Complete Guide to Lupus: Recognizing Symptoms and Effective Dietary Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease, highlighting key symptoms such as skin rashes, fever, hair loss, and fatigue. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and offers detailed dietary strategies, including anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3s, calcium, and antioxidants, to help manage symptoms and prevent organ damage. The article also advises on foods to avoid, like processed and high-fat dairy products, to reduce inflammation. Understanding lupus and adopting proper dietary habits can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life.

Comprehensive Understanding of Lupus: Signs to Watch For and Nutritional Tips for Managing the Disease
Lupus, medically referred to as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune illness that occurs when the immune system mistakenly targets the body's own tissues. This autoimmune response results in widespread inflammation, pain, and tissue damage, which can impact various organs and bodily systems. The disease is complex, with symptoms that can vary greatly from person to person, making early detection and effective management crucial for improving quality of life.
The condition can affect key organs such as the kidneys, brain, heart, lungs, joints, and skin, leading to potential organ damage if not properly addressed. Understanding the hallmark signs and adopting tailored dietary strategies can significantly help in controlling symptoms and preventing disease progression.
Recognizing the early signs of lupus is vital for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Common initial symptoms include:
Skin Rashes
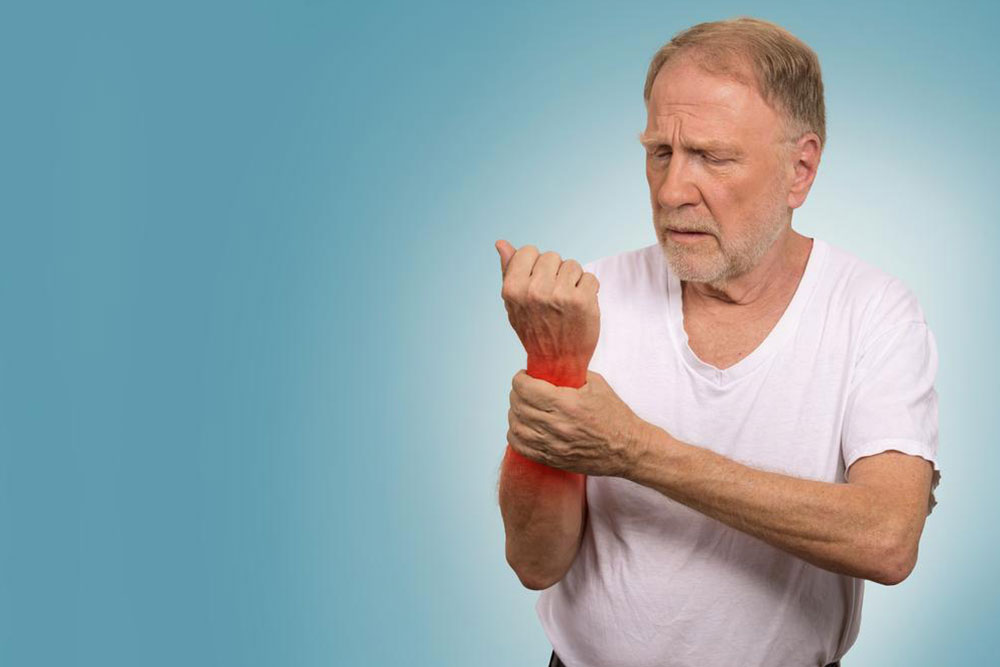
One of the most visible indicators of lupus is a facial rash, often called a 'butterfly rash,' which appears across the cheeks and bridge of the nose. These rashes can develop gradually or suddenly, and they tend to worsen with sun exposure. In some cases, skin lesions may also appear on other parts of the body, indicating immune system activity.
While symptoms tend to differ based on individual health factors, there are some common signs that can hint at lupus:
Persistent Fever
A fever exceeding 100°F (37.8°C) that persists over time is frequently observed in lupus patients. This fever results from the ongoing inflammation and immune response activity within the body, often occurring without an apparent infection.
Hair Loss
Thinning hair or hair loss, known medically as alopecia, is a frequent symptom. It may be patchy or spread diffusely, and though it is not a definitive sign on its own, it often accompanies other symptoms of lupus.
Chronic Fatigue
Many individuals with lupus experience intense fatigue, which is not relieved by rest. This sustained exhaustion results from immune system hyperactivity and inflammation affecting red blood cells, leading to anemia and diminished energy levels.
Effective management of lupus involves a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, and dietary modifications aimed at reducing inflammation, supporting organ health, and minimizing symptoms.
To aid in symptom control and potentially slow disease progression, incorporating specific foods into your diet can be beneficial:
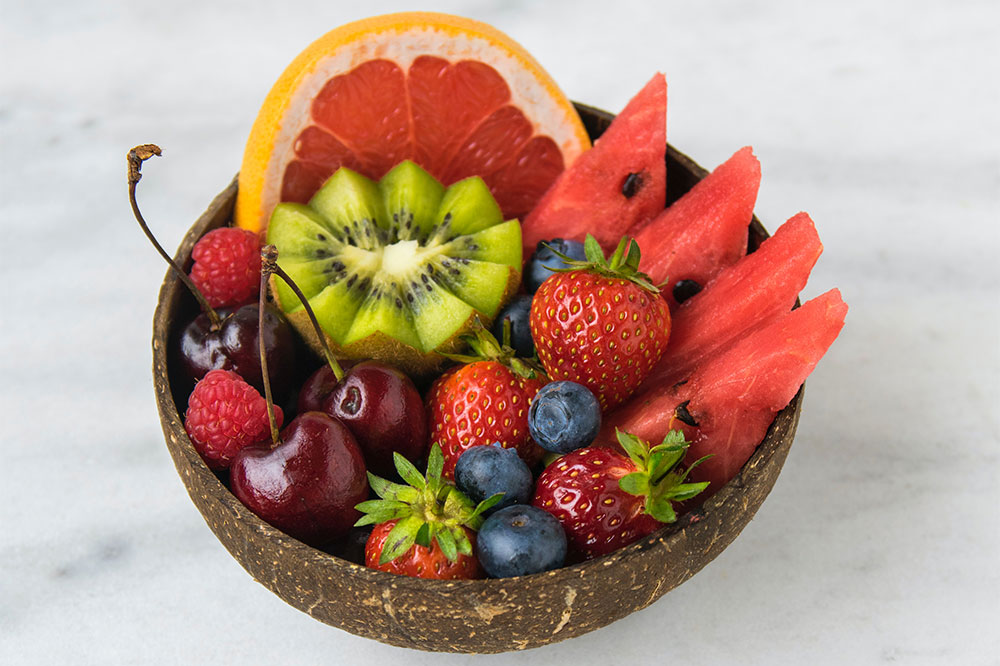
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Rich sources such as walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel have anti-inflammatory properties. Omega-3s help decrease the frequency and severity of flare-ups by modulating immune responses and reducing joint pain and stiffness.
Calcium and Vitamin D Rich Foods
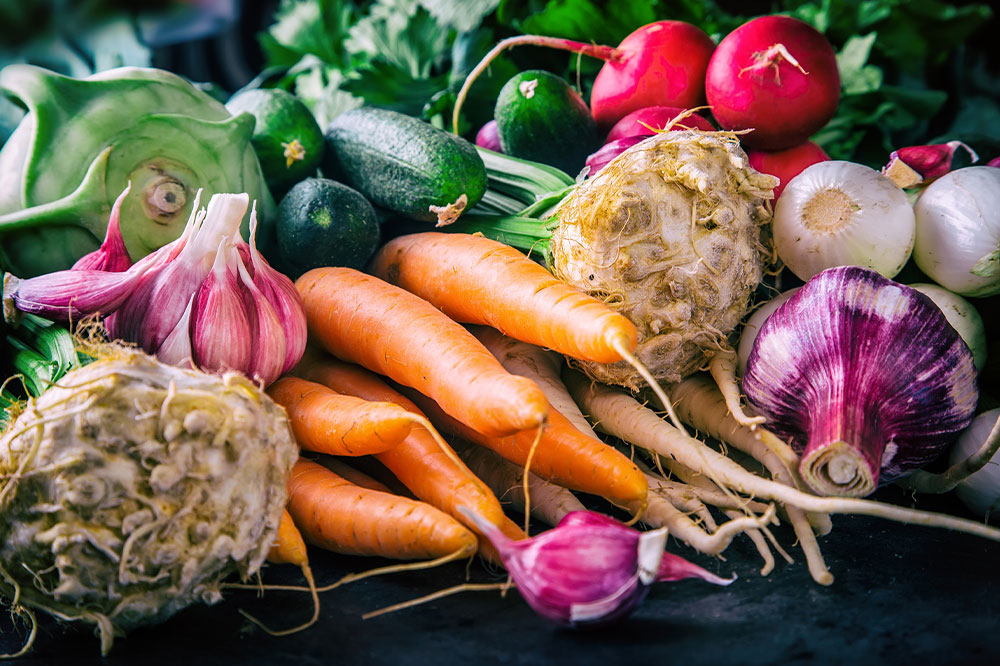
As lupus can lead to osteoporosis and joint issues, including yogurt, leafy greens like spinach and kale, tofu, and fortified foods can strengthen bones and support joint health.
Including antioxidants in your diet may also neutralize free radicals responsible for cellular damage, thereby alleviating some lupus symptoms. Berries, nuts, and colorful vegetables are excellent choices to boost antioxidant levels.
However, dietary management also involves avoiding certain foods that could exacerbate inflammation or promote immune hyperactivity:
High-Fat Dairy Products
Whole milk, cheese, butter, and cream contain saturated fats that may promote systemic inflammation, worsening lupus symptoms.
Red Meats and Processed Foods
Items such as sausages, ham, hot dogs, and fast food are high in saturated fats, sodium, and preservatives, all of which can aggravate inflammation and interfere with effective disease control.
Additionally, it’s essential for lupusy patients to consult with healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment and diet plans, as triggers and symptom severity can vary significantly.
In conclusion, lupus is a complex autoimmune condition that requires vigilant symptom recognition and comprehensive management strategies. A well-balanced diet focusing on anti-inflammatory foods can play a vital part in controlling flare-ups and supporting long-term health. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach involving medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and proper nutrition are key to maintaining a healthy and active life for those living with lupus.