Comprehensive Guide to Detecting and Managing Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
This comprehensive guide explores the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis, highlighting the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment. It covers symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and available treatment options, emphasizing early intervention to prevent joint damage and systemic complications. Understanding these aspects can help individuals seek timely medical care, improving their quality of life and long-term health outcomes.

Understanding the Early Symptoms and Treatment Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Essential insights into early detection, diagnosis, and treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by persistent inflammation of the joints, which can lead to irreversible damage if not identified and managed promptly. This condition commonly affects joints in the knees, hands, feet, and fingers, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and over time, potential joint deformity. The importance of recognizing early signs of RA cannot be overstated, as early intervention significantly improves the prognosis and helps prevent severe complications.
RA develops when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy joint tissues, primarily targeting synovial membranes lining the joints. This autoimmune response results in inflammation, which, if left untreated, can damage the cartilage, bones, and surrounding tissues. Globally, approximately 1.5 million individuals in the United States alone live with rheumatoid arthritis, reflecting its significant impact on public health.
This disease can affect individuals of any gender or age group, though it predominantly targets women aged 30 to 60. Both sides of the body are usually involved symmetrically, especially in the joints of the hands, wrists, knees, and feet. The symmetrical pattern of joint involvement is a typical hallmark of RA. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to mitigate long-term joint destruction and systemic health issues caused by ongoing inflammation.
Vascular complications: Inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) can lead to nerve damage, skin lesions, and impact organ function.
Lung involvement: Pulmonary inflammation may cause breathing difficulties, fibrosis, or pleuritis.
Ocular symptoms: Dry eyes, redness, pain, light sensitivity, or blurred vision may occur due to inflammation.
Skin and mucosal issues: Dryness, small nodules under the skin, or gum irritation are common manifestations.
Early signs and symptoms of RA include:
Persistent fatigue and malaise
Stiffness, especially in the mornings or after periods of inactivity
Swollen, tender joints
Minor joint redness or warmth
Low-grade fever
Numbness, tingling sensations, or a sensation of pins and needles
Reduced joint mobility or range of motion
While RA shares some symptoms with other conditions like fibromyalgia, they are distinct diagnoses. RA is an autoimmune disorder primarily attacking joints and related tissues, whereas fibromyalgia involves widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and mood disorders. Consulting a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis is essential if you experience these symptoms.
Other potential RA symptoms might include sleep disturbances, chest pain during breathing, unexplained weight loss, dry mouth, itchy or red eyes, eye discharge, and loss of appetite. Recognizing these signs early and seeking medical evaluation can significantly impact disease management and outcomes.
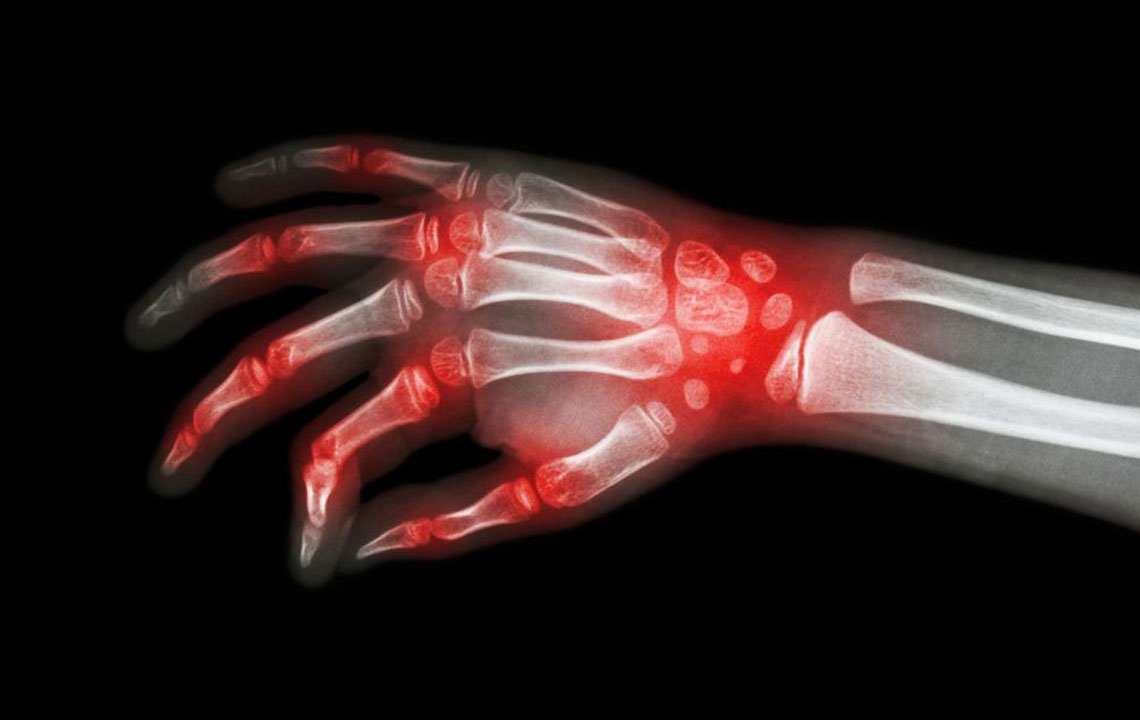
Diagnosing RA involves comprehensive testing, as no single test can definitively confirm the disease. Medical professionals will review your medical history, conduct thorough physical examinations, and may order laboratory and imaging tests. Blood tests for markers of inflammation, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), along with autoantibodies like rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies, aid in diagnosis. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound and X-rays help identify joint damage and inflammation levels. Early diagnosis allows timely initiation of treatment options.
Various treatment strategies are available for RA, aiming to reduce inflammation, manage pain, prevent joint damage, and improve quality of life. Common medications include pain relievers like acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, corticosteroids for acute flare-ups, and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate. Biologic agents, targeting specific immune pathways, are also effective for moderate to severe cases. In some instances, surgical intervention (e.g., joint repair or replacement) becomes necessary, typically as a last resort. The key to successful management lies in early and consistent treatment adherence.
Preventing severe health complications associated with RA, such as cardiovascular issues, lung disease, and osteoporosis, relies heavily on early detection and appropriate medical management. Regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications—such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and smoking cessation—and adherence to prescribed therapies are vital components of comprehensive care.