Early Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis You Should Know
Discover the crucial early signs of rheumatoid arthritis, including persistent fatigue, joint stiffness, and swelling. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely diagnosis and effective treatment, preventing joint damage and improving quality of life. Learn about the key indicators and the importance of prompt medical attention to manage RA effectively.

Understanding the Early Indicators of Rheumatoid Arthritis
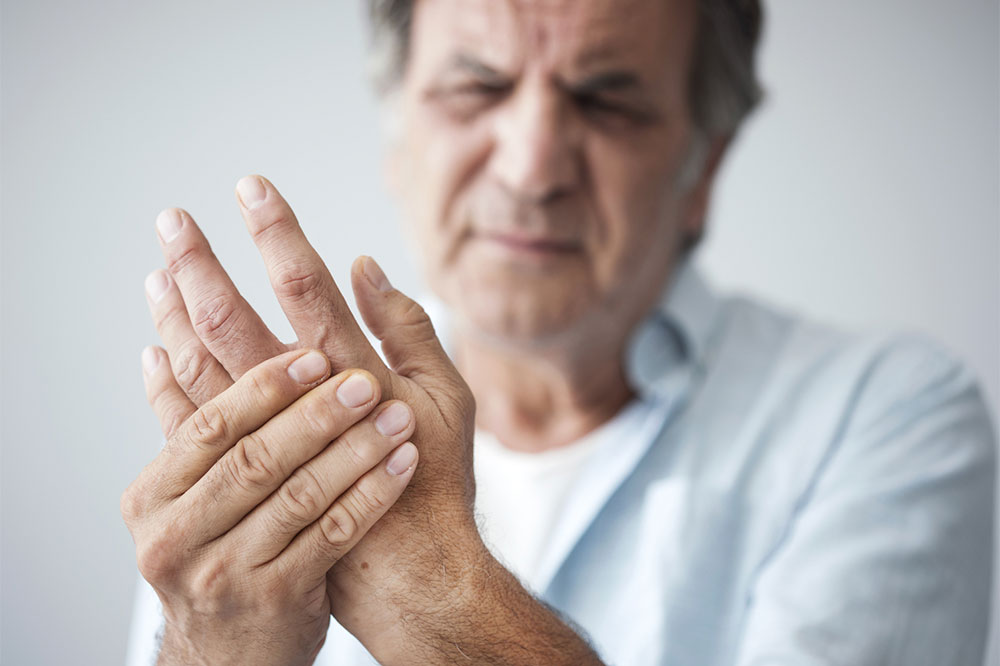
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential joint destruction if not diagnosed and treated early. This condition occurs when the immune system erroneously targets the synovial membrane—the lining of the joints—causing swelling and damage over time. Recognizing RA in its initial stages is crucial because early intervention can significantly slow disease progression, preserve joint function, and improve overall quality of life.
Many individuals may not notice symptoms initially, or they may dismiss early signs as minor or temporary discomforts. However, understanding and identifying the earliest symptoms can lead to prompt medical consultation, early diagnosis, and effective management strategies. This article aims to shed light on the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis, including subtle symptoms that often go unnoticed, and emphasizes the importance of timely medical intervention.
Menacing Fatigue
One of the most common early symptoms is persistent tiredness too severe to be explained by normal exertion or lack of sleep. This fatigue can occur even after adequate rest and may interfere with daily activities, signaling underlying inflammation or immune activation.
Low-grade Fever
Mild but ongoing fever, often unnoticed, can indicate systemic inflammation. Unlike infections, this low-grade fever persists without other apparent signs of illness, marking an early inflammatory response linked to RA.
Unexpected Weight Loss
Unintentional weight reduction over a relatively short period can be an early warning sign, often associated with autoimmune activity and metabolic disturbances caused by inflammation.
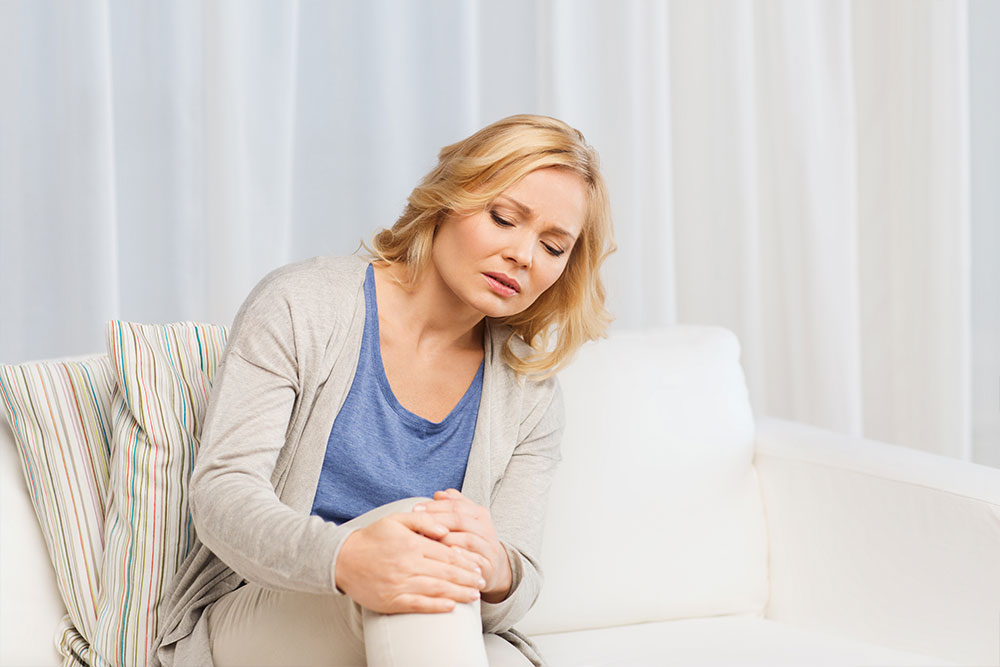
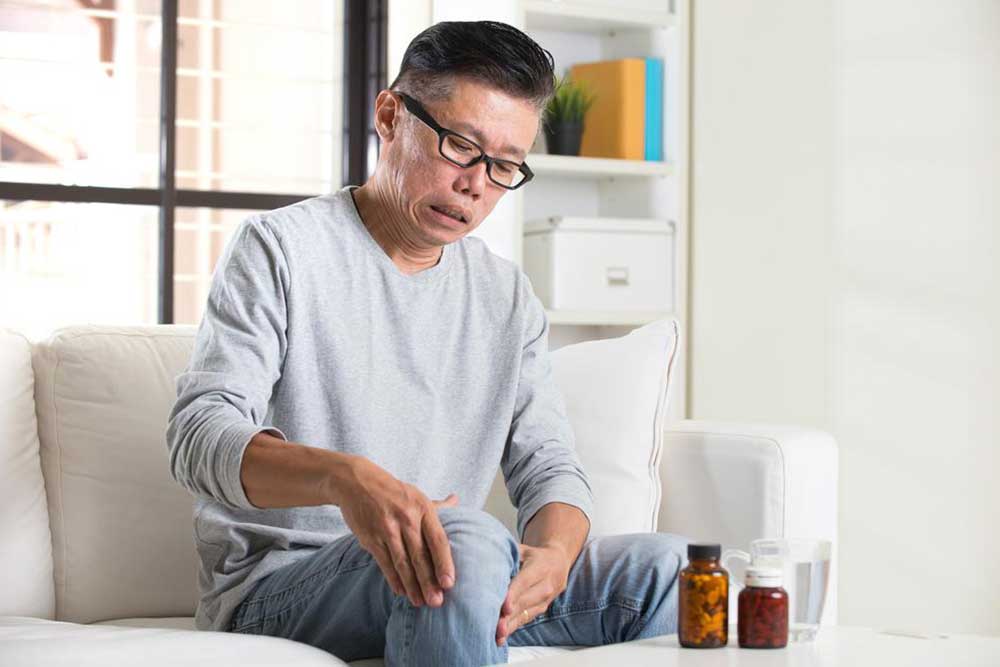
Persistent Joint Stiffness
Stiffness that lasts for hours, especially after periods of inactivity such as mornings or after sitting for extended times, can be an early sign of joint inflammation. This stiffness may affect multiple joints symmetrically, particularly the fingers, wrists, and knees.
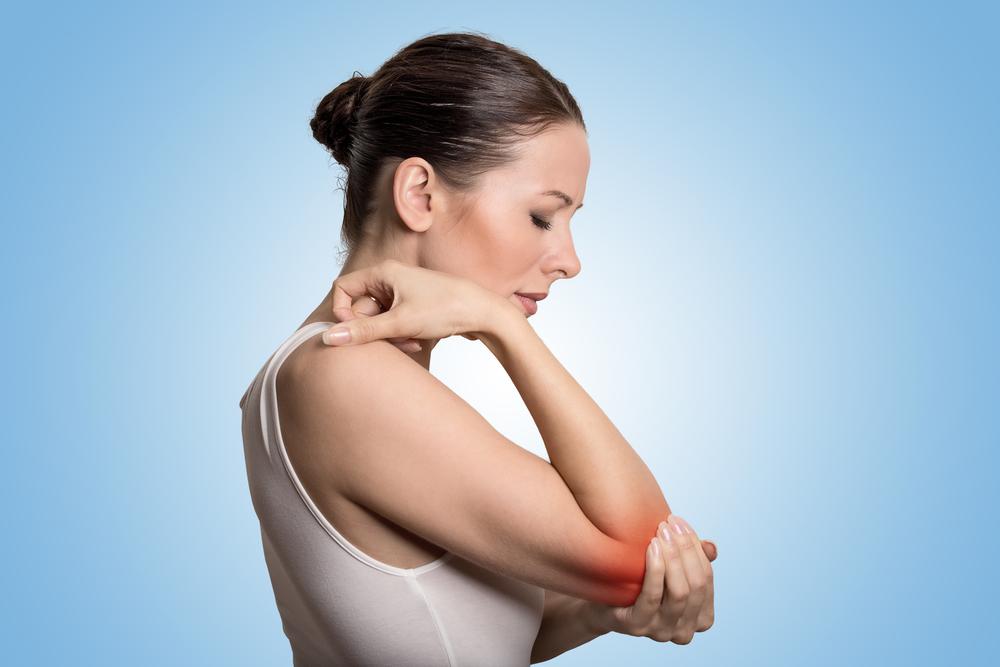
Joint Tenderness and Discomfort
Initially, joints may become tender to touch without obvious swelling. Tenderness often accompanies sensations of warmth, indicating inflammatory processes in the joints.
Noticeable Joint Pain
Pain especially in small joints—fingers, toes, wrists—tends to be a hallmark of early RA. The pain can be dull or throbbing and may worsen with activity but also occur at rest.
Localized Swelling
Inflamed joints may appear visibly swollen, giving a sense of fullness or enlargement, often accompanied by a feeling of tightness.
Redness and Warmth
Affected joints appear visibly red and feel warm compared to surrounding areas, reflecting active inflammation.
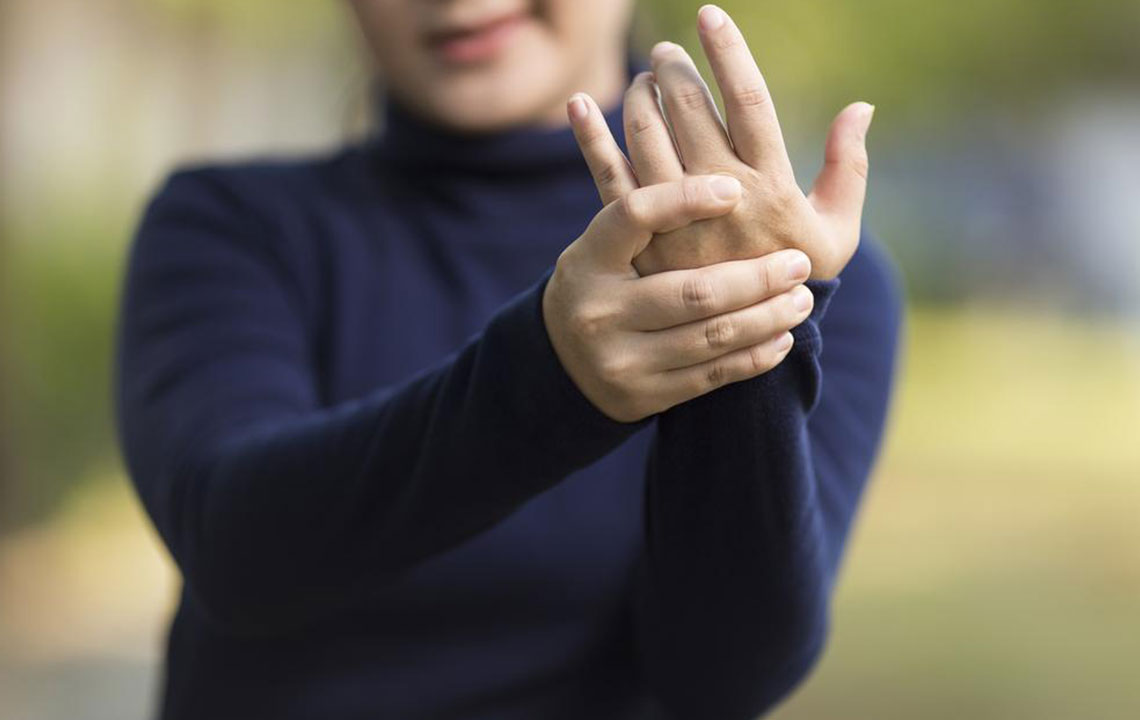
Increased Sensation of Numbness and Tingling
Numbness, tingling, or a pins-and-needles sensation in the fingers, hands, or feet may signal nerve involvement secondary to joint inflammation or swelling.
Early detection of rheumatoid arthritis is vital because, although there is no definitive cure, early treatment can significantly alter its course. Medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, and regular monitoring by healthcare providers are essential components of managing RA effectively. Prompt intervention can reduce flare-ups, prevent irreversible joint damage, and maintain mobility and quality of life.
If you notice these early symptoms, consult a healthcare professional without delay. Early diagnosis and treatment initiation not only help control symptoms but also prevent the long-term consequences of joint destruction. Recognizing the initial signs of rheumatoid arthritis can be life-changing, empowering individuals to take proactive steps toward better health and well-being.