Understanding the Critical Role of Maintaining Stable Blood Glucose Levels for Optimal Health
Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is essential for overall health, preventing diabetes complications, and supporting organ functions. This comprehensive guide explores how blood sugar fluctuates during the day, tools for monitoring, and lifestyle tips for effective management, emphasizing the importance of consistent regulation for long-term well-being.

Understanding the Critical Role of Maintaining Stable Blood Glucose Levels for Optimal Health
Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is a vital indicator of overall health and metabolic function. It represents the amount of glucose present in your bloodstream at any given moment, providing essential energy to our body's cells. Glucose originates primarily from the foods we consume, particularly carbohydrates such as bread, rice, fruits, and vegetables. The body employs intricate regulatory mechanisms involving the pancreas, hormones like insulin and glucagon, and various organs to keep blood glucose levels within a healthy range. Proper regulation prevents dangerous spikes and drops that can impair bodily functions.
Understanding how blood glucose fluctuates during the day helps individuals monitor and manage their health effectively. Typically, levels are lowest during fasting states, such as early morning, and rise after meals as the body digests and absorbs carbohydrates. This rise is necessary for energy but must stay within safe limits to prevent long-term health complications. Maintaining blood glucose within target ranges is especially crucial for people with diabetes, metabolic syndrome, or other health conditions that impact insulin efficiency.
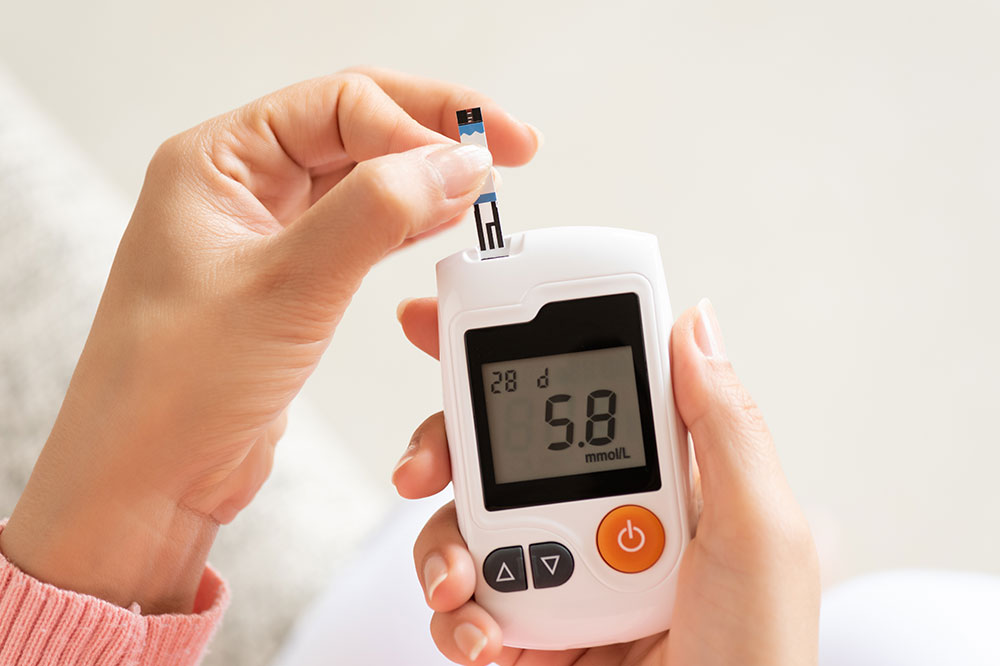
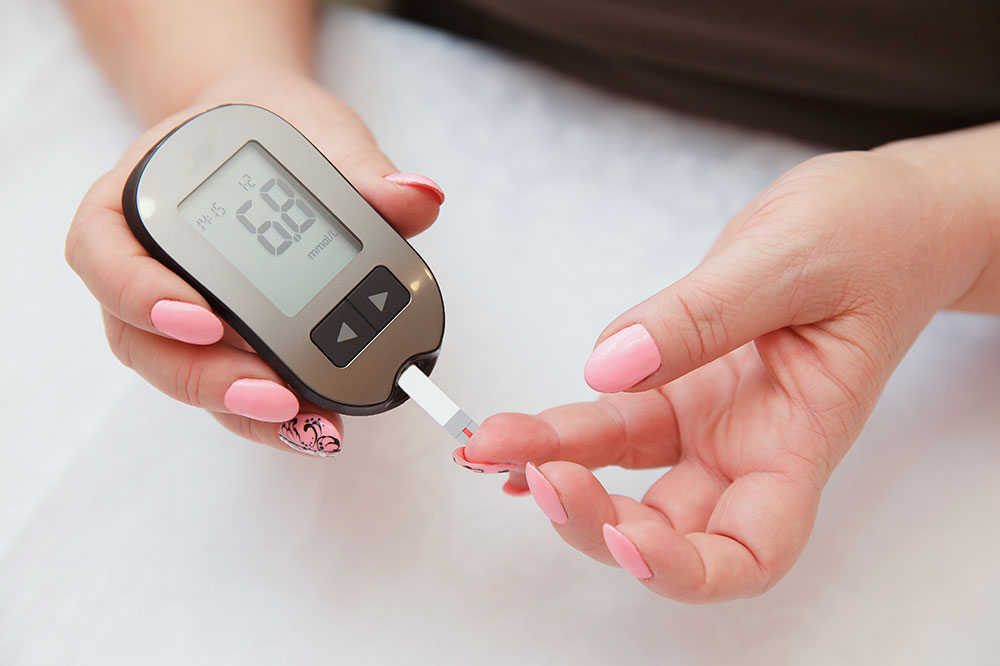
Monitoring blood glucose levels provides valuable insights into one's metabolic health. A comprehensive glucose monitoring chart typically tracks daily fluctuations, revealing patterns that can inform lifestyle and dietary adjustments. For healthy individuals, blood sugar levels tend to stabilize after meals and during periods of fasting. However, for diabetics or those at risk, monitoring is critical to prevent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), both of which can lead to serious health issues if left unmanaged.
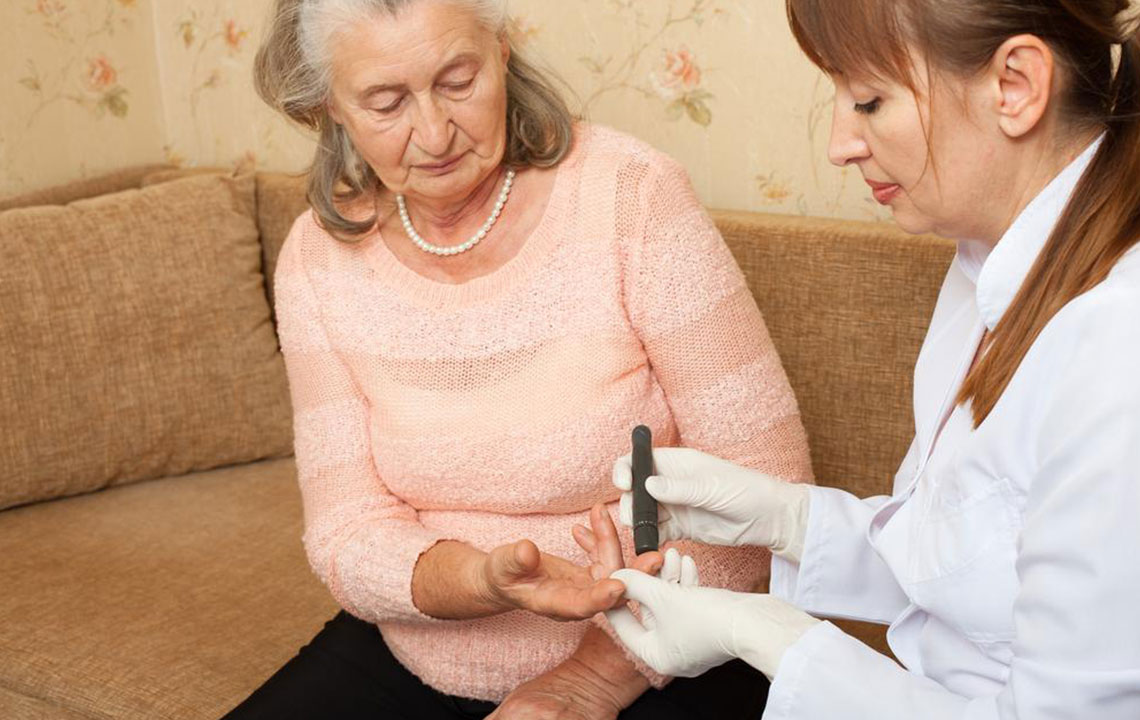
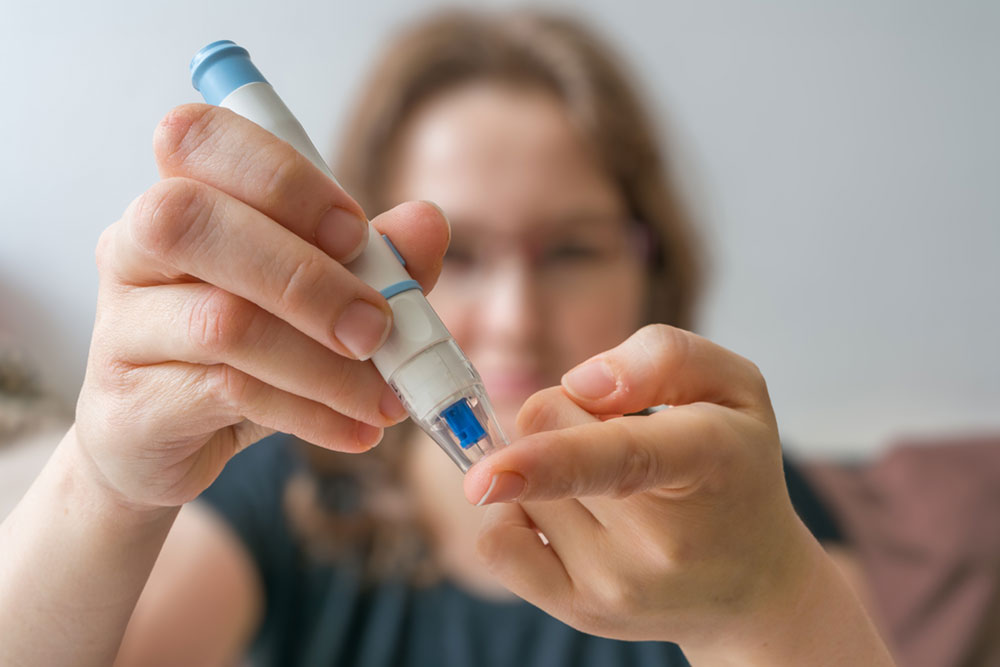
Research emphasizes that consistent blood glucose control reduces the risk of developing complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular monitoring allows timely intervention, helping to maintain optimal organ function and overall well-being. Devices such as glucometers and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are invaluable tools that aid in tracking these levels accurately. Healthcare professionals recommend measuring fasting blood sugar levels, post-meal readings, and, in some cases, conducting A1C tests that reflect average glucose over several months.
Achieving stable blood glucose requires more than just monitoring. Lifestyle modifications play a vital role. Adopting a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and low in refined sugars benefits blood sugar regulation. Physical activity, including walking, jogging, or other moderate exercises, enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes better glucose utilization. Adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption also contribute significantly to metabolic health. Collaborating with healthcare providers ensures personalized strategies to maintain ideal blood sugar levels and prevent potential complications.