Early Detection of Lupus: Recognizing the Key Signs and Symptoms
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease with diverse symptoms. Recognizing early signs such as fatigue, facial rashes, and hair loss can lead to prompt diagnosis and effective treatment. Understanding these symptoms is essential for preventing severe organ damage and improving quality of life. This comprehensive guide provides insights into the early indicators of lupus, emphasizing the importance of awareness and timely medical intervention to manage this unpredictable condition effectively.

Early Detection of Lupus: Recognizing the Key Signs and Symptoms
Lupus, medically known as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), is a complex and chronic autoimmune disease that poses significant challenges for diagnosis and management. It occurs when the body's immune system, which typically protects against infections, mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs, leading to widespread inflammation, tissue damage, and a range of health complications. Due to its unpredictable nature and a wide array of symptoms that can mimic other illnesses, early detection of lupus is critical for effective treatment and improving patients' quality of life.
Understanding the early signs and symptoms of lupus can empower individuals and healthcare professionals to recognize the disease at its onset and initiate appropriate medical evaluation and intervention. Since lupus can affect almost any part of the body, symptoms often vary widely between patients, making awareness essential for timely diagnosis. Typically, lupus develops between the ages of 18 and 30, although it can appear at any age, including childhood or later in life.
Common Initial Symptoms of Lupus
One of the hallmark early indicators of lupus is unexplained fatigue. Patients often report persistent tiredness that doesn't improve with rest and may significantly interfere with daily activities. This fatigue is often accompanied by low-grade fever—something minor but persistent, without any apparent infection or reason. These subtle symptoms can be easily overlooked or attributed to common illnesses, underscoring the importance of awareness.
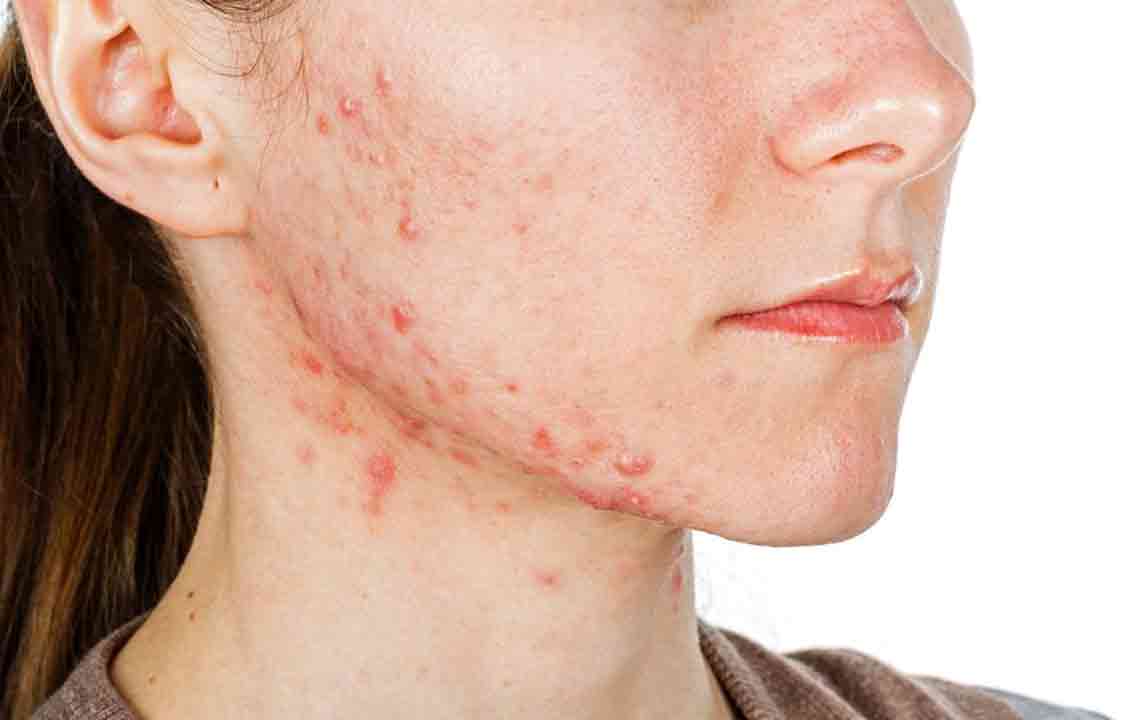
Another recognizable feature of lupus is a distinctive rash that most often appears on the face. This classic presentation is a butterfly-shaped rash that spreads across the cheeks and bridge of the nose, commonly called the malar rash. The rash is typically red, raised, and can be tender or sensitive. Photosensitivity is also notable; exposure to sunlight or artificial light can trigger skin rashes and exacerbate other symptoms. Photosensitivity varies among patients but is a key feature that can aid in diagnosis.
Hair changes are frequent in early lupus. Many individuals notice their hair becomes brittle, thin, or starts falling out, resulting in a characteristic appearance often referred to as "lupus hair." Beyond aesthetic concerns, hair loss can be an early signal of underlying autoimmune activity and warrants medical evaluation.
Progression and Complications
As lupus progresses if left undiagnosed or untreated, it can target vital organs such as the lungs, kidneys, heart, and brain. Involvement of these organs can lead to serious health issues. For instance, kidney inflammation, known as lupus nephritis, can cause swelling, high blood pressure, and potential kidney failure. Pulmonary involvement may cause chest pain, shortness of breath, or conditions like vanishing lung syndrome, where lung tissue progressively deteriorates. Central nervous system involvement can lead to neurological symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and cognitive difficulties.
Early recognition and diagnosis are paramount, as they allow for prompt treatment, which can significantly reduce disease severity and prevent irreversible organ damage. Management strategies often include immune-suppressing medications, corticosteroids, and lifestyle modifications. Regular medical checkups and blood tests enable monitoring of disease activity and response to therapy.
Healthcare professionals also emphasize the importance of patient education. Awareness about symptoms and early signs can facilitate earlier diagnosis, leading to better disease control, fewer complications, and an improved quality of life for those affected by lupus. Recognizing the signs early on can also help distinguish lupus from other autoimmune or autoimmune-like conditions, ensuring patients receive the right treatment promptly.
Ultimately, patience and awareness are key in managing lupus. If you notice symptoms such as persistent fatigue, unexplained fevers, skin rashes, or hair loss, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis not only improves treatment efficacy but also significantly reduces the risk of severe complications, enabling many lupus patients to lead healthier, more active lives.