Comprehensive Guide to Lowering Your A1C Levels for Better Health
Discover effective, comprehensive strategies to lower your A1C levels and enhance your overall health. From personalized diet plans and regular exercise to medication management and lifestyle adjustments, this in-depth guide offers practical advice to help you achieve better blood sugar control and prevent complications. Empower yourself with tailored approaches and expert tips for sustainable health improvements and a longer, healthier life.

Comprehensive Strategies to Lower Your A1C Levels and Enhance Overall Well-being
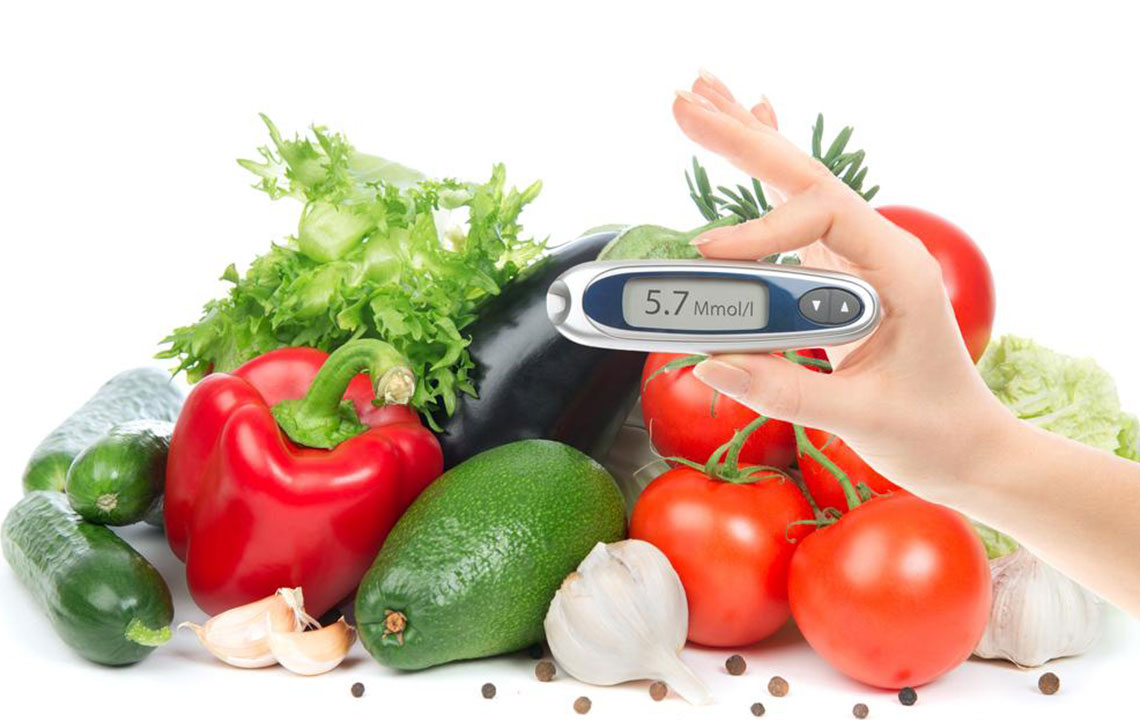
Maintaining optimal A1C levels is a critical aspect of managing diabetes and preventing related health complications such as vision loss, kidney failure, nerve damage, and heart disease. The A1C test, also known as glycated hemoglobin test, offers a snapshot of your average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. Elevated A1C levels signal the need for effective lifestyle modifications and medical interventions to improve health outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we explore proven strategies to help you successfully lower your A1C levels, supporting a healthier lifestyle and reducing your risk for chronic complications.
Understanding the importance of A1C management is the first step toward long-term health improvement. Whether you are recently diagnosed or have been managing diabetes for years, implementing tailored approaches can make a significant difference. Developing a personalized plan that integrates dietary changes, physical activity, medication management, and stress reduction techniques will empower you to achieve and maintain lower A1C levels.
Effective strategies for lowering A1C involve a multifaceted approach, combining nutrition, exercise, medication adherence, and lifestyle adjustments. The following sections detail essential actions you can take to improve your blood sugar control and overall health:
Develop a Personalized Action Plan
Start by consulting with your healthcare provider to design a tailored plan addressing your unique health status and goals. A customized plan ensures that you focus on achievable targets such as weight management, balanced nutrition, stress management, and regular monitoring. Setting realistic, incremental goals helps in tracking progress and maintaining motivation over time.
Prioritize Nutrient-Dense, Low-Carbohydrate Foods
Adopting a diet rich in vegetables and low in simple carbohydrates is fundamental for controlling blood glucose levels. Incorporate plenty of green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, broccoli, and asparagus, which are naturally low in digestible carbs and high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Keeping a food diary or digital tracking app can assist in maintaining consistent healthy eating habits and avoiding blood sugar spikes.
Incorporate Fruits Wisely: Choose fruits that have a low glycemic index and are known for their benefits in lowering LDL cholesterol and promoting heart health. Blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries are excellent options as they contain antioxidants and fiber that support metabolic health and help reduce A1C levels.
Insulin and Medication Management
For individuals with Type 1 diabetes or insulin-dependent Type 2 diabetes, proper insulin administration is vital. Work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the correct type, dosage, and timing of insulin injections. Never adjust your insulin without guidance, and adhere strictly to prescribed schedules to prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity plays a significant role in lowering blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or jogging, per week. Incorporate strength training exercises twice a week to build muscle mass, which further aids glucose utilization. Exercise also supports weight loss, boosts cardiovascular health, and enhances overall energy levels, creating a positive cycle of health improvements.
Choose Healthy, Lean Proteins and Fats
Incorporate lean protein sources like grilled chicken, turkey, and seafood into your diet. Emphasize omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel, which help reduce triglycerides and improve insulin response. Limiting saturated and trans fats is also crucial for cardiovascular health.
Prioritize Routine Medical Check-Ups and Monitoring
Regular visits to your healthcare team are crucial for tracking your progress, adjusting treatment plans, and ensuring your efforts are yielding results. Routine blood tests, including the A1C, fasting blood glucose, and lipid profile, provide valuable insights into your overall health and help tailor ongoing management strategies.
Implement Stress Reduction and Lifestyle Improvements
Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels and hinder glycemic control. Incorporate stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Adequate sleep, hydration, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption further support optimal health and A1C management.
In conclusion, lowering your A1C levels requires a comprehensive approach that combines dietary mindfulness, consistent physical activity, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications. With ongoing support from healthcare professionals and a committed effort, you can achieve better blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and enjoy an improved quality of life. Remember, individualized plans and continuous monitoring are key to sustained success on your health journey.