Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Preventing Diabetes for Better Health
This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention, and management of diabetes. It emphasizes lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, regular exercise, and blood sugar monitoring to prevent and control this widespread health condition effectively. Empower yourself with knowledge to lead a healthier life and reduce complications associated with diabetes.
Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Preventing Diabetes for Better Health
Diabetes mellitus, commonly referred to as diabetes, is a complex metabolic disorder that impacts millions of people worldwide. Characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, it results from either the body's inability to produce enough insulin or the ineffective use of insulin by the body’s cells. Understanding the intricacies of diabetes is essential to preventing its onset and managing it effectively if diagnosed.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention strategies, and management techniques associated with diabetes. Our goal is to empower individuals with knowledge, enabling them to adopt healthier lifestyles and avoid potential complications.
What is Diabetes? An Overview
Diabetes is a chronic condition that disrupts how your body processes blood sugar (glucose), which is a primary energy source derived from the foods we eat. Glucose enters the bloodstream through digestion, and insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, facilitates the entry of glucose into body cells. These cells use glucose to produce energy necessary for daily functioning.
In diabetes, this process is impaired due to either insufficient insulin production (Type 1 diabetes) or inadequate response to insulin (Type 2 diabetes). Without proper regulation, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia, which can damage various organs over time.
Types of Diabetes and Their Causes
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It often develops in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes: The more common form, typically developing in adults, but increasingly seen in younger populations due to lifestyle factors. It results from insulin resistance, where cells become less responsive to insulin, coupled with a gradual decline in insulin production.
Gestational Diabetes: A type that occurs during pregnancy, increasing the risk for both mother and child to develop Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Diabetes
Many individuals with early-stage diabetes may not experience noticeable symptoms. However, common signs include:
Persistent thirst and dry mouth
Frequent urination, especially during the night
Increased hunger, even after eating
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue and weakness
Blurred vision and slow healing of cuts or wounds
Recurrent infections, such as urinary tract infections or yeast infections
If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to severe complications like cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, eye disorders, and increased risk of infections. Early detection and intervention are vital for better health outcomes.
Risk Factors Contributing to Diabetes
Genetics: Family history of diabetes increases the risk.
Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, significantly raises the likelihood of developing diabetes.
Physical inactivity: Sedentary lifestyles contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Unhealthy diet: Diets high in refined sugars, trans fats, and processed foods promote obesity and metabolic imbalance.
Age: The risk increases with age, especially after 45 years old.
Other factors: Conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and polycystic ovary syndrome are also linked.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Diabetes Risk
Prevention is the most effective way to combat diabetes and its complications. Key preventive strategies include:
Healthy Eating: Emphasize a diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of refined sugars, sugary beverages, and trans fats.
Regular Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight reduces insulin resistance and lowers the risk of developing diabetes.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Drinking in moderation, if at all, helps prevent metabolic issues.
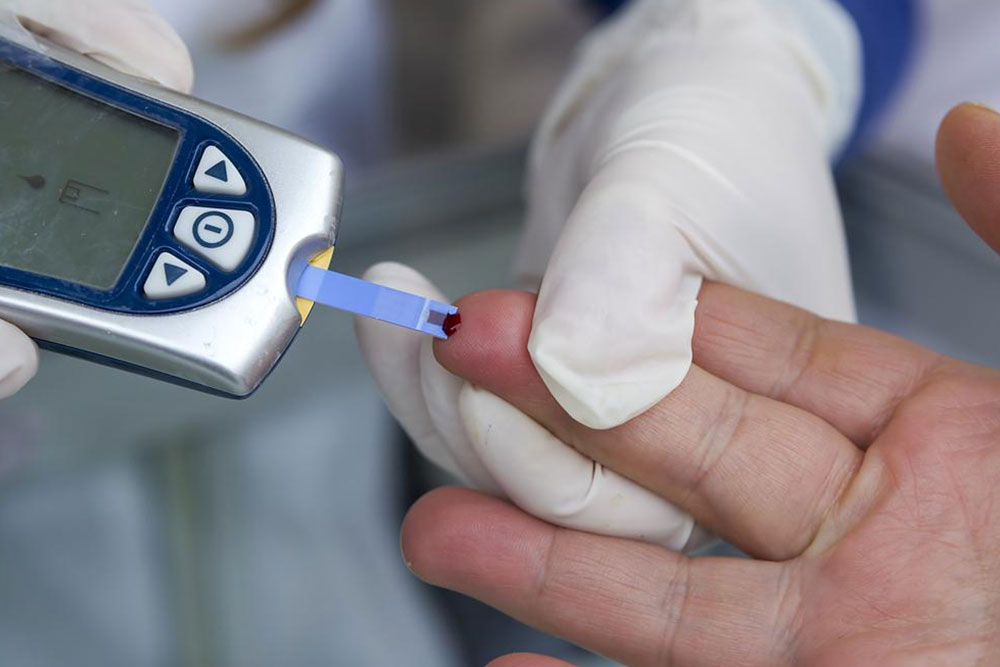
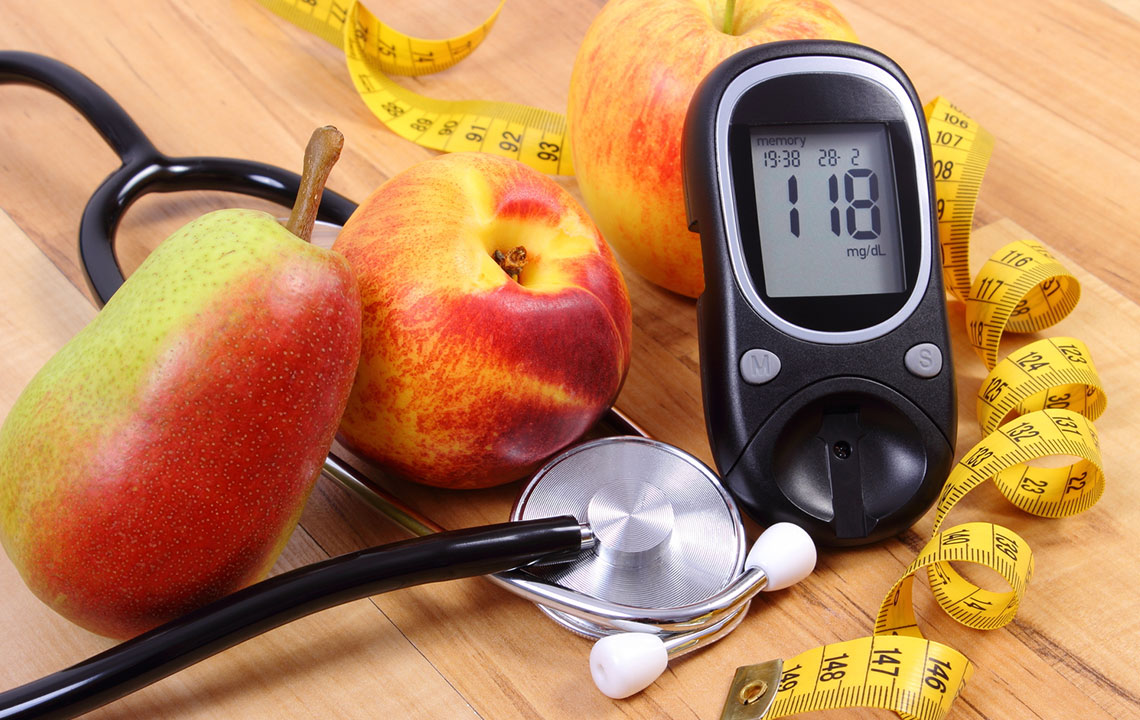
Regular Screening: Periodic blood glucose testing enables early detection and management of prediabetes, preventing progression to diabetes.
Managing and Controlling Diabetes
If diagnosed with diabetes, effective management involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical treatments. Strategies include:
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regular testing helps individuals understand their patterns and take timely action to prevent spikes or drops.
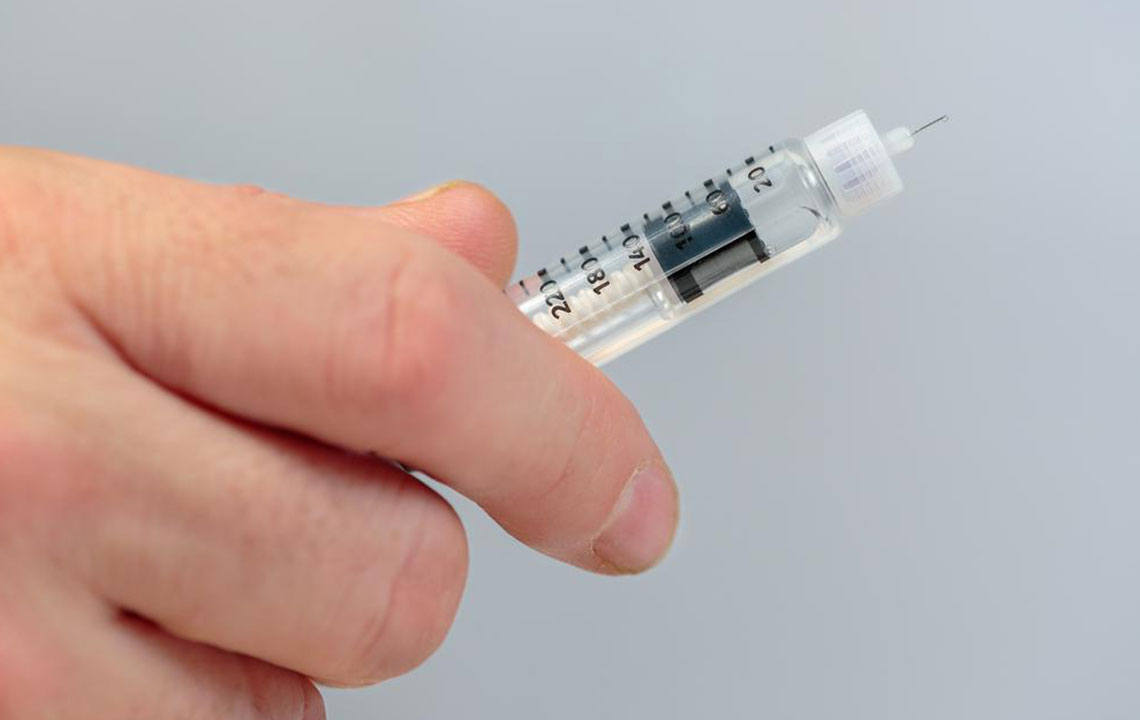
Medications and Insulin Therapy: Depending on the type and severity, doctors may prescribe oral hypoglycemics, insulin, or other medications.
Healthy Lifestyle: Consistent diet control, physical activity, and weight management are critical components.
Education and Support: Diabetes education programs empower patients with knowledge about disease management, nutrition, and preventing complications.
Addressing Comorbidities: Managing associated conditions such as high blood pressure and cholesterol improves overall health and reduces risks.
Conclusion: Take Charge of Your Health Today
Understanding diabetes and taking proactive steps can significantly diminish the risk of developing this chronic condition. Prioritize healthy eating, stay physically active, maintain a healthy weight, and undergo regular health screenings. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, adhere to your healthcare provider’s recommendations and lead a lifestyle that supports optimal blood sugar levels. Remember, with the right knowledge and habits, you can lead a healthy, fulfilling life despite a diabetes diagnosis.