Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Early Signs and Symptoms of Lupus Autoimmune Disease
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disorder with early signs that can be subtle yet indicative of serious health issues. Recognizing symptoms such as fatigue, skin rashes, joint pain, and kidney problems is essential for early diagnosis. This comprehensive guide details the symptoms, urgency of diagnosis, and management strategies to help individuals understand and identify lupus early. Timely intervention can prevent severe complications and improve quality of life. Stay informed about the warning signs to ensure prompt medical attention and effective treatment for this challenging disease.
Understanding the Early Indicators of lupus and How to Detect Them
Lupus, medically termed systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a complex autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs. This misdirected immune response leads to widespread inflammation and tissue damage, affecting multiple organ systems including skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and the nervous system. Recognizing the early signs of lupus is critical for timely diagnosis and effective management, which can significantly improve quality of life and prevent severe complications.
While the exact cause of lupus remains unknown, it involves a combination of genetic, environmental, hormonal, and immune factors. The condition predominantly affects women during their reproductive years, usually between the ages of 14 and 45, although men and children can also develop the disease. Early detection relies on awareness of subtle symptoms that often develop gradually over time, punctuated by periods of flare-ups and remission. Being vigilant about these initial signs can lead to earlier medical intervention, which is essential for controlling disease progression and minimizing organ damage.
Persistent Fatigue
A hallmark symptom of lupus is extreme, persistent fatigue that doesn't improve with rest. Individuals often feel overwhelmingly tired during the day, sometimes needing frequent naps to regain energy. This fatigue stems from the body's ongoing inflammatory response and immune system dysfunction. Patients may also experience sleep disturbances, such as insomnia, further exacerbating exhaustion and reducing overall vitality.
Unexplained Recurrent Fever
Many lupus patients experience low-grade or persistent fevers without an apparent infection. These fevers, often unexplained, are a sign of systemic inflammation. When accompanied by other symptoms, they should prompt healthcare providers to consider lupus as a potential diagnosis and conduct appropriate blood tests and assessments.
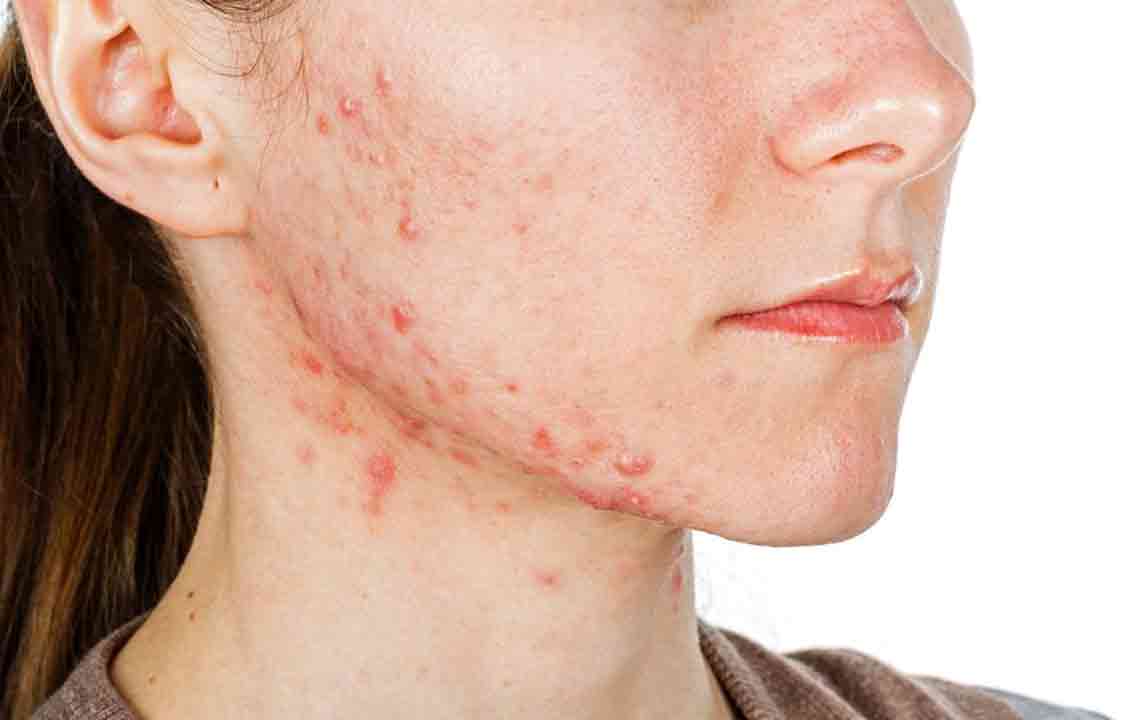
Hair Loss and Skin Changes
Hair thinning or patchy hair loss, particularly on the scalp, is common in lupus due to skin inflammation and immune activity. Unusual hair loss outside typical patterns, such as in eyebrows or eyelashes, warrants medical evaluation. Additionally, skin rashes—especially on the cheeks and bridge of the nose—are characteristic. These rashes, often referred to as "butterfly rashes," worsen with sun exposure. Discoloration or redness in fingers and toes, known as Raynaud's phenomenon, may also occur without itching or pain.
Breathing Difficulties and Pulmonary Symptoms
Involvement of the lungs is a serious concern in lupus. Lung inflammation can cause chest pain, particularly when taking deep breaths, as well as shortness of breath and reduced lung capacity. Pulmonary hypertension or pleurisy might also develop, leading to further respiratory issues that warrant prompt medical attention.
Kidney Involvement (Nephritis)
Kidney inflammation, or lupus nephritis, is a common and potentially serious manifestation. Symptoms include swelling in limbs, high blood pressure, dark urine, and increased frequency of urination, especially at night. Since kidneys play a vital role in filtering blood, damage can lead to kidney failure if not diagnosed and treated early. Regular monitoring of kidney function through blood tests and urinalysis is essential after diagnosis.
Joint Pain and Swelling
Many lupus patients experience joint stiffness, discomfort, and swelling, often worse in the mornings. This inflammatory arthritis can mimic other joint conditions but requires specific management. Chronic joint inflammation may lead to joint damage if left untreated, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis.
Digestive and Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Gastrointestinal issues such as acid reflux, heartburn, and abdominal pain are common. Managing diet plays a key role—smaller, more frequent meals and avoidance of caffeine and spicy foods may help. Persistent digestive symptoms should be evaluated to rule out lupus-related inflammation or other gastrointestinal conditions.
Thyroid Function Alterations
Thyroid abnormalities, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, are frequently seen in lupus patients. Symptoms like dry skin, weight fluctuations, hair thinning, and mood changes might suggest concurrent thyroid issues, which require hormonal evaluation and targeted treatment.
Dry Eyes and Mouth (Sjogren’s Syndrome)
Many individuals with lupus also develop Sjogren’s syndrome, leading to dryness of the eyes, mouth, and sometimes vagina. The immune attack on salivary and tear glands results in discomfort, increased risk of dental decay, and eye irritation. Recognizing this overlap is essential for comprehensive disease management.
Additional Manifestations
Other symptoms include dizziness, mouth ulcers, muscle pain, osteoporosis, depression, and cognitive difficulties. Many of these arise from systemic immune dysregulation. Early diagnosis, comprehensive testing, and a multidisciplinary treatment approach are vital in managing these diverse symptoms effectively.
In conclusion, lupus is a multifaceted autoimmune disease with a wide spectrum of early signs that can often be overlooked or mistaken for other conditions. Awareness of these symptoms, combined with prompt medical evaluation, is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention. Modern treatment options, lifestyle adjustments, and continuous monitoring can help those affected manage symptoms effectively and lead healthier lives. If you suspect you have any of these signs, consulting a healthcare professional promptly can make a significant difference in your health outcome.