Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Chronic Dry Eye Syndrome
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing persistent dry eye syndrome, emphasizing early diagnosis, personalized treatments, and lifestyle modifications. It highlights the importance of professional eye care, various medical options like artificial tears and punctal plugs, and everyday practices to enhance eye comfort. Patients affected by dry eye can find practical advice to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications, leading to improved quality of life. The article aims to educate readers on understanding dry eye disease and adopting holistic approaches for long-term eye health and comfort.
Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Chronic Dry Eye Syndrome
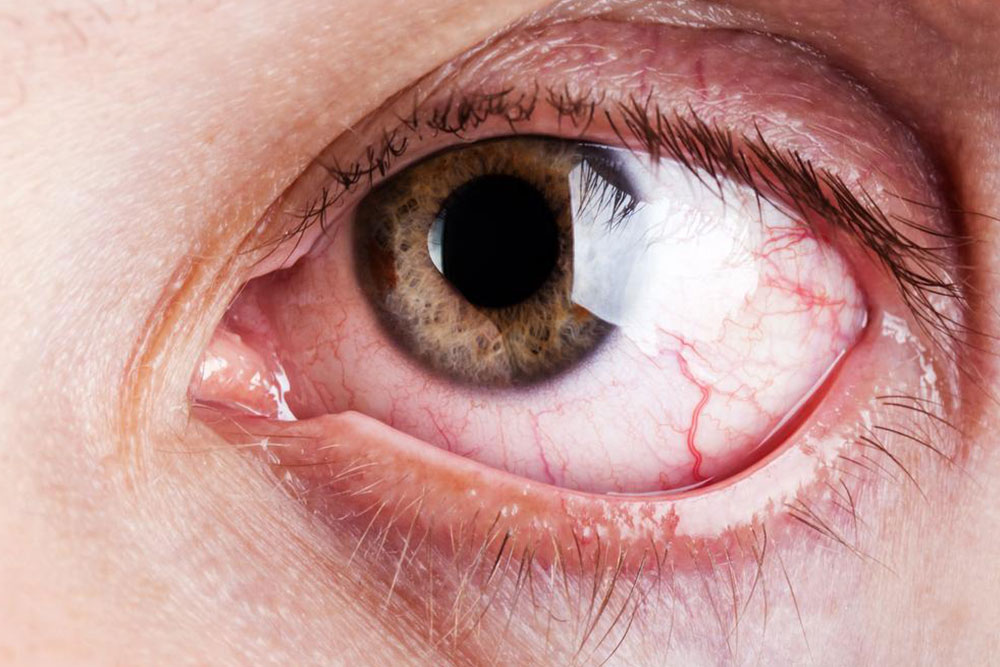
Dry eye syndrome, a prevalent and often persistent ocular condition, affects millions of individuals worldwide, considerably impacting their daily comfort and quality of life. In particular, it is estimated that over five million Americans aged 50 and above suffer from this condition, which can be both frustrating and challenging to manage. Although there is currently no definitive cure that guarantees full restoration of normal tear production, a wide range of effective strategies and treatments are available to alleviate symptoms and improve ocular health for those affected.
Understanding Dry Eye Disease: Dry eye syndrome, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is characterized by inadequate tear production or abnormal tear composition. Tears serve a crucial role in maintaining eye hydration, nourishment, and protection. When the eyes fail to produce enough tears, or when tears evaporate too quickly due to poor quality or composition, symptoms such as irritation, burning, redness, and visual disturbances can develop. The condition often results from an imbalance between tear production and tear film stability, disrupting normal eye function.
Numerous factors contribute to the development of dry eye syndrome, including the natural aging process, prolonged use of contact lenses, environmental exposures such as wind, dry air, or pollution, and underlying health issues like autoimmune diseases or hormonal imbalances. Recognizing these factors is essential in both preventing and managing the condition effectively.
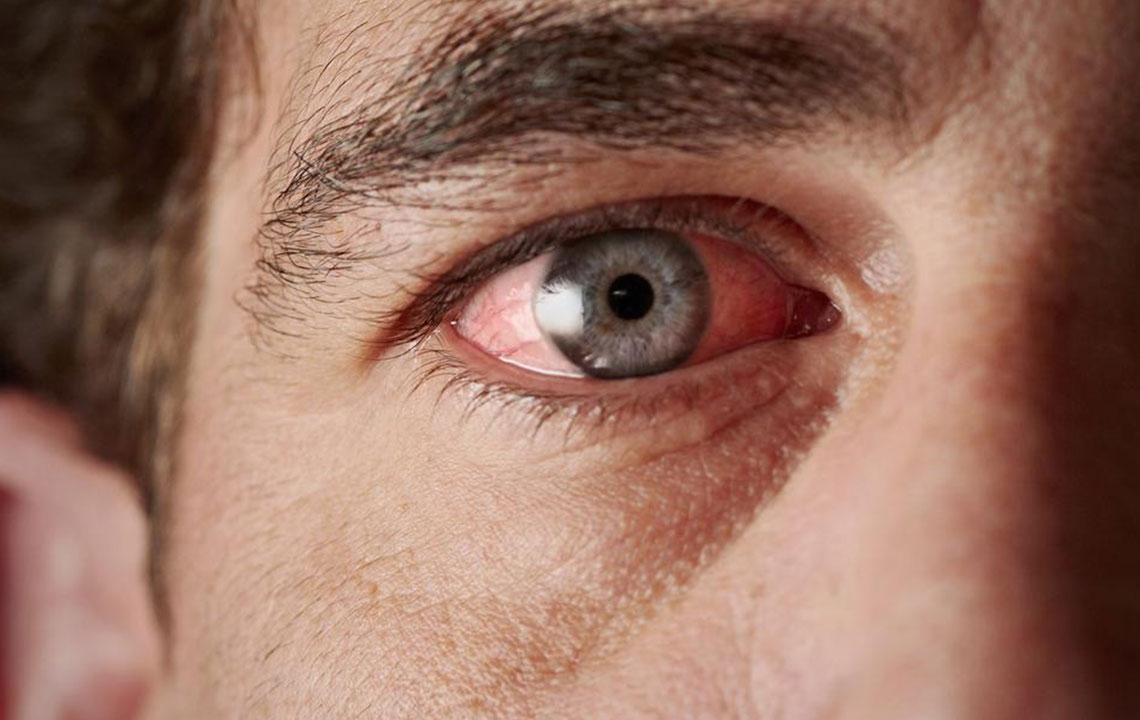
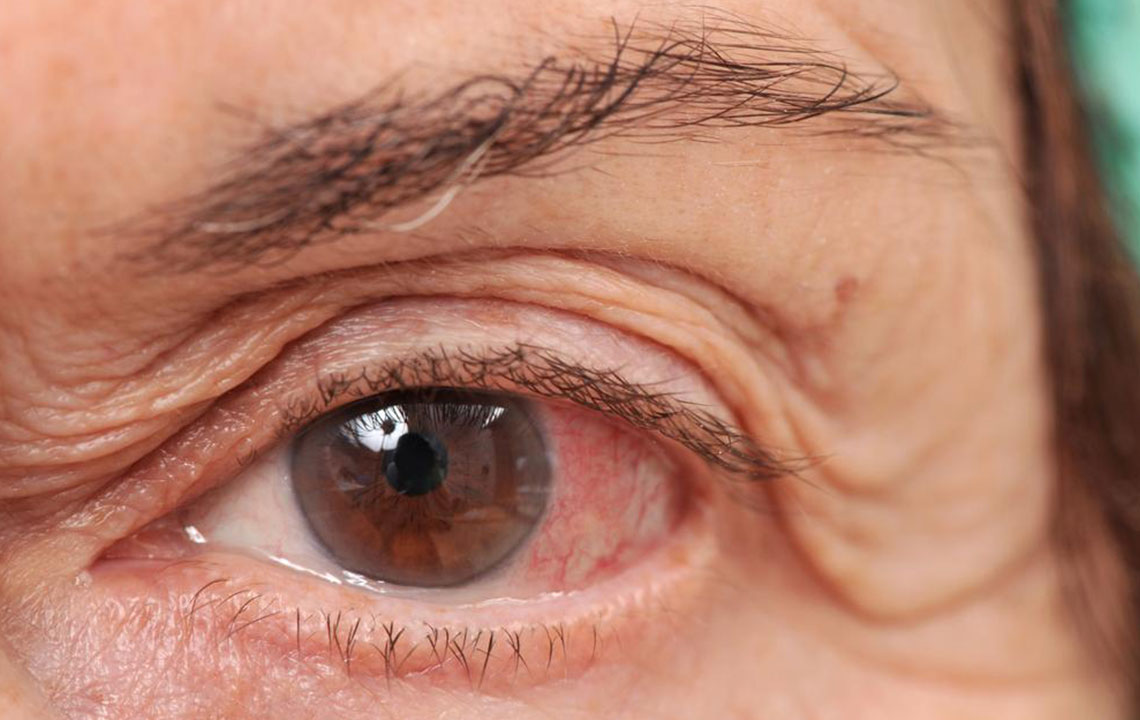
Recognizing Symptoms and Signs: The symptoms of dry eye syndrome are diverse and can often be confusing for patients. Common complaints include a burning sensation, persistent irritation, the sensation of grittiness or foreign body presence, excessive tearing paradoxically accompanied by dryness, redness, blurred vision, and discomfort especially in low humidity environments. Interestingly, the presence of excessive tearing in dry eye patients results from reflex tearing, which occurs as the eyes attempt to compensate for dryness but fails to provide proper lubrication despite increased tear production. This paradox highlights the importance of accurate diagnosis.
Importance of Professional Eye Examination: Once symptoms are observed, seeking evaluation from an eye care professional is critical. An ophthalmologist or optometrist conducts a comprehensive eye examination, including tests that measure tear production, such as the Schirmer test, evaluation of tear film breakup time, and assessment of eyelid and corneal health. These evaluations help determine the severity and underlying causes of dry eye, guiding personalized treatment plans.
Management of dry eye syndrome involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications. Some of the most common treatment modalities include the prescription of medicated eye drops like lubricating eye ointments or artificial tears designed to supplement natural tears, and procedures like punctal plugs that block tear drainage ducts to retain moisture within the eyes. Additionally, ophthalmic inserts, sometimes referred to as punctual inserts, can provide sustained lubrication. Regular eyelid hygiene, including gentle cleansing to remove any debris or bacteria that may contribute to inflammation, along with warm compresses applied to the eyelids to stimulate oil secretion from meibomian glands, can significantly reduce symptoms and support tear film stability.
It is vital to understand that early intervention not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents the progression of dry eye disease to more serious ocular surface damage. Persistent dryness can lead to corneal abrasions, increased risk of infection, and long-term visual impairment if left unaddressed. Therefore, individuals experiencing dry eye symptoms should seek prompt professional advice and adhere to the prescribed treatment regimens for optimal outcomes.
In addition to conventional medical treatments, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing dry eye. These include maintaining good hydration, using humidifiers indoor environments, avoiding exposure to smoke and wind, taking regular breaks during prolonged visual tasks (such as using computers), and wearing wraparound sunglasses to shield the eyes from environmental irritants. Dietary modifications to include omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties, may also benefit tear quality and overall eye health.
In conclusion, while chronic dry eye syndrome remains a challenging condition, adopting a holistic management approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and professional guidance can significantly enhance comfort and preserve eye health. Patients should remain vigilant for symptoms and consult eye care specialists early to receive tailored interventions that effectively address their unique needs. With proper care, individuals can enjoy improved ocular comfort and a better quality of life despite the persistent nature of dry eye disease.