Comprehensive Guide to the A1C Chart: Your Essential Tool for Effective Diabetes Management
This comprehensive guide explains the significance of the A1C chart in managing diabetes effectively. It covers the basics of diabetes types, symptoms, and the importance of regular A1C monitoring. Learn how to interpret A1C results, set appropriate targets, and implement lifestyle changes to maintain optimal glucose control. By understanding this essential tool, patients can actively participate in their treatment plans to reduce complications and improve their overall health. The article emphasizes that while diabetes is incurable, proper management through regular testing and lifestyle adjustments empowers patients to lead healthier lives.

The A1C Chart: An Integral Component in Managing Diabetes Effectively
Diabetes mellitus is a prevalent chronic health condition affecting millions globally. This disorder is primarily characterized by disturbances in insulin production and function, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Proper management of diabetes is crucial to prevent severe complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss. Among the many tools healthcare professionals and patients use to monitor and control this condition, the A1C chart stands out as one of the most vital metrics. Understanding how to interpret and utilize the A1C chart can significantly improve long-term health outcomes for individuals living with diabetes.
To comprehend the significance of the A1C chart, it is essential to understand the fundamentals of diabetes. The disease is broadly categorized into two primary types: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in little to no insulin production, necessitating lifelong insulin therapy for management. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes, which typically manifests in adulthood but is increasingly diagnosed in younger populations, involves insulin resistance and relatively inadequate insulin secretion. In this form, the body either does not produce enough insulin or the cells become less responsive to insulin, disrupting normal glucose metabolism.
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the severity and type but often include persistent excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, blurred vision, numbness or tingling sensations in the extremities, and slow wound healing. Some individuals may remain asymptomatic, especially in the early stages, making regular screening crucial for early detection and management.
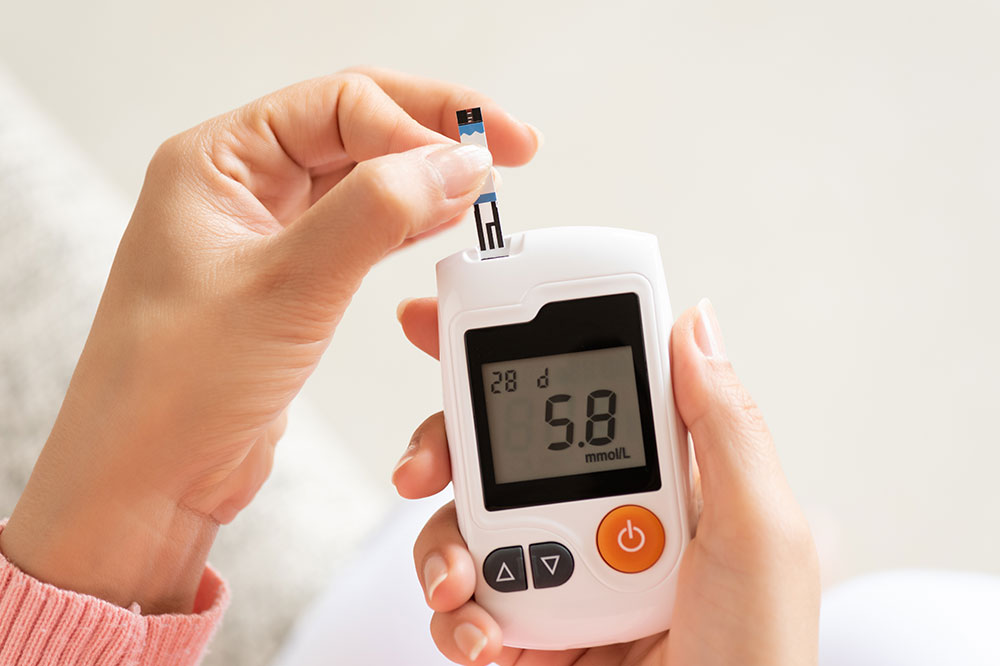
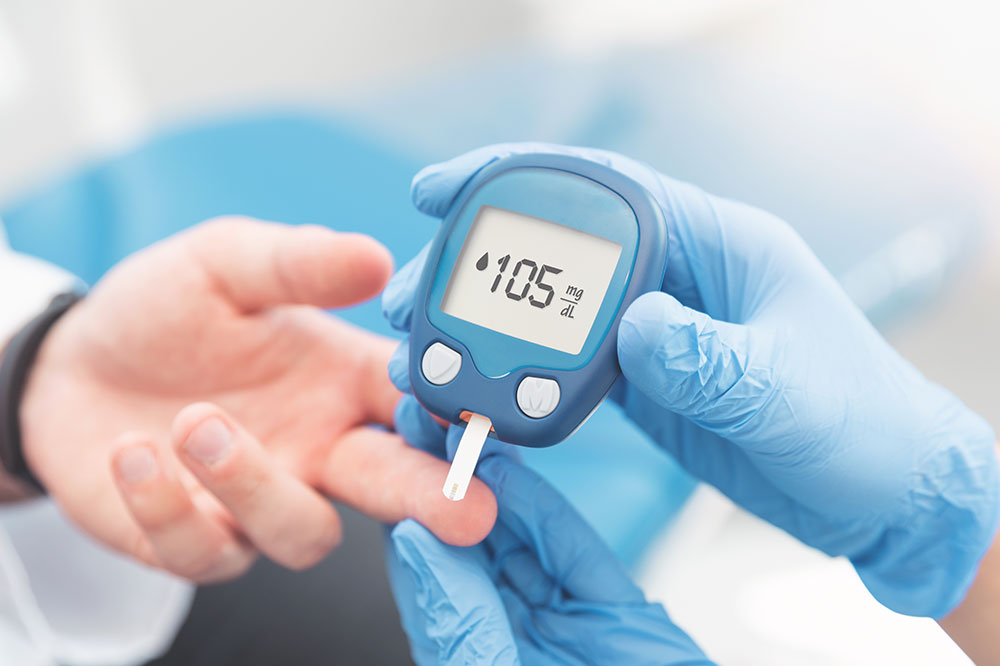
The A1C, also known as glycated hemoglobin or hemoglobin A1C, reflects the average blood glucose levels over the preceding two to three months. This diagnostic test measures the percentage of hemoglobin molecules in the blood that have been coated with sugar. A higher percentage indicates poorer glucose control and an increased risk of diabetes-related complications. Consequently, regular monitoring through the A1C test allows patients and healthcare providers to assess how well the current treatment plan is working and to make necessary adjustments.
Maintaining optimal A1C levels is a key objective for diabetes management. Generally, an A1C level below 7% is considered desirable for most adults with diabetes, although targets may vary depending on individual health conditions and treatment goals. For example, some older patients or those with multiple health issues may have more lenient targets to balance the benefits of control against the risk of hypoglycemia.
Achieving and maintaining target A1C levels requires a multifaceted approach. Patients are encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle habits such as engaging in regular physical activity, adhering to prescribed medication regimens, and following a balanced, nutritious diet. Meal planning plays a vital role in controlling blood glucose levels—limiting intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, sweetened beverages, and alcohol is recommended. Consistency is crucial; eating meals at regular intervals and monitoring blood sugar levels frequently help identify patterns and prevent dangerous spikes or drops.
The importance of regular blood testing cannot be overstated. Patients should collaborate closely with their healthcare team to understand their specific A1C targets and employ tools like blood glucose meters and continuous glucose monitors for daily management. Making timely adjustments to medication and lifestyle based on these insights can dramatically reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Although diabetes is currently considered an incurable disease, controlling blood glucose levels effectively can minimize symptoms and prevent or delay the onset of serious health issues. The A1C chart provides a clear, comprehensive picture of a patient’s glucose control over time, empowering individuals to take proactive steps in their health journey. Education, support, and consistent management are the keys to living well with diabetes. Ultimately, understanding and utilizing the A1C chart is an essential cornerstone in the ongoing effort to optimize health outcomes for millions worldwide.