Unlocking the Health Benefits of a Low-Carbohydrate Diet Plan
This article explores the numerous health benefits of adopting a low-carb diet, including improved blood sugar control, reduced diabetes-related complications, increased energy, and potential reversal of type-2 diabetes. Emphasizing safe implementation, it offers insights into how a low-carb lifestyle enhances overall well-being, supported by scientific evidence. Suitable for those seeking healthier living, this guide underscores the importance of medical consultation and gradual dietary changes for optimal results.
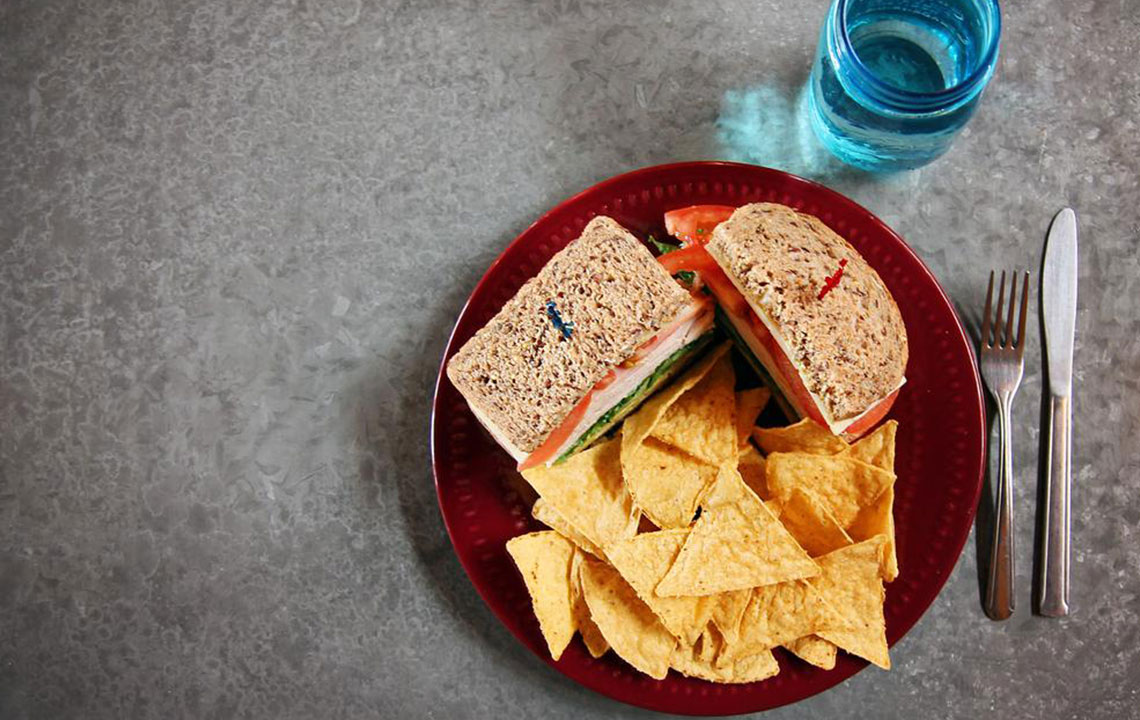
The Significant Health Advantages of Adopting a Low-Carbohydrate Diet
When discussing dietary modifications, especially reducing carbohydrate intake, many people instantly associate it with weight loss efforts. While weight management is a prominent benefit, adopting a low-carb eating plan offers a wide array of health improvements that extend beyond just losing pounds. This dietary approach can profoundly enhance your overall health, boost energy levels, and support the prevention of chronic diseases, making it a worthwhile consideration for anyone aiming for a healthier lifestyle.
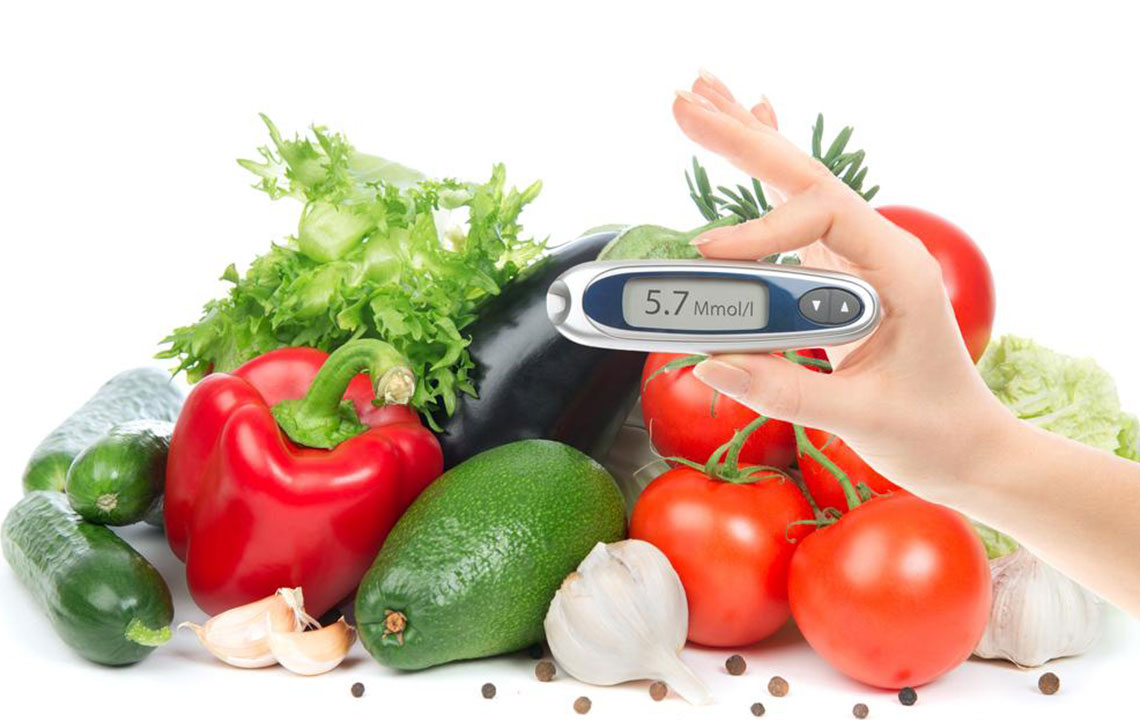
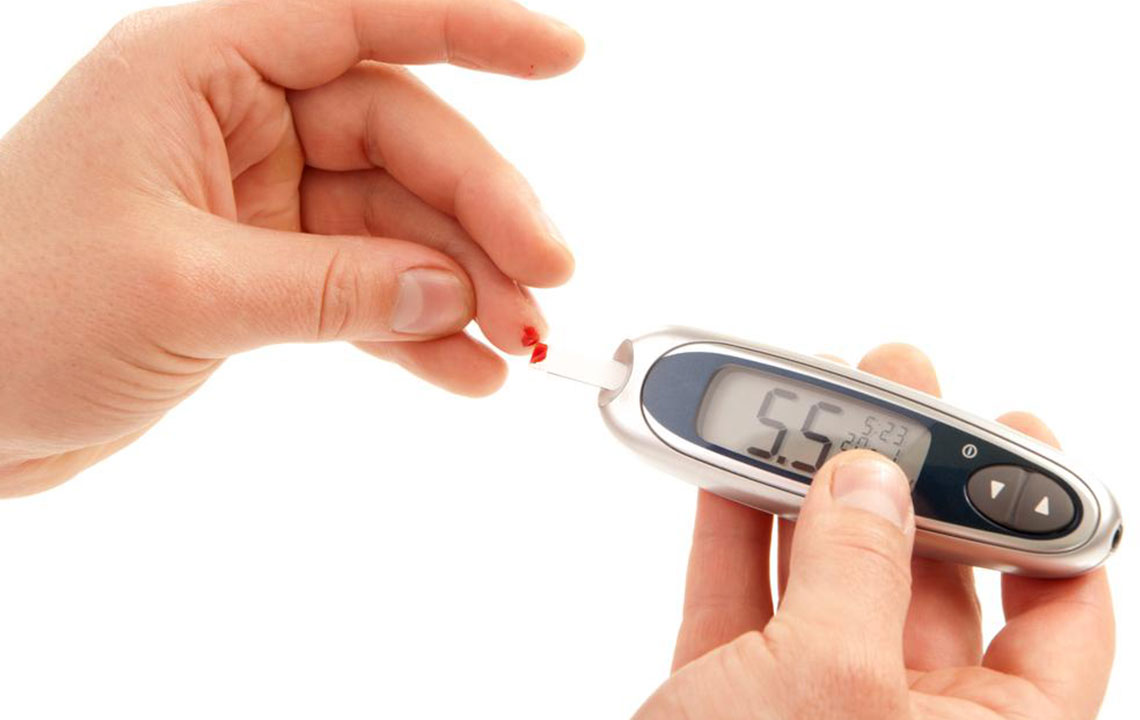
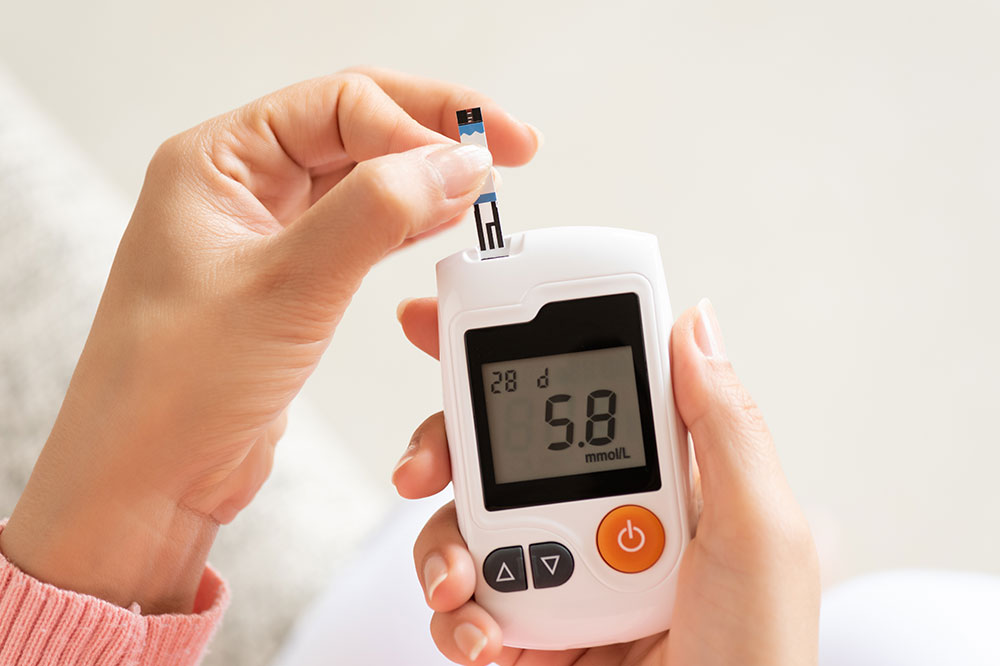
So, why should you consider a low-carb diet? The advantages are numerous and backed by scientific research. Consuming fewer carbohydrates helps regulate blood sugar levels more effectively, leading to improved insulin sensitivity. This can result in lower glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, which is vital for managing and preventing diabetes complications. Additionally, a low-carb diet can reduce the frequency and severity of severe hypoglycemic episodes, improve cognitive function, increase vitality, curb sugar cravings, and foster better mental clarity. These benefits contribute to reducing the long-term risks associated with metabolic and cardiovascular diseases, making it a comprehensive approach to health enhancement.
Lowering HbA1c levels is a critical aspect of controlling diabetes and preventing severe complications. Scientific studies reveal that individuals with diabetes who adopt a low-carb diet can reduce microvascular complications like retinopathy (eye damage), neuropathy (nerve damage), and nephropathy (kidney issues) by approximately 25%. Maintaining stable blood glucose levels helps safeguard eyesight, nerve health, and kidney function. For those managing type-2 diabetes, a mere 1% decrease in HbA1c can significantly diminish risks of developing cataracts, experiencing heart failure, undergoing amputations, and facing vascular-related mortality. Notably, low-carb diets enable many type-2 diabetics to control their blood sugar levels effectively without relying heavily on medications. Furthermore, individuals with type-1 diabetes also benefit from more stable blood sugar levels, although they should consult their healthcare providers before making significant dietary changes.
Incorporating natural vegetables, high-fiber foods, and wholesome, minimally processed options into your diet naturally helps modulate insulin levels. Such dietary habits can potentially reverse early-stage type-2 diabetes, reducing dependency on medication and promoting metabolic health. It’s important to recognize that dietary shifts should be tailored to individual health profiles and implemented gradually under medical supervision.
While the positive impacts of reducing carbohydrate intake are well established, it’s essential to approach this dietary change cautiously. Consulting with your healthcare provider is crucial, especially if you are on medications like insulin or sulfonylureas, which can increase the risk of hypoglycemia when carbs are decreased. Pregnant women or those planning conception should avoid abrupt dietary modifications without medical advice, as rapid carbohydrate reduction might lead to adverse effects such as fatigue, brain fog, headaches, constipation, or nutritional deficiencies. An individualized, balanced approach ensures that the benefits of a low-carb diet are maximized while minimizing potential risks.