Effective Lifestyle Changes to Lower Your A1C Levels and Manage Diabetes Better
Discover comprehensive strategies to effectively lower your A1C levels and improve diabetes management. This article provides actionable lifestyle tips, including exercise, diet, routine habits, and medical adherence, to help you achieve better blood sugar control and prevent complications. Incorporate these proven methods into your daily life for lasting health benefits and improved quality of life.

Effective Lifestyle Changes to Lower Your A1C Levels and Manage Diabetes Better
Managing diabetes effectively is vital to prevent severe health complications and improve quality of life. The A1C test is a critical measure that reflects your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, providing essential insight into your diabetes control. Keeping your A1C within the recommended target range can significantly reduce the risk of developing complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and cardiovascular problems. Achieving optimal A1C levels often requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular health monitoring.
Proven Strategies for Lowering A1C Levels
Utilizing the guidance provided by the A1C chart, individuals with diabetes can implement multiple effective strategies to maintain better blood glucose control and enhance overall health.
Key approaches to lowering A1C include:
Engaging in consistent physical activity plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or jogging. Physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity, helping your body use glucose more effectively, thereby reducing A1C levels over time.
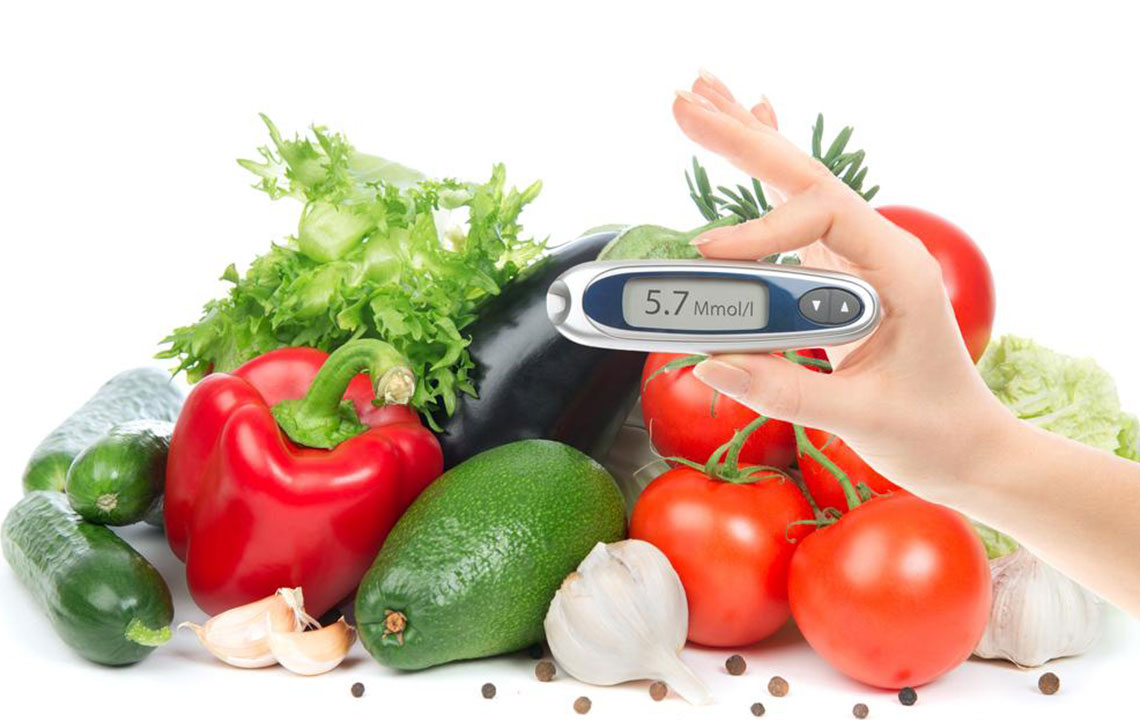
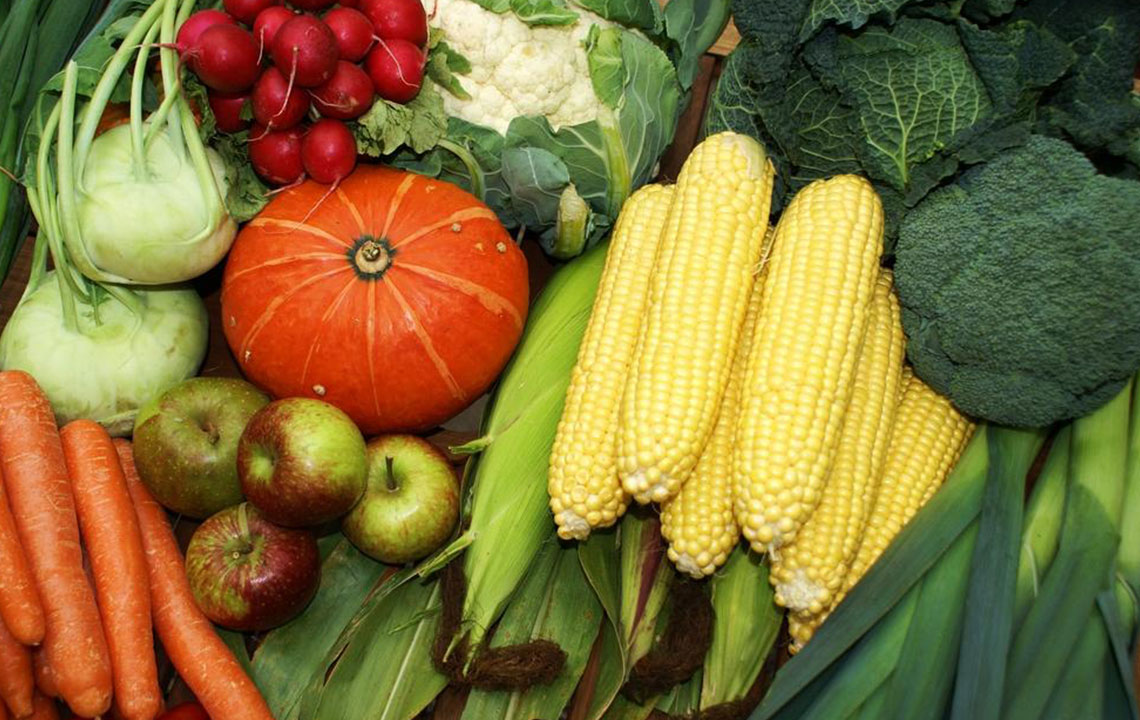
Adopting a nutritious, well-balanced diet is fundamental. Focus on consuming a variety of non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and peppers. Monitor portion sizes carefully for fruits, grains, and proteins to avoid excessive carbohydrate intake. Incorporate complex carbohydrates such as sweet potatoes, whole grains, and legumes because they have a lower glycemic index and promote stable blood sugar levels.
Maintaining consistent meal times and avoiding long fasting periods help prevent unwanted blood sugar fluctuations. Skipping meals or irregular eating patterns can lead to spikes or drops in blood glucose, complicating diabetes management. Structured eating routines support steady glucose levels, making it easier to keep A1C within the target range.
Following your healthcare provider’s treatment plan diligently is key to effective diabetes management. This includes taking prescribed medications, insulin therapy if recommended, and regular check-ups. Adjustments to your treatment plan may be needed based on your blood sugar monitoring results and overall health progress.
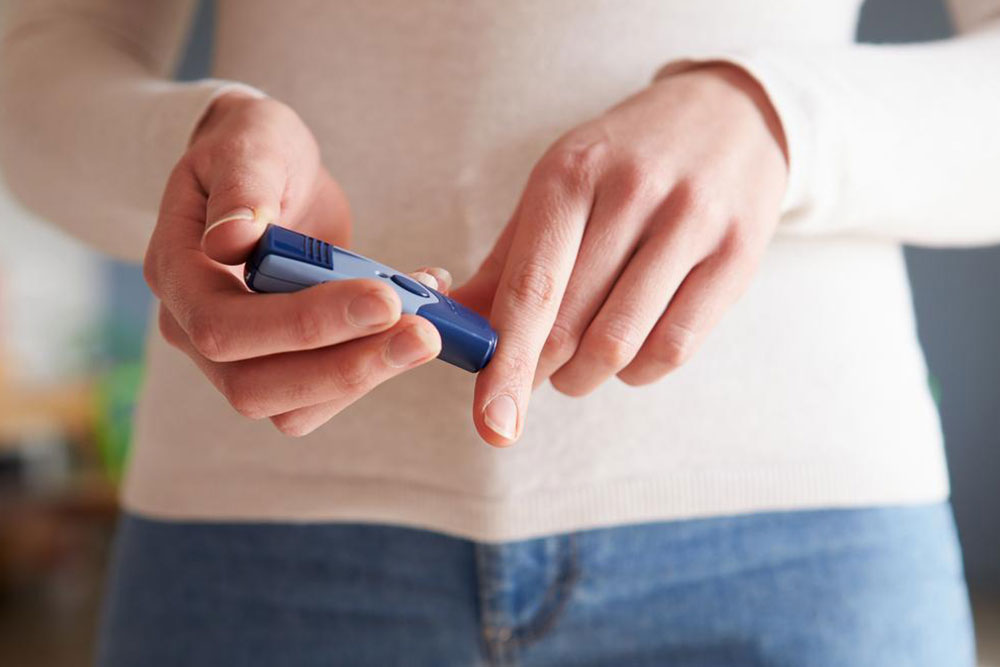
Regular blood glucose monitoring provides real-time feedback on how your lifestyle choices impact your levels. Using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM), check your blood sugar as advised by your healthcare team. Prompt detection of high or low readings allows for timely interventions, reducing the risk of complications and helping to sustain optimal A1C levels.
By consistently applying these lifestyle modifications, individuals can successfully lower their A1C levels, which can delay or prevent the progression of diabetes and related health issues. Remember, small, sustained changes often lead to the most significant long-term benefits, and working closely with your healthcare provider ensures personalized and effective management of your condition.