Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Persistent Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
This comprehensive guide highlights the early signs and progression of rheumatoid arthritis, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and management. Learn about symptoms, diagnosis, and lifestyle strategies to effectively control RA and prevent joint damage. A must-read resource for patients and healthcare providers aiming to improve quality of life.

Understanding the Critical Indicators of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the joints, which can lead to joint damage and functional impairment if left untreated. Its onset tends to be insidious, often beginning with subtle symptoms that gradually worsen over weeks or months. Recognizing the early warning signs of RA is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention, which can significantly improve prognosis and quality of life.
RA affects approximately 1% of the global population and is more prevalent among women than men. It involves an abnormal immune response where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the synovial tissue lining the joints. The progression of the disease varies among individuals, with some experiencing frequent flare-ups and others undergoing periods of remission. Understanding the distinguishing features of RA can help patients and healthcare providers collaborate for effective management.
Early Symptoms and Warning Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
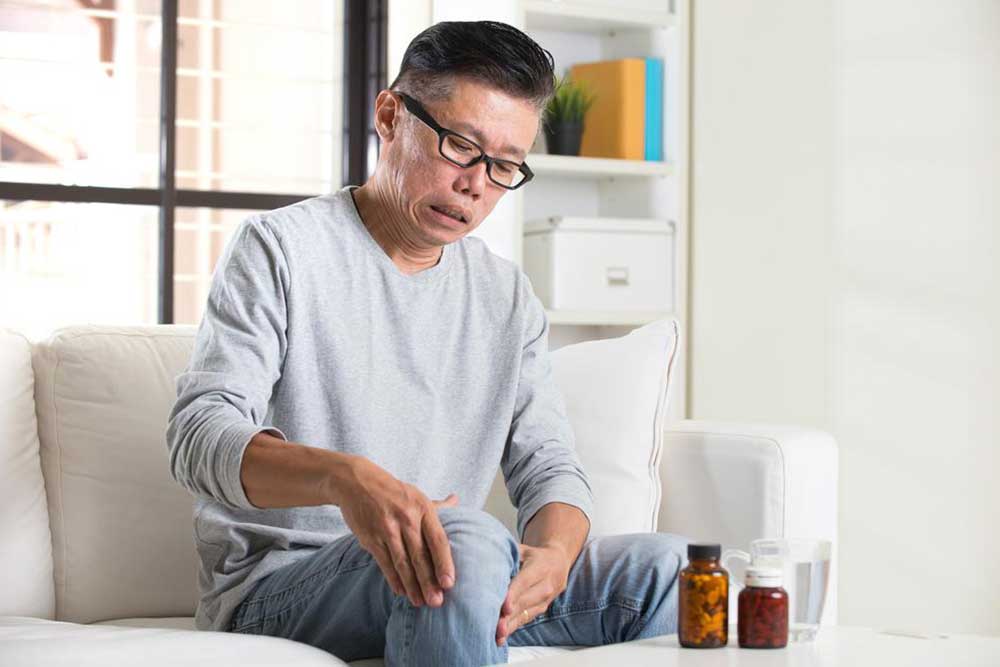
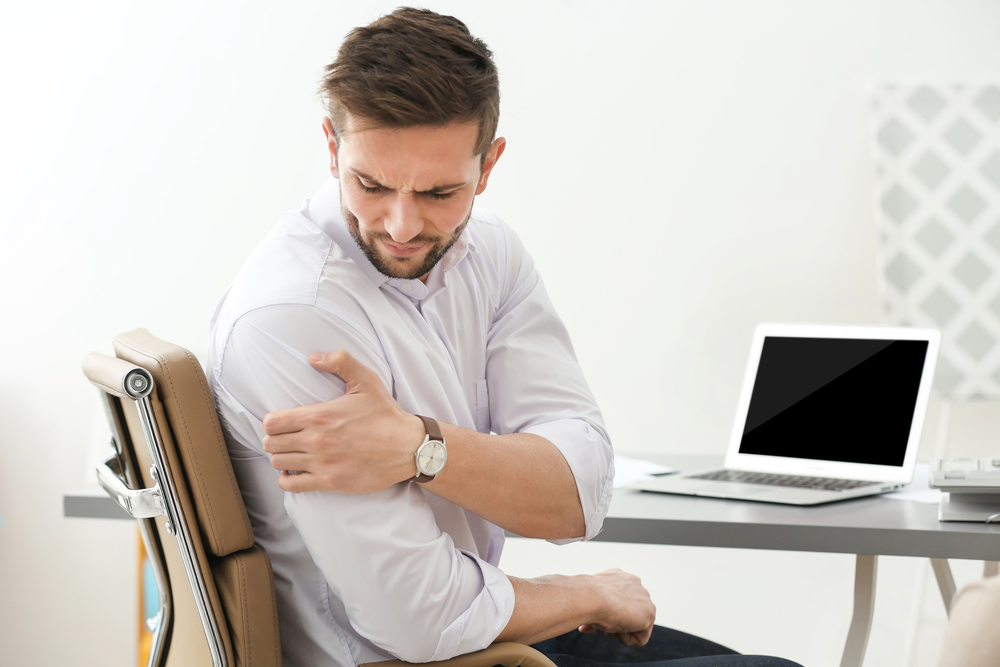
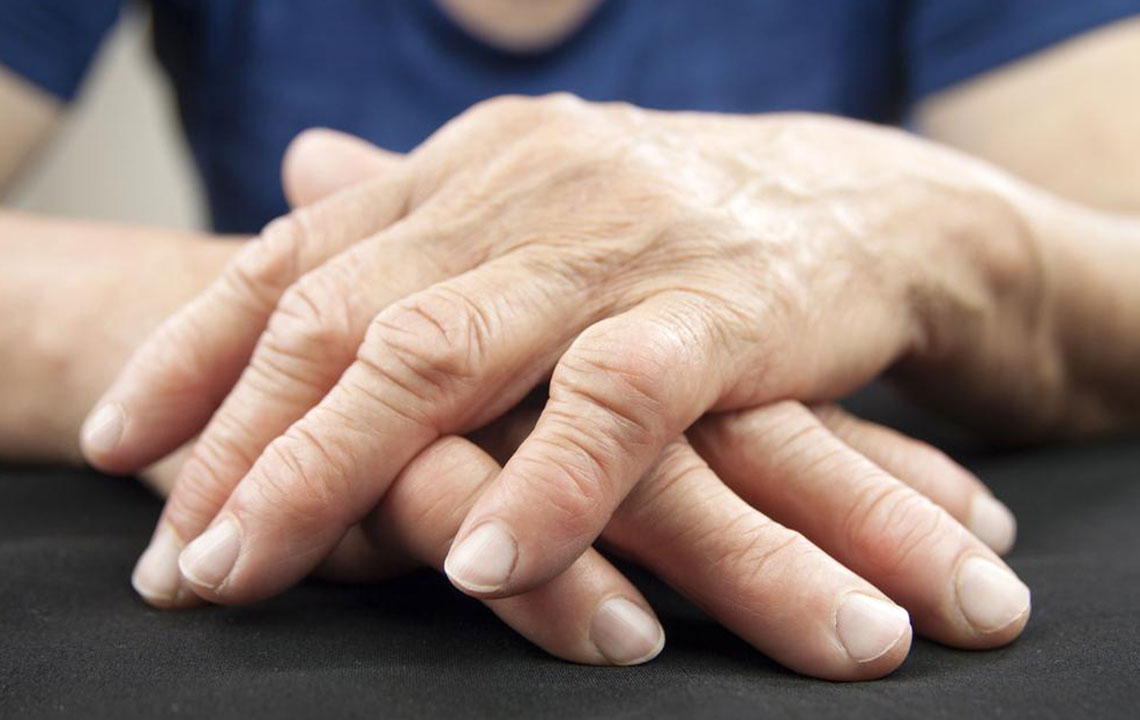
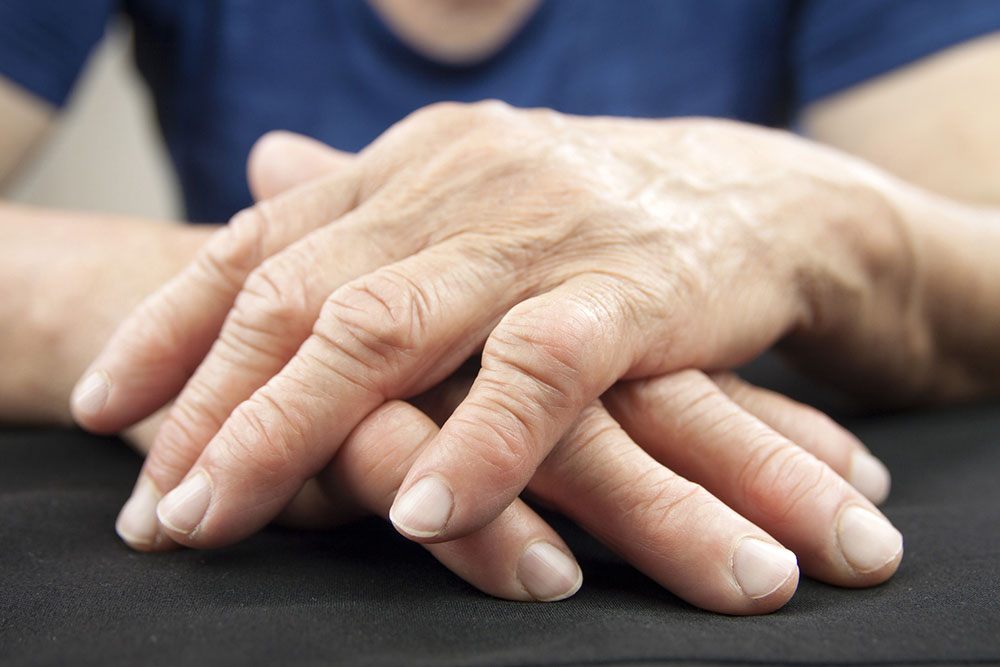
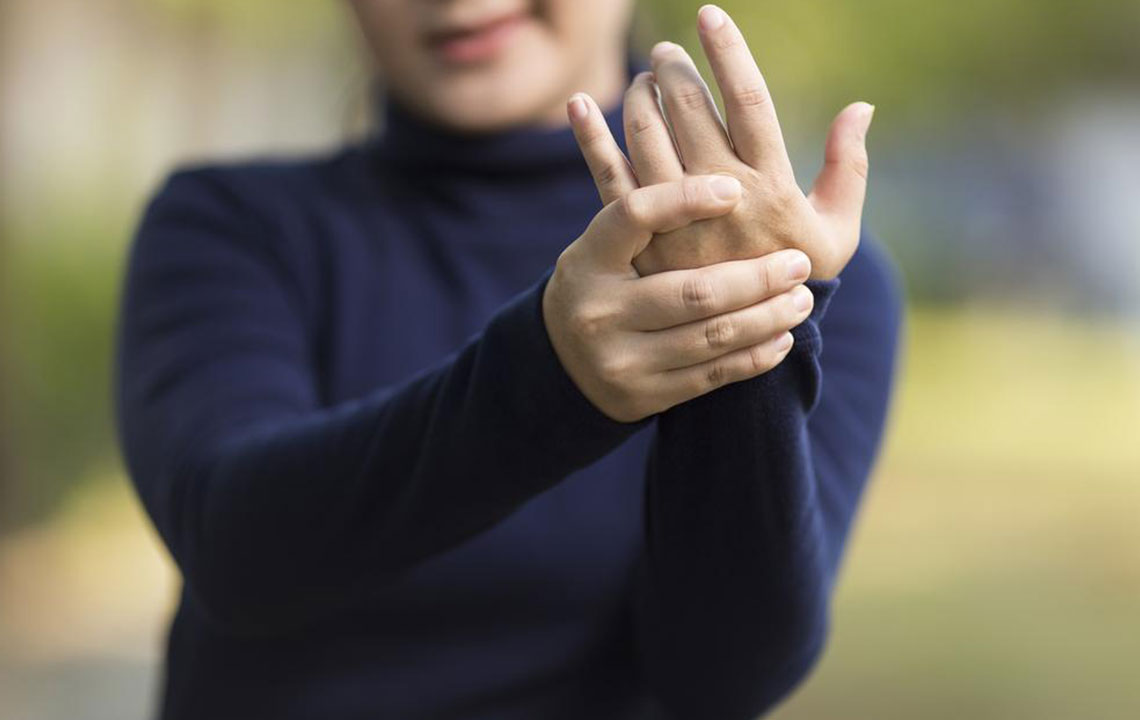
Initially, RA typically presents with joint pain—especially in smaller joints such as those of the hands, wrists, and feet. Patients may notice persistent stiffness, especially in the mornings or after periods of inactivity, lasting more than an hour in many cases. Swelling of the affected joints due to synovial inflammation is common and often accompanied by warmth and tenderness.
Fatigue, a general feeling of tiredness and lack of energy, is also a prominent early symptom, affecting daily activities and overall well-being. Some individuals may experience mild fever and unexplained weight loss, further indicating systemic involvement. Recognizing these signs early can prompt appropriate medical evaluation and diagnosis.
Progression and Other Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis
As RA progresses, joint damage can become irreversible if not managed effectively. The persistent inflammation may lead to erosion of cartilage and bone, deformities, and decreased joint function. Beyond joints, RA can also affect other organs, contributing to complications such as lung fibrosis, cardiovascular disease, and ocular problems like dry eyes or scleritis.
Physical symptoms may include nodules under the skin, especially around bony prominences, and in some cases, vasculitis leading to skin ulcers. These systemic signs highlight the importance of comprehensive medical assessment for individuals suspected of having RA.
Diagnosis and Management Strategies
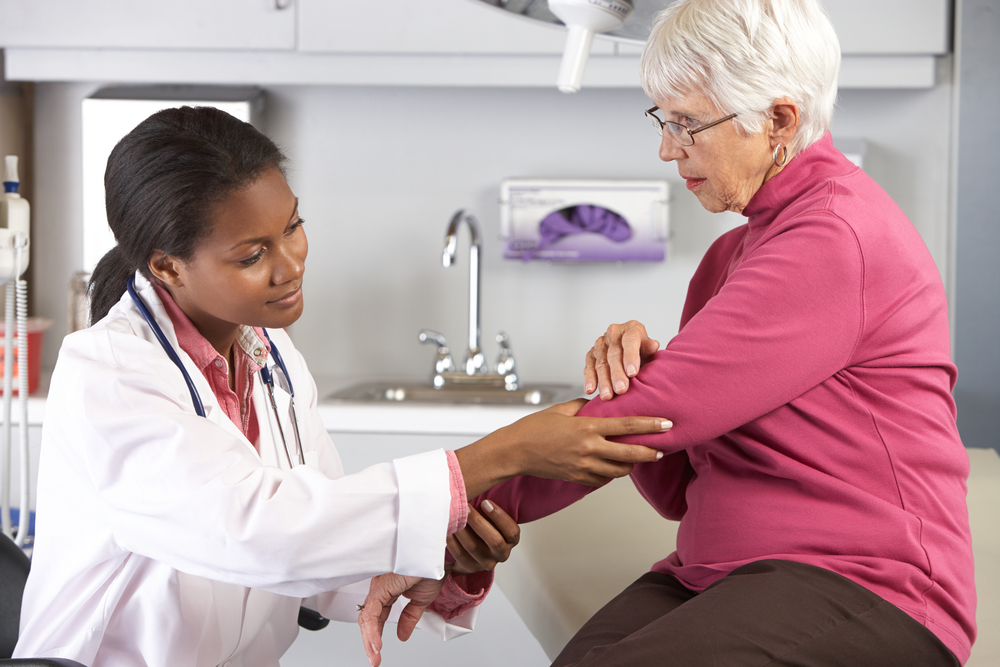
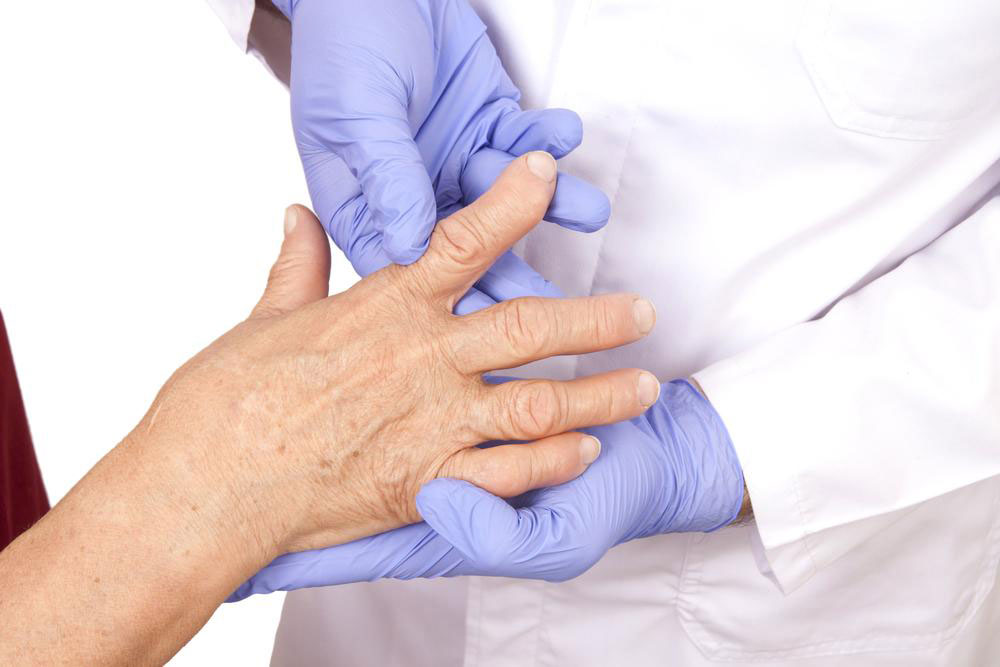
Diagnosing RA typically involves a combination of clinical examination, laboratory tests (such as rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies), and imaging studies like X-rays or ultrasound. Early diagnosis is key to initiating disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), which can slow disease progression and prevent joint destruction.
Management of RA aims to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, prevent joint damage, and improve quality of life. Besides pharmacological therapy, physical and occupational therapy play vital roles in maintaining joint function. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, smoking cessation, and stress management are also beneficial.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
While RA is a chronic condition, many individuals achieve good disease control with appropriate treatment. Education about the disease, early intervention, and adherence to prescribed therapies are crucial for optimal outcomes. Patients are encouraged to monitor their symptoms, maintain regular medical follow-ups, and adopt a proactive approach to health management.
In conclusion, recognizing the key signs of rheumatoid arthritis—such as persistent joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and systemic symptoms—is essential for early diagnosis and effective management. Advances in medical research continue to improve treatment options, enabling many patients to lead active, fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis.