Comprehensive Guide to Lowering Hemoglobin A1C Levels and Managing Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective, practical strategies to lower Hemoglobin A1C levels in diabetes management. Emphasizing regular meal timing, balanced nutrition, physical activity, hydration, weight management, and healthy lifestyle choices, it offers actionable tips for long-term blood sugar control. Suitable for diabetics or those at risk, the article highlights the importance of consistent habits and professional guidance to improve health outcomes and prevent complications associated with high A1C. A must-read for anyone seeking sustainable ways to manage diabetes effectively.

Comprehensive Strategies for Reducing Hemoglobin A1C Levels and Managing Diabetes
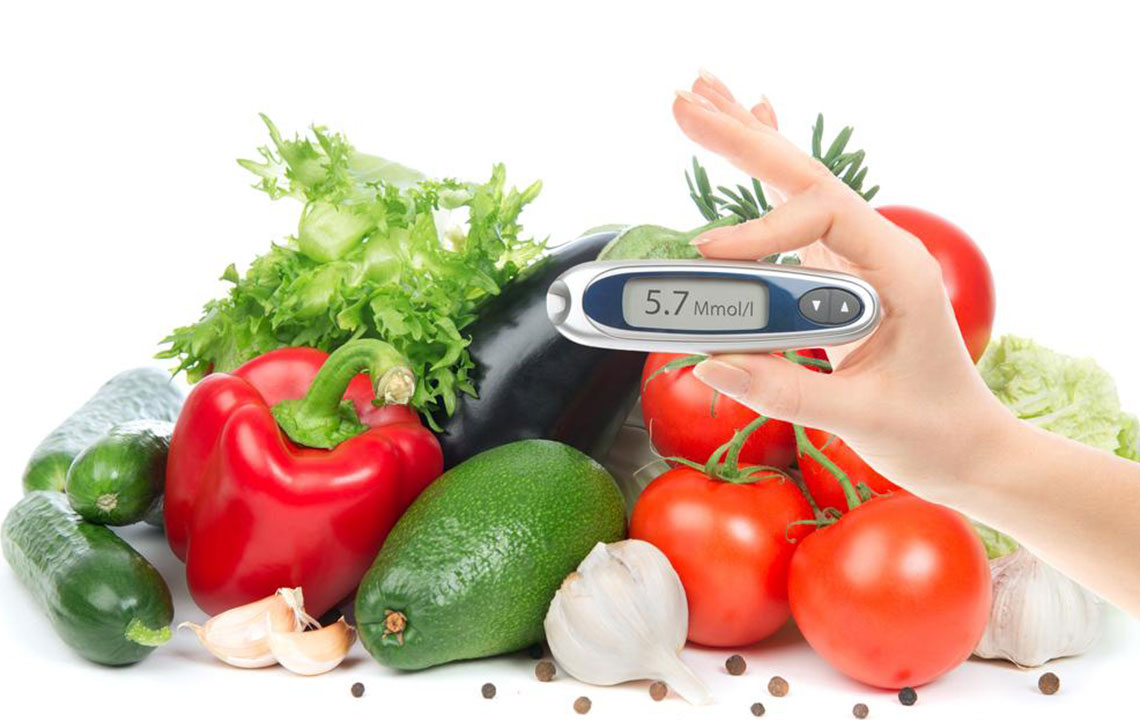
Living with diabetes requires ongoing management and lifestyle adjustments to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. In today's fast-paced world, many individuals face challenges maintaining stability due to irregular routines, unhealthy eating habits, and limited physical activity. Hemoglobin A1C testing offers an insight into your average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months and is a crucial marker for effective diabetes management. Although quick fixes may not drastically impact A1C levels, making consistent, sustainable changes can lead to significant improvements in long-term health outcomes. This comprehensive guide explores proven strategies to help lower Hemoglobin A1C levels effectively, enabling diabetics and those at risk to take control of their health.
Importance of Maintaining Regular Meal Times — Consistency in meal timing is fundamental for stable blood sugar levels. Skipping meals or eating at irregular intervals can cause glucose fluctuations, making it harder to control A1C levels. It’s recommended to have regular, well-spaced meals throughout the day, including a healthy breakfast, which sets the tone for stable blood glucose. A routine helps the body anticipate food intake and manage insulin response efficiently. For individuals with busy schedules, planning meals ahead or setting reminders can support meal consistency and prevent unnecessary blood sugar spikes.
Adopting a Well-Balanced, Nutritious Diet — A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in managing blood glucose. Focus on a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fiber-rich vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Portion control is vital to prevent overeating, which can impair blood sugar regulation. Consulting with a registered dietitian can help craft a personalized meal plan tailored to your specific needs. Incorporating measurement tools like food scales and portion guides can assist in maintaining proper serving sizes. Avoiding empty calories from processed foods and refined sugars ensures more stable glucose levels and aids in lowering A1C.
Incorporate Fruits Wisely — Including fruits in your diet provides essential vitamins and antioxidants beneficial for overall health. Fruits such as berries, cherries, grapes, and apples contain natural sugars but also offer fiber and nutrients that moderate blood glucose spikes when consumed in moderation. It’s advisable to monitor fruit intake and opt for fresh or frozen options over fruit juices or sweetened dried fruits, which can cause rapid increases in blood sugar. Fruits support cardiovascular health and can improve insulin sensitivity when included as part of a balanced diet.
Avoid Processed and Junk Foods — Processed foods, candy, fast food, and sugary beverages are major contributors to poor blood sugar control. These foods are often high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and preservatives that disrupt digestion and cause insulin resistance. Limiting or eliminating these products from your diet is essential for maintaining stable A1C levels. Reading nutrition labels carefully and choosing whole, unprocessed foods can significantly improve your health trajectory. Preparing meals at home provides better control over ingredients and portion sizes.
Keep Diabetic-Friendly Snacks Accessible — When busy schedules prevent timely meals, having diabetic-friendly snacks such as nuts, seeds, low-sugar protein bars, or shakes can help prevent blood sugar dips or spikes. These snacks are convenient options to sustain energy and keep blood glucose levels steady throughout the day. Planning snack options in advance and carrying portable, healthy options ensures you are never caught unprepared, reducing the temptation to reach for unhealthy alternatives.
Switch to Healthier Beverages — Green Tea and More — Replacing sugary drinks like sodas, sweetened teas, and energy drinks with healthier alternatives such as green tea, herbal infusions, or infused water can support blood sugar control. Green tea contains antioxidants and compounds that enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation, proving beneficial for long-term diabetes management. Staying hydrated with water aids in flushing out excess glucose and supports metabolic processes vital for lowering A1C levels.
Prioritize Proper Hydration — Adequate water intake is essential daily, especially since dehydration can be a consequence of excessive urination due to high blood sugar. Proper hydration helps maintain blood volume, supports kidney function, and facilitates the body's efforts to lower glucose levels. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, adjusting based on activity level and climate. Limit or avoid sugary drinks that can worsen hydration issues and blood sugar spikes.
Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Weight — Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, exacerbates insulin resistance and elevates A1C levels. Losing even a modest amount of weight through a combination of diet and exercise can substantially improve blood sugar control. Regularly monitoring your BMI and setting realistic weight loss goals can motivate long-term adherence to a healthy lifestyle. Consulting healthcare professionals for guidance on safe weight management strategies is highly recommended for effective results.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity — Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes the utilization of glucose by muscles. Incorporate at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Including strength training exercises two to three times per week helps build muscle mass, which further improves metabolic health. Even light physical activities like yoga or stretching can contribute to better blood sugar regulation. Consistency is key; find activities you enjoy to maintain long-term commitment.
Managing diabetes effectively involves a combination of early diagnosis, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing monitoring. Regular blood sugar checks, stress management, and adherence to medical advice complement these strategies. With dedication and the right approach, achieving lower Hemoglobin A1C levels and better overall health is entirely possible. Remember, personalized guidance from healthcare providers can optimize your management plan and ensure sustainable health improvements.