Ultimate Guide to Blood Sugar Testing: Ensuring Optimal Diabetes Management
This comprehensive guide to blood sugar testing explains the importance of monitoring glucose levels for managing diabetes effectively. It covers the basics of blood glucose, risks of abnormal levels, insulin's role, testing methods, and practical tips for home monitoring. Suitable for those with diabetes or interested in understanding blood sugar health, this article emphasizes the significance of regular testing to prevent complications and maintain overall well-being.
Comprehensive Understanding of Blood Sugar Testing and Its Importance
Blood sugar testing is an essential aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. It involves measuring the concentration of glucose present in your blood, providing vital information that can guide dietary choices, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. This detailed guide aims to elucidate everything you need to know about blood glucose measurement, from its fundamental concepts to practical testing methods, ensuring you stay informed and proactive in your health journey.
What is blood glucose and why does it matter? Glucose, a simple sugar, is a primary energy source that circulates through your bloodstream, fueling vital organs such as the brain, heart, liver, and kidneys. Maintaining balanced blood glucose levels is crucial because fluctuations can significantly impact bodily functions and overall well-being. When your blood glucose levels are within a healthy range, your body operates efficiently, mental clarity is preserved, and chronic conditions like diabetes are better managed.
Glucose is primarily derived from the carbohydrates you consume. When you eat carbohydrate-rich foods, they are broken down during digestion into glucose molecules, which then enter the bloodstream. Besides carbohydrates, proteins can also be converted into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis, mainly occurring in the liver, ensuring a steady supply of energy during fasting or prolonged physical activity. Fats, however, contribute minimally to blood glucose levels, as they are typically metabolized differently, providing alternative energy sources through fatty acid breakdown.
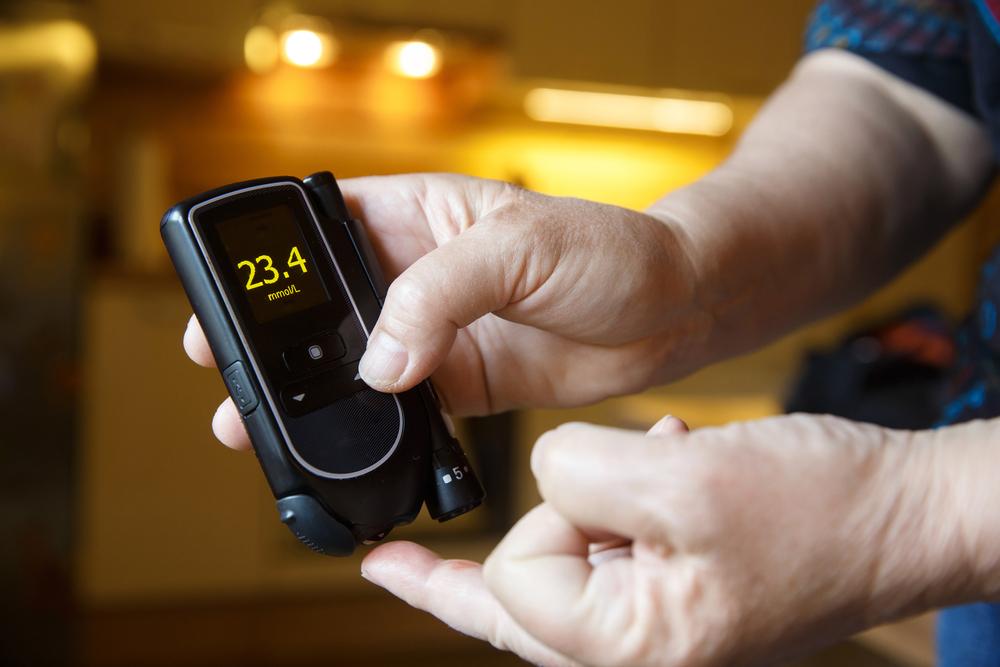
Why high blood sugar is dangerous Elevated blood glucose levels, or hyperglycemia, are common concerns for individuals with diabetes, but they also pose risks for everyone. Persistently high blood sugar can damage blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of developing heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, vision impairment, and nerve damage. On the other hand, hypoglycemia or low blood sugar can lead to confusion, dizziness, seizures, loss of consciousness, and in severe cases, can be life-threatening if not promptly treated. Recognizing these risks underscores the importance of regular blood sugar monitoring.
The critical role of insulin Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, is central to the regulation of blood sugar levels. After consuming food, insulin helps cells absorb glucose to be used as energy or stored for later use. Proper insulin function ensures blood sugar stays within safe limits. In individuals with diabetes, insulin production or its effectiveness is impaired, causing glucose to accumulate dangerously. Managing insulin levels and monitoring blood sugar are, therefore, fundamental to effective diabetes control.
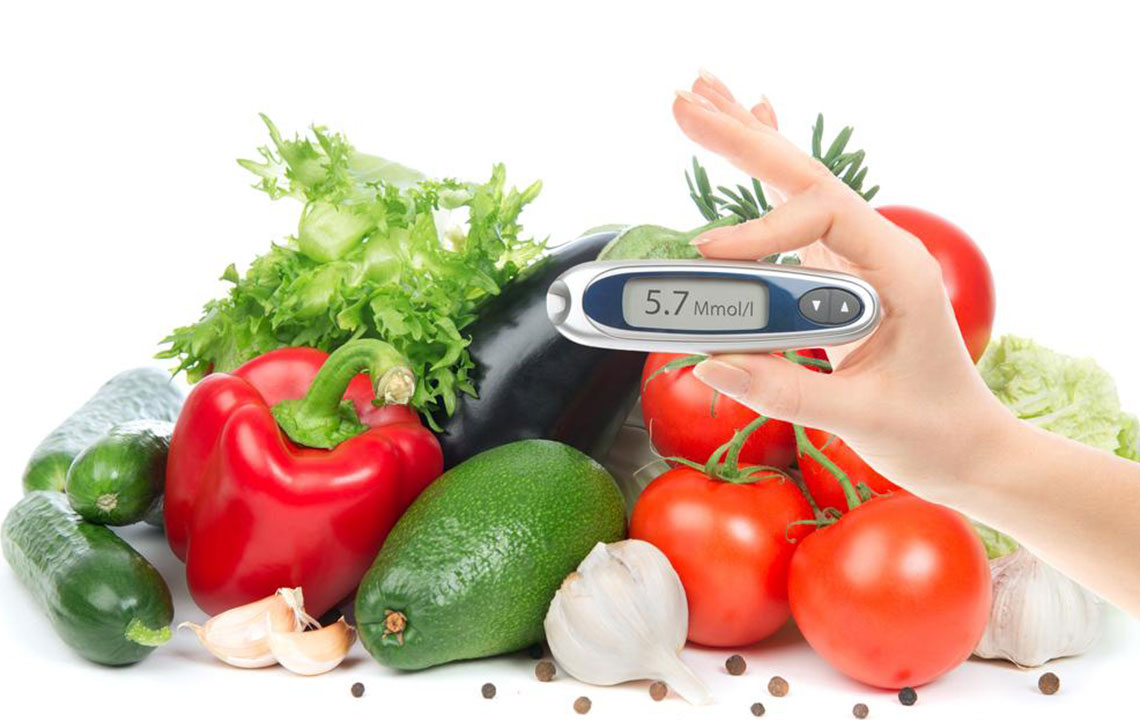
Understanding blood glucose testing Blood sugar testing involves measuring the amount of glucose present in a blood sample. Results are usually expressed in millimoles per liter (mmol/L) or milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Blood glucose levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day due to various factors, including meals, activity levels, and insulin response. In diabetes, these fluctuations are often exaggerated or poorly regulated, leading to prolonged periods of high or low blood sugar. Regular testing helps detect these changes early, allowing for timely interventions.
Normal blood glucose levels Typically, blood glucose levels fall within the following ranges:
Below 59 mg/dL: considered low, though sometimes acceptable in specific medical contexts
80-120 mg/dL: optimal fasting blood sugar for healthy individuals
100-140 mg/dL: common for older adults or those with certain health conditions
Maintaining these levels is essential for overall health and to prevent complications related to diabetes.
Various blood glucose testing methods Healthcare professionals recommend specific testing schedules based on individual health status. Common testing methods include:
Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG): measures blood sugar after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. This test provides baseline data for diagnosing and managing diabetes.
A1C Test: indicates the average blood glucose over the past two to three months by measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin. It is invaluable for assessing long-term glycemic control.
Random Blood Glucose Test: performed at any time regardless of last meal, providing immediate snapshot of blood sugar levels.
Specialized tests for gestational diabetes include Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests (OGTT) and Glucose Challenge Tests, which evaluate how your body processes sugar during pregnancy.
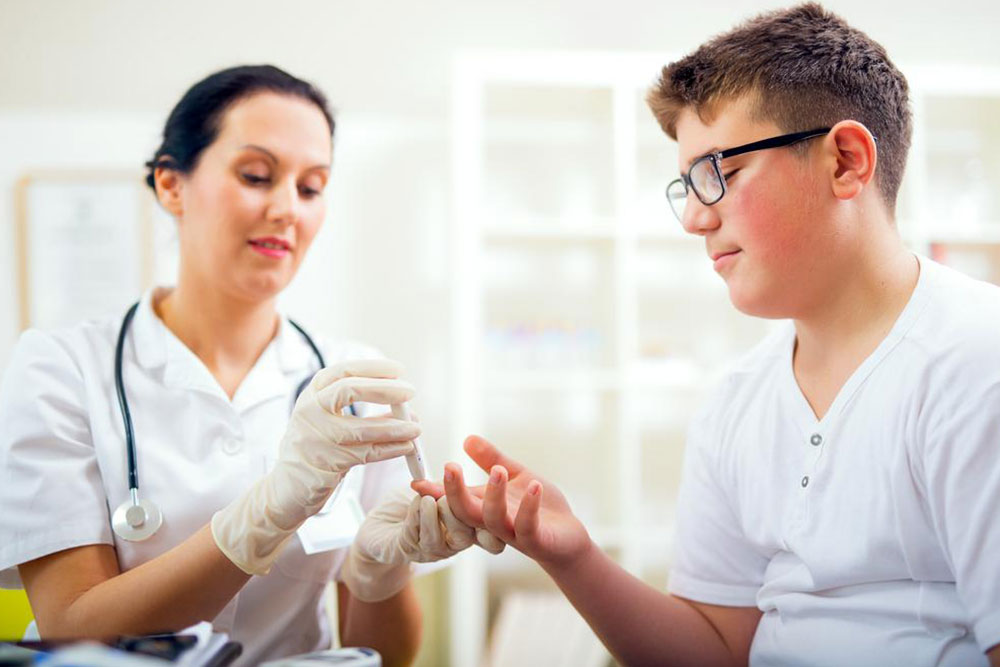
Laboratory testing involves drawing blood samples from veins—usually from the arm—to analyze glucose concentrations accurately. These tests use advanced reagents, such as glucose oxidase, to ensure precision. Only trained medical personnel conduct these procedures in clinical settings.
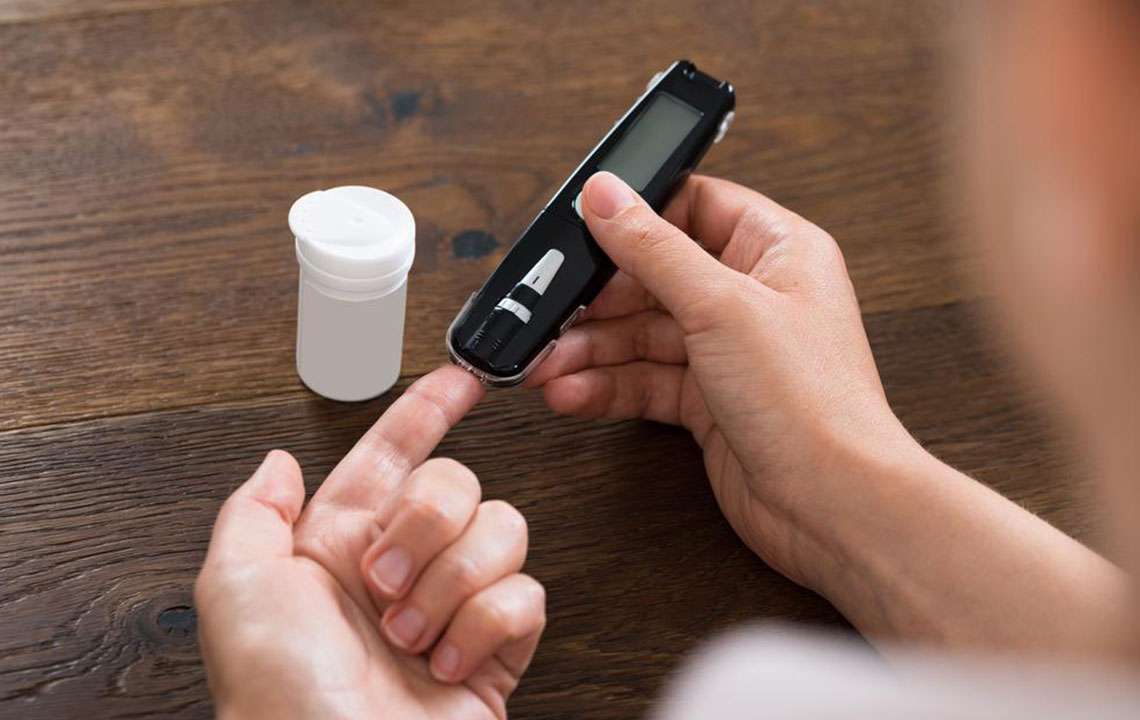
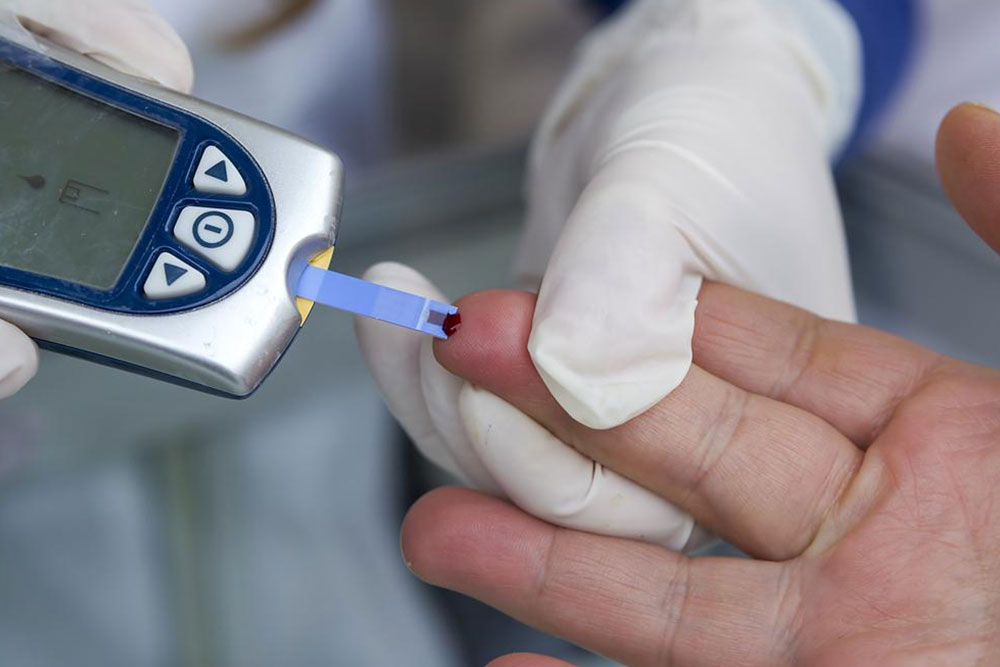
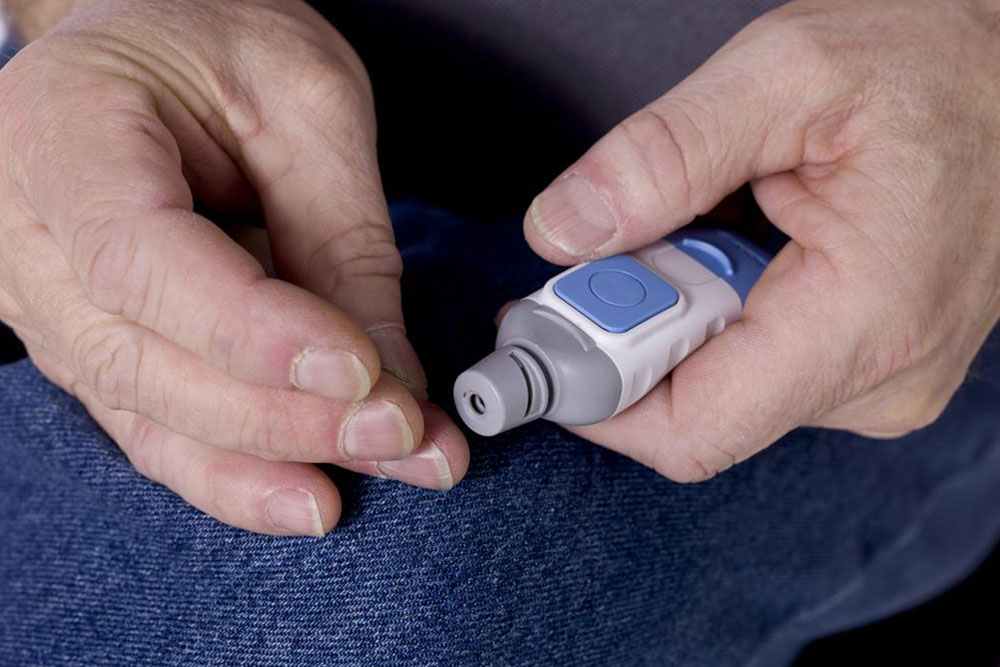
DIY blood sugar testing at home Many people managing diabetes rely on portable glucometers to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly. The process involves pricking the fingertip with a lancet to obtain a small blood sample. The blood is then placed on a test strip inserted into a device, which displays the reading within seconds. Home testing supports daily monitoring, helping individuals make informed decisions about diet, activity, and medication.
In summary, understanding blood sugar levels, their regulation, and the testing methods available is vital for preventing and controlling diabetes. Regular monitoring facilitates early detection of abnormal fluctuations, promoting healthier lifestyles and preventing long-term complications.
For more comprehensive information, consult sources like the Wikipedia page on Glucose, Blood Sugar Level overview, and trusted health resources such as Healthline's Blood Sugar Testing Guide.