Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Controlling Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing Type 2 diabetes through diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring. Learn how to control blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve quality of life with tailored lifestyle adjustments and medical support. Empower yourself with knowledge and practical tips for long-term health management of this chronic condition.
Comprehensive Strategies for Managing and Controlling Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is recognized as a chronic, lifelong health condition that impacts millions of people worldwide. Unlike some other ailments, it currently has no complete cure, making effective management essential for maintaining health and preventing serious complications. Managing Type 2 diabetes requires a dedicated approach involving lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, physical activity, and possibly medication. This extensive guide aims to provide individuals with an in-depth understanding of how to control and manage Type 2 diabetes effectively, ensuring a better quality of life and preventing long-term health issues.
Core Principles for Managing Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
Achieving optimal control over Type 2 diabetes hinges on a combination of balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, appropriate medication, and consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels. While each person's condition may vary, integrating these components into daily life can significantly improve health outcomes.
Focus on Nutrition
Proper nutrition is foundational for blood sugar regulation in individuals with diabetes. Carefully planned dietary habits can help prevent blood sugar spikes and drops, contributing to overall stability.Collaborating with healthcare professionals such as registered dietitians can help craft a personalized diet plan tailored to specific needs and health conditions. Typical dietary recommendations for managing blood glucose include:
Increasing the intake of fresh fruits, a variety of vegetables, and whole grains that provide essential nutrients and fiber.
Consuming meats, especially lean options, and limiting intake of saturated fats, processed foods, salty snacks, and sugary treats.
Maintaining regular and consistent meal timings to help stabilize blood glucose levels and prevent sudden fluctuations.
Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Routine
Exercise plays a critical role in improving insulin sensitivity and controlling blood sugar. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new physical activity regimen.A balanced exercise routine combining aerobic activities, resistance training, yoga, and stretching exercises offers comprehensive benefits.
Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, jogging, and strength training can be integrated into weekly schedules—no need to exercise every day, but consistency is key.
Physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels and enhances overall metabolic health. If you are on diabetes medication, consider consuming a light snack beforehand to prevent hypoglycemia during exercise.
Medication and Blood Sugar Monitoring
While lifestyle modifications are essential, some individuals with Type 2 diabetes require medications for effective blood sugar control. The need for medication varies depending on disease severity, and treatment plans are tailored accordingly.Initial treatments often include oral medications that improve insulin sensitivity or stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
In some cases, insulin injections become necessary, especially if blood sugar levels remain high despite other treatments.
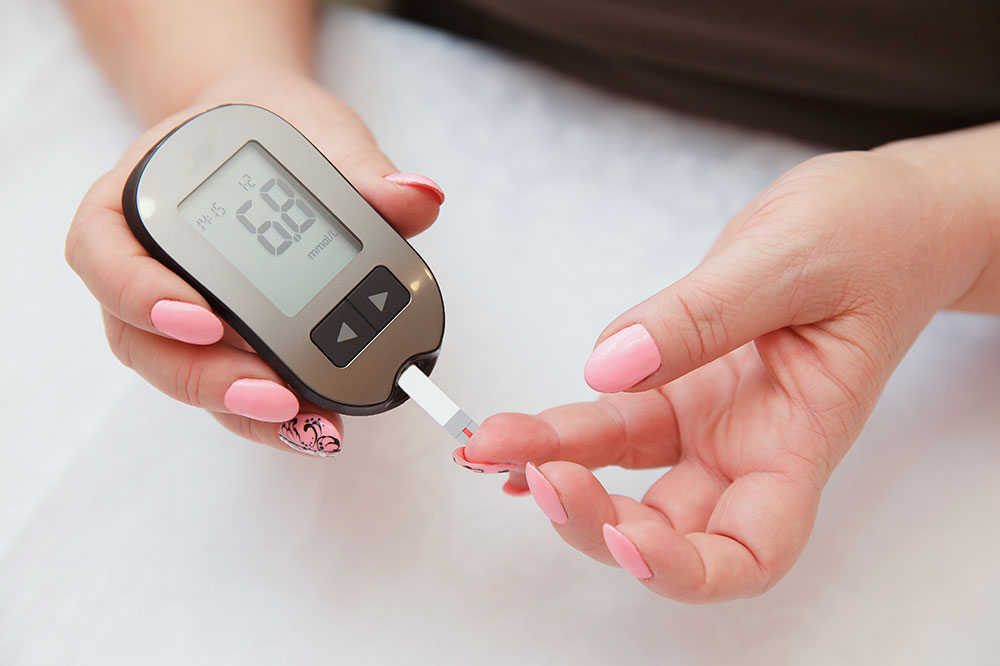
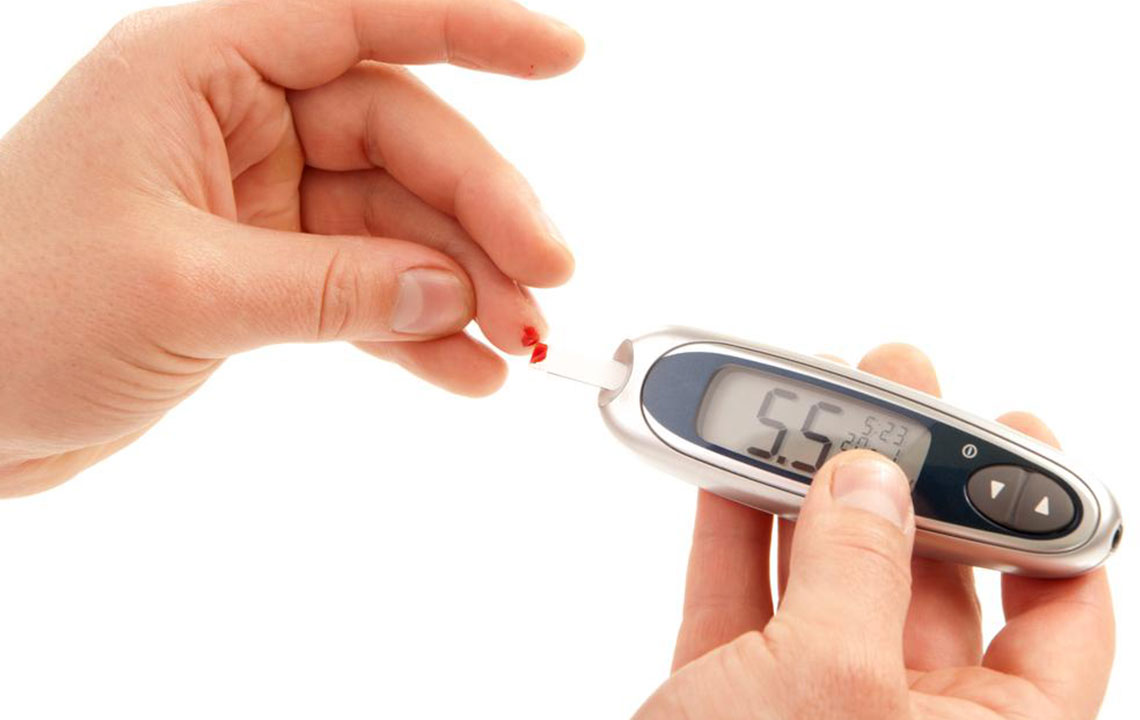
Regular blood glucose monitoring is vital for effective diabetes management. Your healthcare provider will guide you on the appropriate methods and frequency for testing, aiming to keep blood sugar within target ranges. With disciplined management, some patients may even reduce or discontinue medication over time, but this should always be done under medical supervision.
Managing Type 2 diabetes involves a comprehensive approach encompassing lifestyle, diet, medication, and regular health checks. Staying informed and proactive is the key to living well with this condition, preventing complications, and maintaining overall health and vitality.