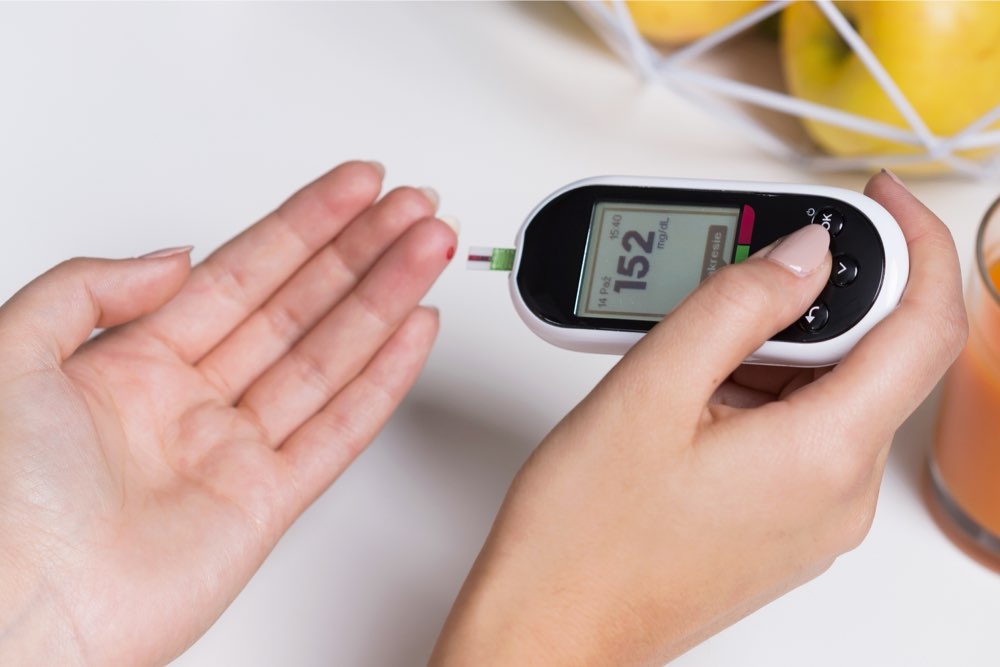
Regularly Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Frequent blood glucose testing provides critical insights into how your body responds to different foods, activities, and lifestyle changes. Keeping track of your levels helps identify patterns and triggers, enabling you to make necessary adjustments. Use a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) if recommended by your healthcare professional. Regular monitoring not only assists in maintaining control but also empowers you to participate actively in your health management and communicate effectively with your medical team.
Prioritize Quality Sleep and Stress Management
Adequate, restful sleep is fundamental to hormonal balance, immune function, and stress reduction—all of which influence blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, establish a regular sleep routine, and create a sleep-friendly environment. Managing stress through mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises can help reduce cortisol levels, a hormone that can raise blood sugar. Both sleep quality and stress management are integral strategies for consistent glucose control and overall health improvement.
Integrating these scientifically supported strategies into your daily routine can lead to significant improvements in blood glucose management. Remember, consistency and patience are crucial—long-term success depends on making gradual but sustainable changes. Regularly consult with healthcare professionals to tailor these recommendations to your specific needs, ensuring you stay on track towards a healthier, more balanced lifestyle. With dedication and the right approach, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is entirely achievable, leading to better health outcomes and an improved quality of life.