Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes Testing and Effective Disease Management
This comprehensive guide delves into diabetes testing and management, highlighting the importance of regular blood sugar monitoring, understanding types of diabetes, and early diagnosis. It provides detailed insights into diagnostic methods like fasting blood glucose, OGTT, and hemoglobin A1c tests. The article emphasizes proactive strategies to prevent complications and maintain a good quality of life through informed decision-making and lifestyle adjustments. Ideal for patients and caregivers, it underscores the significance of timely detection and continuous monitoring for effective diabetes control.

Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes Testing and Effective Disease Management
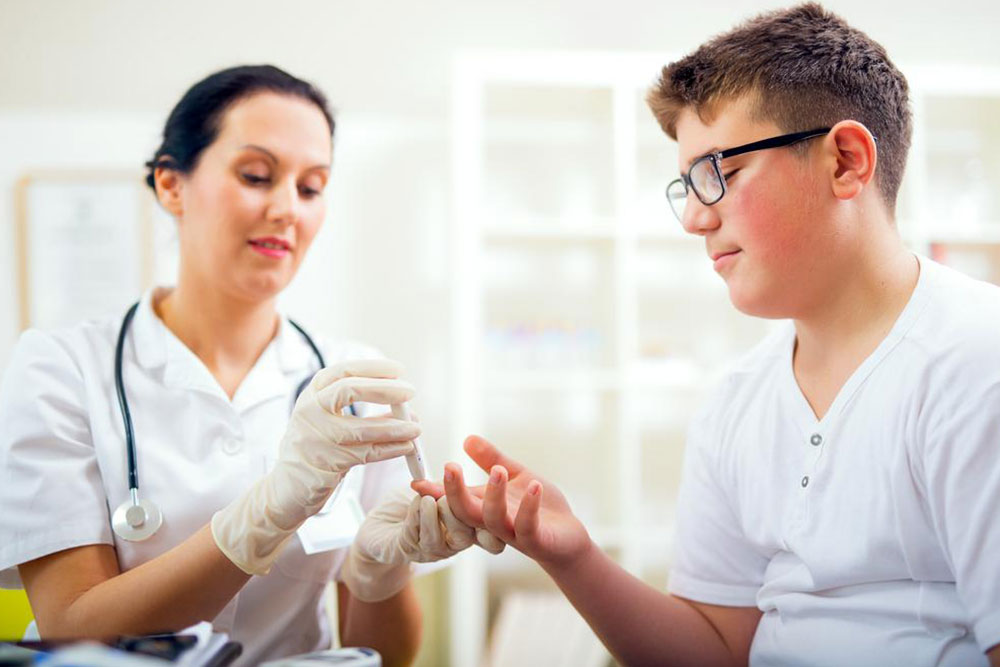
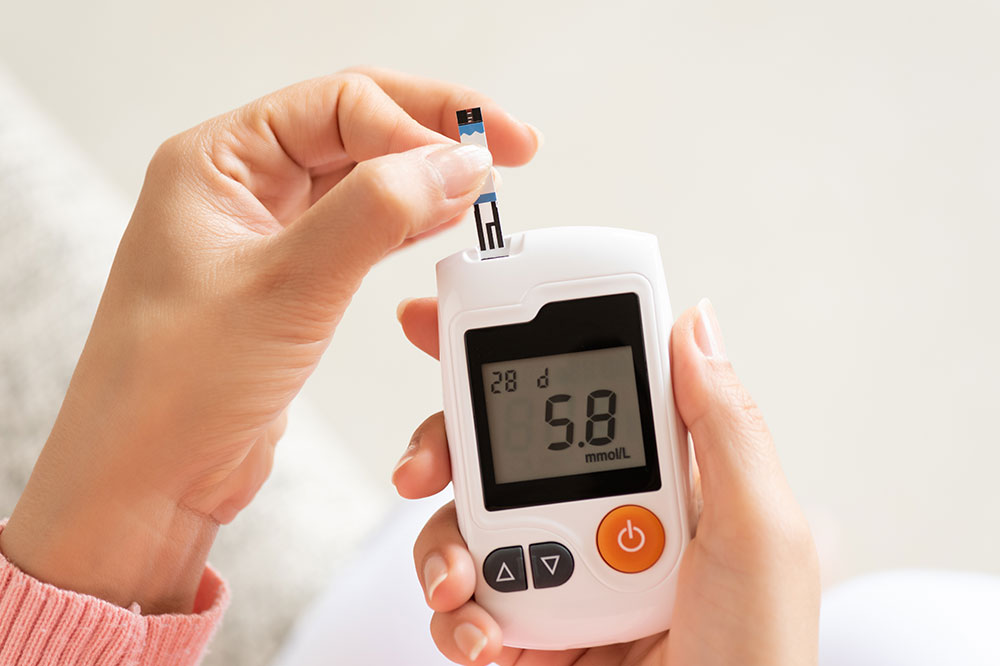
Managing diabetes in a proactive and informed manner is crucial for maintaining health and preventing long-term complications. Continuous monitoring of blood sugar levels through various testing methods is the cornerstone of effective diabetes management. Regular testing not only helps in tracking the progression of the disease but also provides vital insights that guide treatment decisions. By understanding your blood glucose patterns, you can work closely with healthcare providers to optimize medication, diet, and lifestyle adjustments to keep your condition under control.
Blood sugar testing offers critical information about your current health status. It helps in evaluating how well your treatment plan is working, detecting fluctuations in blood glucose levels, and understanding the impact of your dietary choices and physical activity. Consistent monitoring enables early intervention if blood sugar levels become unmanageable, reducing the risk of serious health complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. The earlier deviations are detected, the more effectively they can be addressed, emphasizing the importance of routine testing.
Understanding the different types of diabetes and the factors that influence diagnosis is essential for patients and healthcare providers. There are primarily two forms of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2, each with unique characteristics and management requirements. Accurate diagnosis through appropriate testing methods ensures that patients receive tailored treatment plans to suit their specific needs, minimizing potential health risks. Recognizing early symptoms and risk factors also enables timely screening and intervention, helping to prevent the development of severe complications.
Regular blood sugar monitoring plays a vital role in managing diabetes effectively
Understanding the impact of diet and lifestyle on blood glucose levels
Detecting early signs of disease progression to optimize treatment
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. It generally develops early in life and requires lifelong insulin therapy. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes usually appears later in life and is characterized by insulin resistance combined with an eventual decline in insulin production. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, obesity, and genetic predisposition significantly influence the development of Type 2 diabetes.
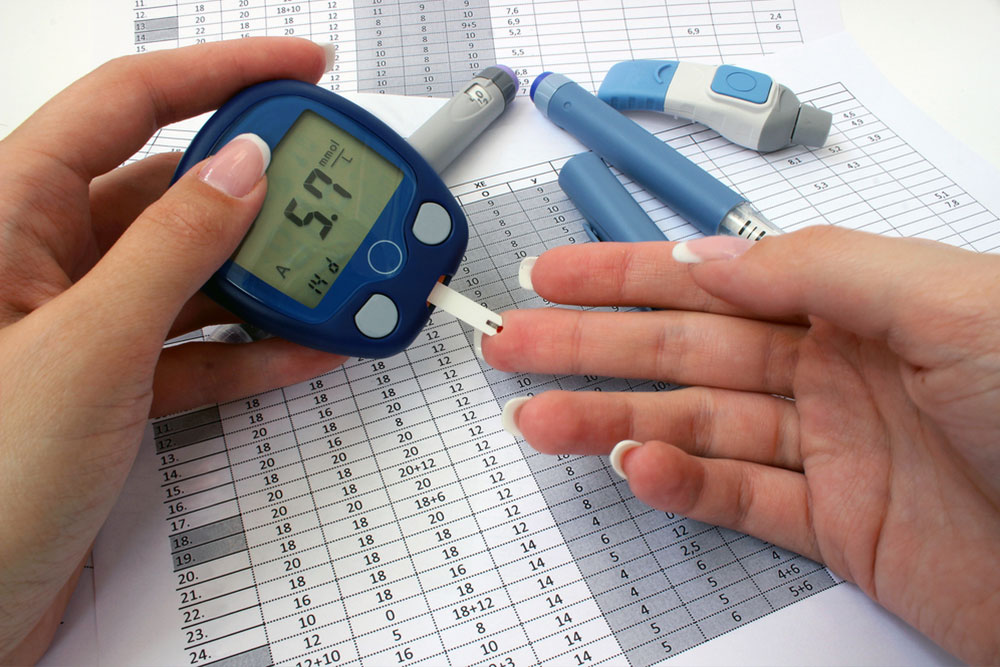
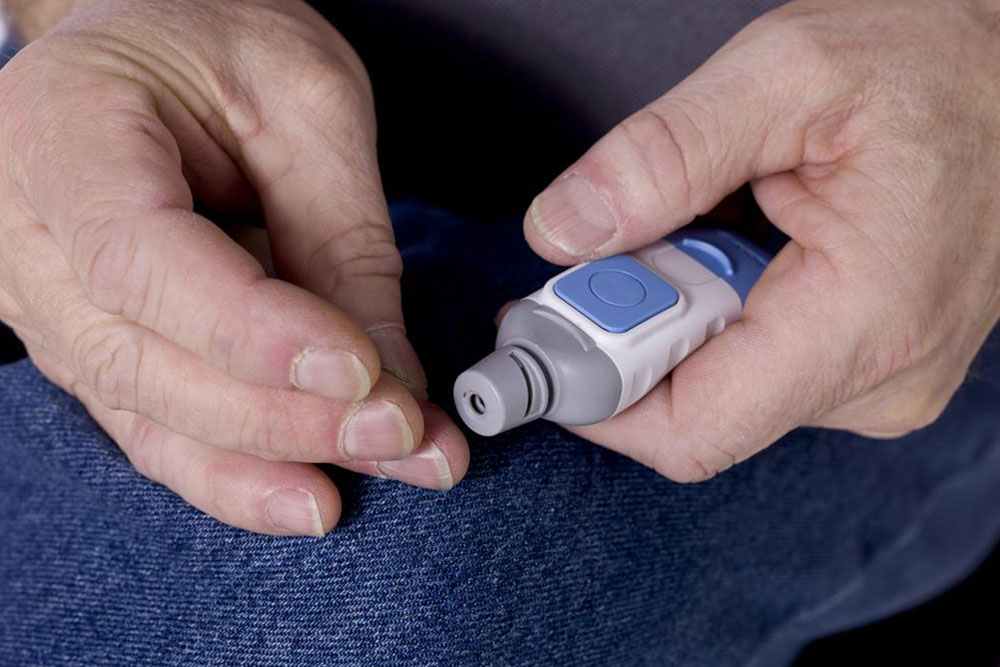
Diagnosing these conditions accurately involves various tests including fasting blood glucose tests, oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT), and hemoglobin A1c tests. Fasting blood glucose tests measure blood sugar after an overnight fast, while OGTT involves consuming a sugary drink and measuring blood sugar at intervals to assess how efficiently the body processes glucose. The A1c test provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months, offering insights into long-term control.
Timely and accurate testing is essential in preventing the silent progression of diabetes, which can damage vital organs without immediate symptoms. Early detection through routine testing allows healthcare providers to develop personalized management plans that include medication, dietary adjustments, physical activity, and lifestyle modifications. Patients who engage in regular monitoring are better equipped to make informed decisions that improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of severe complications.
In conclusion, effective diabetes management hinges on a thorough understanding of testing procedures, early diagnosis, and continuous monitoring. Staying vigilant about blood sugar levels, understanding how lifestyle factors influence the disease, and promptly addressing abnormal readings are key steps toward maintaining optimal health. Empowered with knowledge and supported by healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetes can lead healthier lives and prevent the progression of this chronic condition.