Comprehensive Guide to Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels for Optimal Health Management
This comprehensive guide emphasizes the importance of monitoring blood glucose levels for health optimization and disease prevention. It covers how blood sugar varies, methods for tracking levels, interpreting results using charts, and lifestyle strategies to maintain healthy glucose levels. Whether you're managing diabetes or seeking to improve metabolic health, regular blood glucose monitoring empowers you to make informed choices, reducing risks associated with high or unstable blood sugar, and ensuring overall well-being.
Comprehensive Guide to Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels for Optimal Health Management
Understanding and tracking blood glucose levels is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing chronic diseases such as diabetes. Blood glucose, or blood sugar, is the concentration of glucose present in your bloodstream at any given moment. This vital biological metric reflects how well your body is managing sugar intake and utilization. Proper management of blood glucose levels can significantly reduce the risk of developing serious health complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss.
Blood glucose originates primarily from the foods we consume, especially carbohydrate-rich meals. After eating, blood sugar levels rise as the carbohydrates are broken down into glucose and absorbed into the bloodstream. The body’s endocrine system, particularly the pancreas, plays a critical role in regulating these levels by releasing insulin, a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells for energy or storage. When functioning efficiently, blood glucose levels remain within a healthy range, typically between 70-130 mg/dL, depending on timing and individual health status.
Fluctuations in blood sugar happen naturally throughout the day, influenced by meals, physical activity, stress, hormonal changes, and sleep patterns. In healthy individuals, fasting blood sugar levels are generally below 100 mg/dL, with post-meal peaks rarely exceeding 140 mg/dL. However, in individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes, these fluctuations can be more pronounced and harder to control.
Monitoring blood glucose is an essential aspect of health management. For diabetics, regular testing is vital to prevent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which can have immediate and long-term health impacts. For non-diabetics, tracking can help detect early signs of metabolic imbalances, allowing for timely lifestyle modifications.
A comprehensive blood glucose trend chart illustrates how blood sugar levels vary during different parts of the day. These charts provide valuable insights into an individual’s metabolic responses to meals, physical activity, and stressors. They are especially useful for diabetics to tailor their treatment plans and for health-conscious individuals aiming to maintain stable glucose levels for overall well-being.
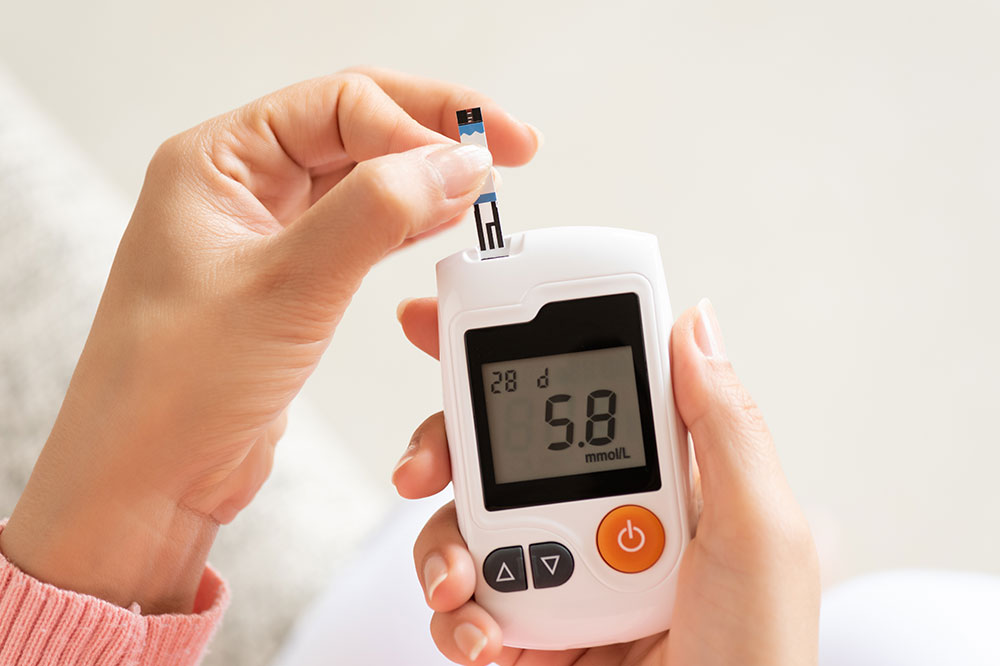
Consistent charting of blood glucose levels helps in early detection of potential issues, enabling proactive adjustments in diet, exercise, or medication. Regular monitoring not only assists in preventing acute episodes but also minimizes the risk of long-term damage to vital organs such as the kidneys, eyes, and heart. Devices like glucometers and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) have made tracking easier, more accurate, and more convenient.
Why Monitoring Blood Glucose Is Critical for Your Health
Regular blood glucose monitoring offers critical insights into your body's metabolic health. It helps identify abnormal patterns that could indicate insulin resistance or the onset of diabetes, even before symptoms become apparent. Early detection through consistent tracking enables timely interventions, including dietary changes, increased physical activity, or medication adjustments.
For people living with diabetes, maintaining blood sugar within target ranges significantly reduces the risk of complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, cardiovascular disease, and kidney failure. These complications can severely impair quality of life and lead to life-threatening conditions if unmanaged. Therefore, accurate and frequent measurement becomes an essential part of daily health routines.
Understanding Blood Glucose Charts and Their Components
Most blood glucose charts include key measurements: fasting blood sugar, post-meal readings, and possibly bedtime levels. Normal fasting blood sugar typically remains below 100 mg/dL, whereas post-meal levels should be maintained under 140 mg/dL for healthy individuals. For diabetics, fasting levels below 130 mg/dL and post-prandial levels under 180 mg/dL are often recommended targets.
To interpret these charts effectively, it’s important to consider lifestyle factors such as diet composition, physical activity levels, sleep quality, and stress management. Implementing regular exercise, like brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, can help enhance insulin sensitivity. Consuming a balanced diet high in fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates supports stable blood sugar levels. Adequate sleep and stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, are also instrumental in maintaining metabolic health.
Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake are important steps toward better glucose regulation. Healthcare providers can help set personalized target ranges and interpret blood glucose data to craft effective health plans. Digital tools and smart devices make tracking more straightforward, helping users stay motivated and informed about their health status.
In conclusion, monitoring blood glucose levels is a vital component of health management, whether you are diabetic or simply striving for optimal wellness. Through consistent tracking, lifestyle adjustments, and professional guidance, you can maintain stable blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve your overall quality of life.