Comprehensive Guide to Effective Blood Glucose Monitoring for Diabetes Management
This comprehensive article delves into effective strategies for blood glucose monitoring, emphasizing the importance of insulin management, diet, and lifestyle. It provides valuable tips for diabetics to maintain optimal blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. From using home glucose meters accurately to adopting healthy habits, the guide equips readers with practical insights for successful diabetes control and overall well-being.
Comprehensive Guide to Effective Blood Glucose Monitoring for Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes effectively requires diligent monitoring of blood glucose levels. Blood sugar management is a cornerstone of diabetes care, helping to prevent acute symptoms and long-term complications. Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, leads to elevated blood glucose levels caused by the body's inability to produce or respond to insulin efficiently. Understanding how to monitor and control blood sugar is crucial for maintaining overall health and enjoying a better quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores the best practices for blood glucose monitoring, insulin use, dietary management, and lifestyle adjustments essential for effective diabetes control.
Optimizing Insulin Usage for Better Blood Glucose Control
Proper management of blood sugar hinges significantly on how insulin is administered and utilized. Insulin is a vital hormone that facilitates the entry of glucose into cells, providing energy and maintaining blood sugar balance. For individuals with diabetes, especially Type I and advanced Type II, insulin therapy often becomes necessary. Correct insulin use involves precise timing, dosage, and understanding the different types of insulin—rapid-acting, long-acting, and intermediate-acting—each serving specific purposes. Working closely with your healthcare provider ensures your insulin regimen is tailored to your unique needs, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Regular insulin injections, combined with lifestyle measures, help stabilize blood glucose levels, prevent complications, and promote overall well-being.
How to Monitor and Interpret Blood Glucose Levels Effectively
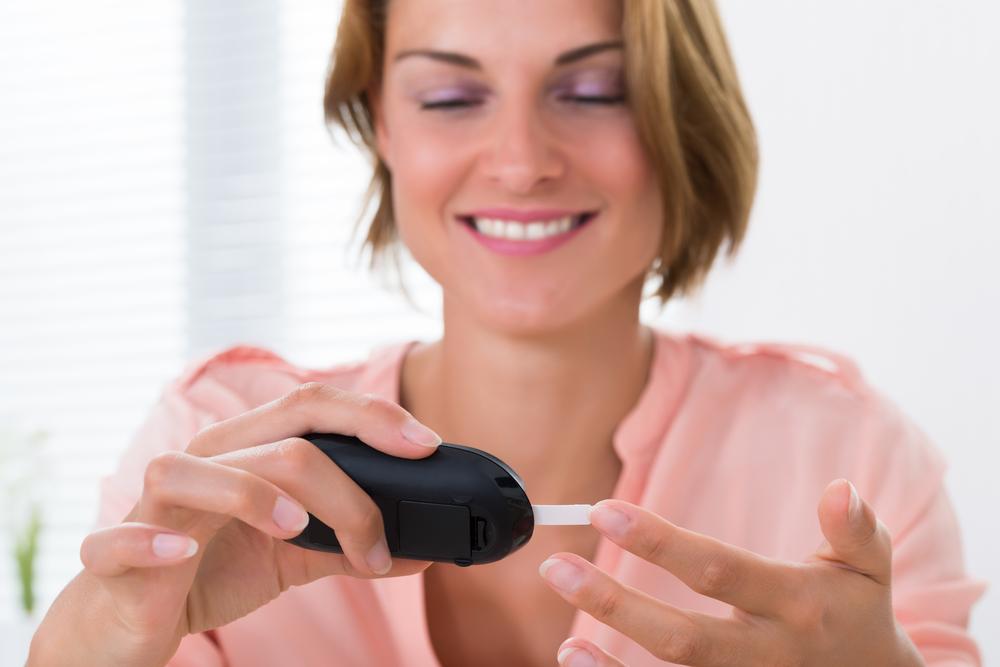
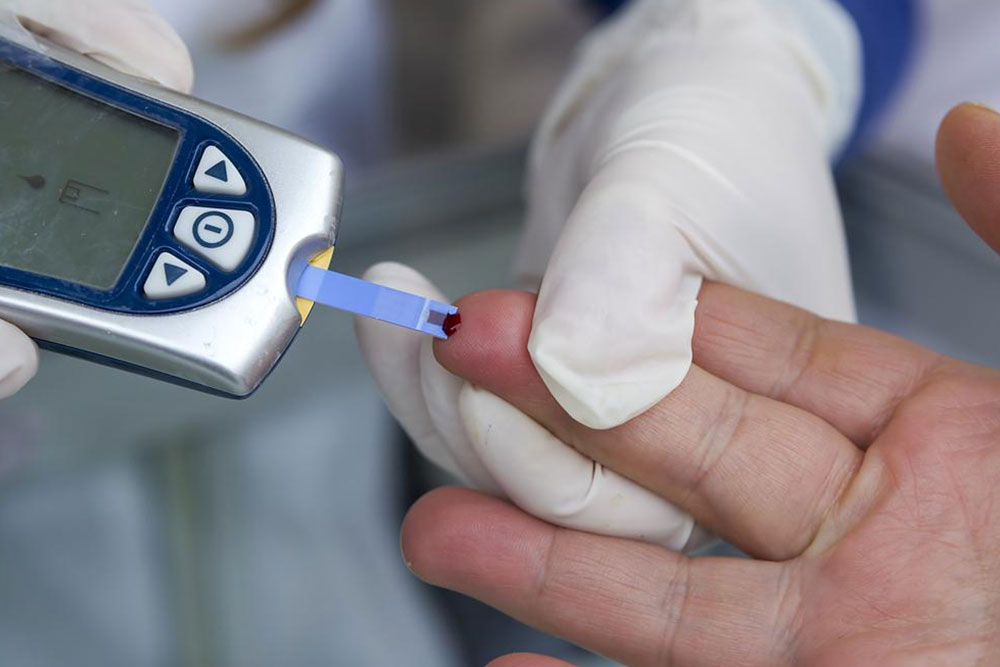
Monitoring blood glucose levels involves using a reliable home glucose meter. This device provides immediate feedback on blood sugar levels, enabling timely adjustments in diet, medication, or activity. To obtain accurate readings, test your blood first thing in the morning before eating, which is known as fasting blood sugar. This measurement offers insights into your baseline glucose control. When readings exceed 10 mmol/L, it signals a need for urgent medical consultation to prevent further complications. Variability in blood sugar can result from factors such as stress, illness, physical activity, or dietary intake. Therefore, maintaining a log of your blood glucose readings helps identify patterns and triggers, facilitating better management strategies. Striving to keep your blood sugar within target ranges—often between 4 to 7 mmol/L for fasting and 5 to 10 mmol/L post-meal—is essential to avoiding both immediate risks and long-term damage.
Dietary and Lifestyle Strategies to Support Blood Sugar Control
Blood sugar management is not solely reliant on medication; a balanced diet and lifestyle play a crucial role. Eating a diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and low in processed sugars helps regulate blood glucose. Incorporating foods like vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce post-meal sugar spikes. Portion control and regular meal times prevent sudden fluctuations in blood glucose levels. Additionally, staying physically active enhances insulin effectiveness, supports weight management, and improves overall cardiovascular health. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, ensuring adequate sleep, and avoiding smoking or excess alcohol consumption further contribute to optimal blood glucose control. Regular check-ups and continuous education about your condition empower you to make informed decisions and adapt your strategies as your needs change.
In conclusion, effective blood glucose monitoring combined with proper insulin use, dietary control, and lifestyle modifications forms the foundation of successful diabetes management. Adopting these strategies helps prevent dangerous complications such as diabetics' neuropathy, nephropathy, and cardiovascular disease. Empower yourself with the right knowledge, tools, and support systems to take charge of your health and lead a healthier, more balanced life.