Effective Strategies for Lowering Your A1C and Managing Diabetes Effectively
Discover proven strategies to effectively lower your A1C levels through lifestyle modifications, diet, and medical management. This comprehensive guide covers exercise routines, balanced nutrition, meal planning, and helpful foods to aid in controlling blood sugar and preventing diabetes complications. Ideal for individuals seeking to improve their diabetes management, this article provides practical tips and expert advice to achieve and maintain optimal A1C levels for better health.

Effective Strategies for Lowering Your A1C and Managing Diabetes Effectively
Proven methods to control and reduce your A1C levels
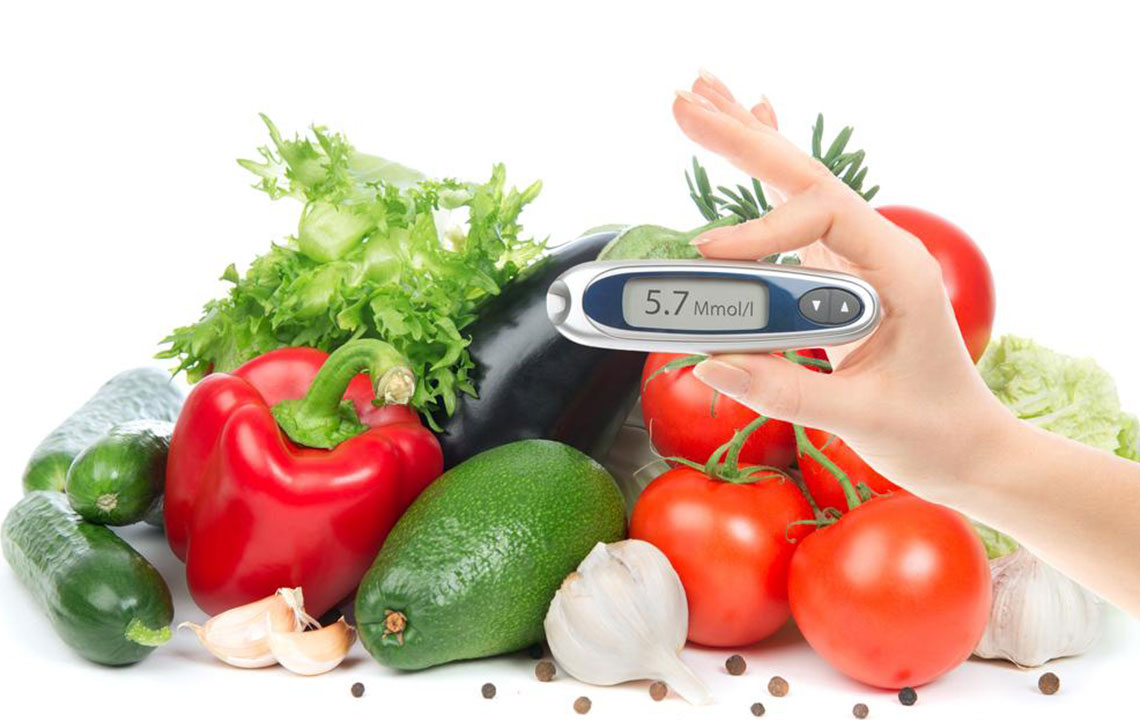
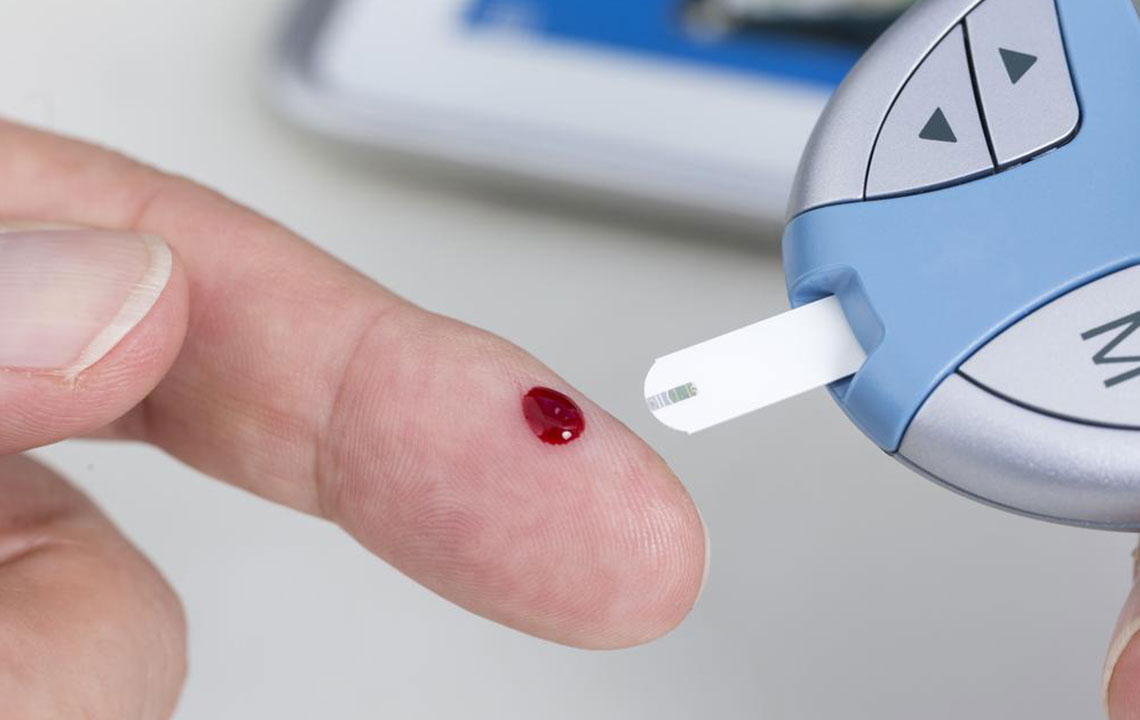
The A1C blood test is a vital tool used to gauge the average level of blood sugar (glucose) over the past three months. It offers insights into how well diabetes is being managed by measuring the percentage of hemoglobin in red blood cells (RBCs) that have glucose attached to them. Since RBCs typically live about three months before being replaced, the A1C provides a comprehensive overview of blood sugar control over this period. For a healthy individual, an A1C level below 5.7% is considered normal. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, suggesting a higher risk of developing diabetes if lifestyle modifications aren't made. An A1C of 6.5% or above usually points to diabetes, and the goal for those diagnosed is often to keep the level below 7% to prevent complications. Maintaining lower A1C levels is essential for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of long-term health issues.
Achieving optimal blood sugar control and reducing your A1C involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medical management. Here are comprehensive strategies that can help you lower your A1C effectively:
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in consistent exercise is one of the most effective ways to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood glucose levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or participating in outdoor sports are excellent options. Spreading out your exercise sessions over five days ensures steady blood sugar levels and enhances overall health. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new workout routine, especially if you have existing health conditions or complications related to diabetes.
Adopt a Balanced and Nutritious Diet
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar. Focus on incorporating a variety of vegetables—particularly leafy greens like spinach and kale—that are low in starch but rich in vital nutrients. Choose moderate portions of fruits, emphasizing berries and non-starchy options, while limiting high-sugar fruits. Lean proteins such as poultry, fish, eggs, and plant-based sources support nutritional balance without spiking blood sugar. Healthy carbohydrates, particularly complex carbs like whole grains, should be monitored and portioned appropriately. Avoid processed foods, sugary beverages, and sodas, which can cause sudden spikes in blood glucose. Consulting with a registered dietitian can help craft a personalized meal plan that supports consistent blood sugar control and promotes overall health.
Maintain Consistent Eating Patterns
Regular meal times help stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day. Skipping meals or overeating can lead to fluctuations that make management more challenging. Keeping a food diary can help identify patterns and habits that influence your blood glucose. Small, frequent meals may be beneficial for some, while others may prefer three balanced meals. It’s essential to work with your healthcare team to develop an eating schedule that fits your lifestyle and health goals.
Adherence to Prescribed Treatment Plans
Managing diabetes successfully often requires a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring. Collaborate closely with your healthcare provider to develop a tailored treatment plan that considers your specific needs, medication regimen, blood sugar targets, and emergency protocols. Regular follow-ups ensure that your management plan remains effective and adaptable to any changing conditions. Never adjust medication doses without medical guidance, and always communicate any concerns or side effects to your healthcare team.
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Consistent self-monitoring of blood glucose levels helps you understand how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. Use a reliable glucometer as advised by your doctor, and record your results to identify trends. Regular monitoring allows timely adjustments to your diet, physical activity, or medication doses, helping you stay within your target A1C range. Some individuals may also benefit from continuous glucose monitoring systems for more detailed insights.
Supporting foods that can help lower A1C include:
Fatty Fish
Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent for managing weight and reducing inflammation. Proper preparation—grilled or baked rather than fried—maximizes health benefits and helps support cardiovascular health, which is especially important for diabetics.
Leafy Greens like Spinach
Spinach provides essential nutrients like Vitamin K, magnesium, and fiber which aid blood sugar regulation. Eating raw or lightly cooked spinach preserves its nutrients and integrates easily into salads or side dishes.
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil
Contains oleic acid, which helps reduce triglyceride levels and increase HDL cholesterol — the “good” cholesterol. Incorporating olive oil into your diet can improve heart health and assist in overall diabetes management.
Cruciferous Vegetables like Broccoli
Broccoli contains sulforaphane, a compound with anti-inflammatory properties and potential to lower A1C levels. Its consumption can also strengthen cardiovascular health and protect against related complications.
Eggs
A high-quality protein source that, in moderation, can improve satiety, support weight management, and contribute to A1C reduction. Eggs can be included in various meals to enhance nutritional diversity.
Remember, diet alone isn't enough. Combining these dietary habits with physical activity, medication adherence, and regular monitoring creates a comprehensive approach to managing blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy A1C.